| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1234746 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 6 Pages |
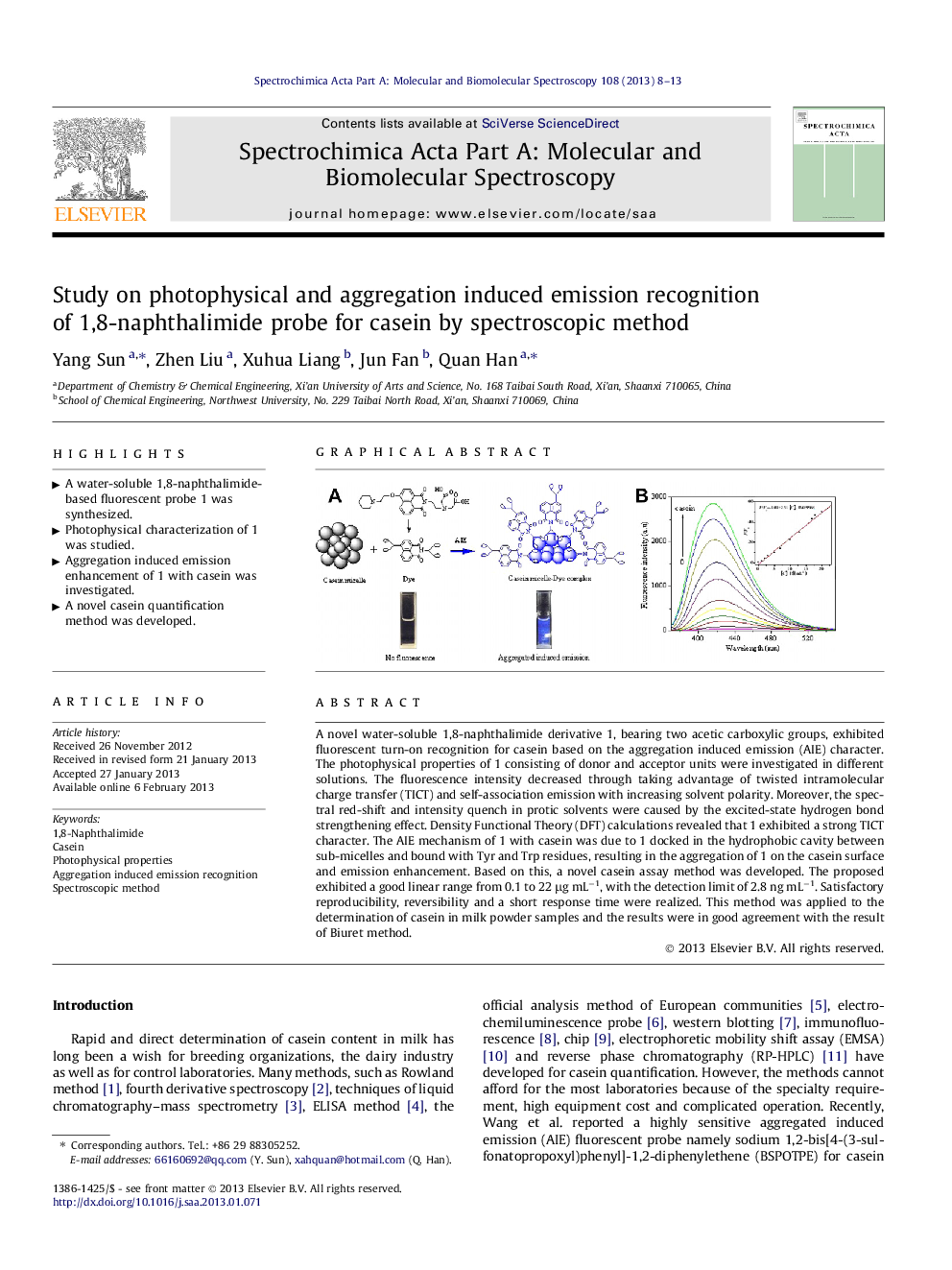
A novel water-soluble 1,8-naphthalimide derivative 1, bearing two acetic carboxylic groups, exhibited fluorescent turn-on recognition for casein based on the aggregation induced emission (AIE) character. The photophysical properties of 1 consisting of donor and acceptor units were investigated in different solutions. The fluorescence intensity decreased through taking advantage of twisted intramolecular charge transfer (TICT) and self-association emission with increasing solvent polarity. Moreover, the spectral red-shift and intensity quench in protic solvents were caused by the excited-state hydrogen bond strengthening effect. Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations revealed that 1 exhibited a strong TICT character. The AIE mechanism of 1 with casein was due to 1 docked in the hydrophobic cavity between sub-micelles and bound with Tyr and Trp residues, resulting in the aggregation of 1 on the casein surface and emission enhancement. Based on this, a novel casein assay method was developed. The proposed exhibited a good linear range from 0.1 to 22 μg mL−1, with the detection limit of 2.8 ng mL−1. Satisfactory reproducibility, reversibility and a short response time were realized. This method was applied to the determination of casein in milk powder samples and the results were in good agreement with the result of Biuret method.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► A water-soluble 1,8-naphthalimide-based fluorescent probe 1 was synthesized. ► Photophysical characterization of 1 was studied. ► Aggregation induced emission enhancement of 1 with casein was investigated. ► A novel casein quantification method was developed.