| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1234752 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 5 Pages |
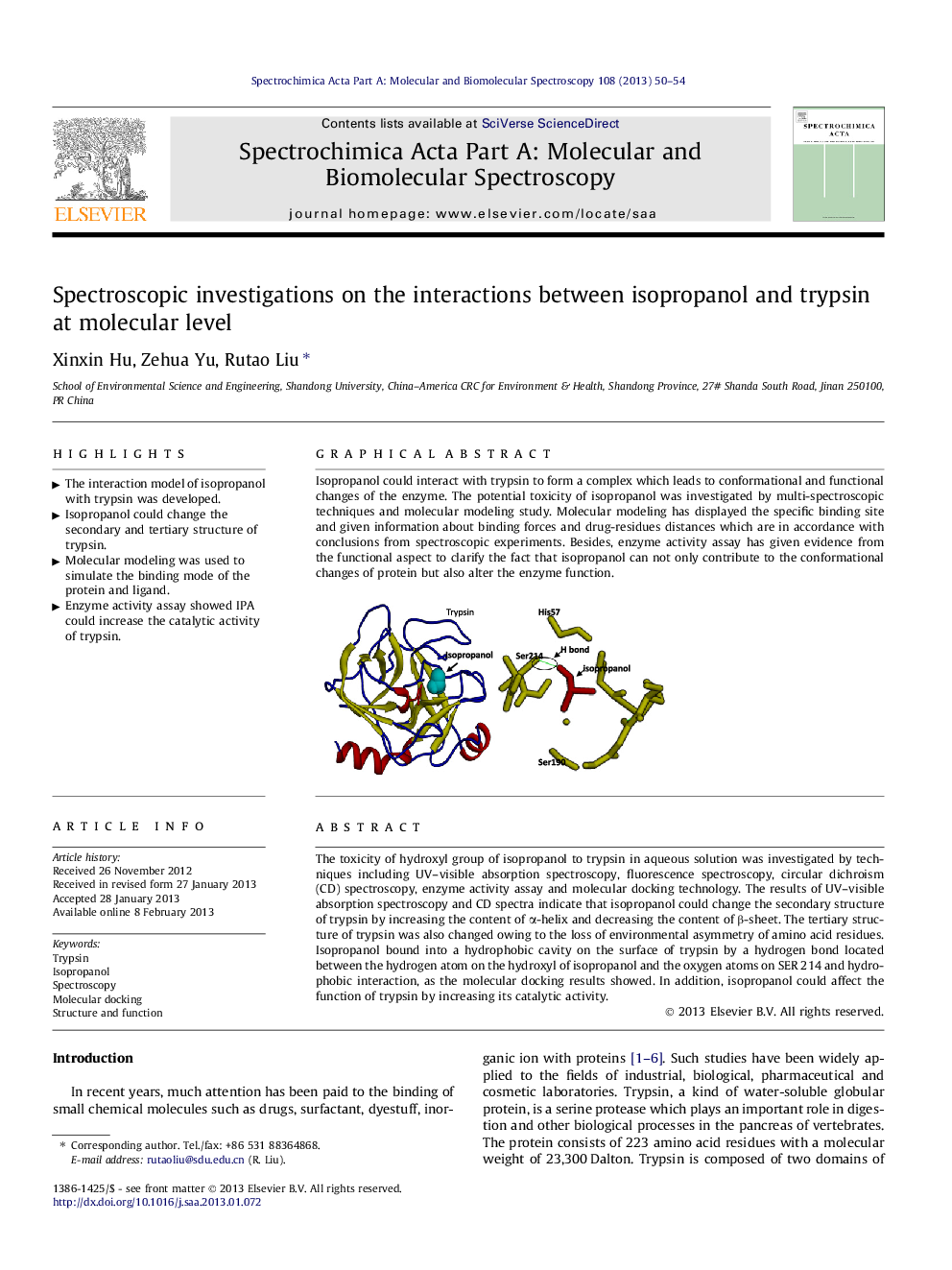
The toxicity of hydroxyl group of isopropanol to trypsin in aqueous solution was investigated by techniques including UV–visible absorption spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy, enzyme activity assay and molecular docking technology. The results of UV–visible absorption spectroscopy and CD spectra indicate that isopropanol could change the secondary structure of trypsin by increasing the content of α-helix and decreasing the content of β-sheet. The tertiary structure of trypsin was also changed owing to the loss of environmental asymmetry of amino acid residues. Isopropanol bound into a hydrophobic cavity on the surface of trypsin by a hydrogen bond located between the hydrogen atom on the hydroxyl of isopropanol and the oxygen atoms on SER 214 and hydrophobic interaction, as the molecular docking results showed. In addition, isopropanol could affect the function of trypsin by increasing its catalytic activity.
Graphical abstractIsopropanol could interact with trypsin to form a complex which leads to conformational and functional changes of the enzyme. The potential toxicity of isopropanol was investigated by multi-spectroscopic techniques and molecular modeling study. Molecular modeling has displayed the specific binding site and given information about binding forces and drug-residues distances which are in accordance with conclusions from spectroscopic experiments. Besides, enzyme activity assay has given evidence from the functional aspect to clarify the fact that isopropanol can not only contribute to the conformational changes of protein but also alter the enzyme function.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The interaction model of isopropanol with trypsin was developed. ► Isopropanol could change the secondary and tertiary structure of trypsin. ► Molecular modeling was used to simulate the binding mode of the protein and ligand. ► Enzyme activity assay showed IPA could increase the catalytic activity of trypsin.