| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1234754 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 13 Pages |
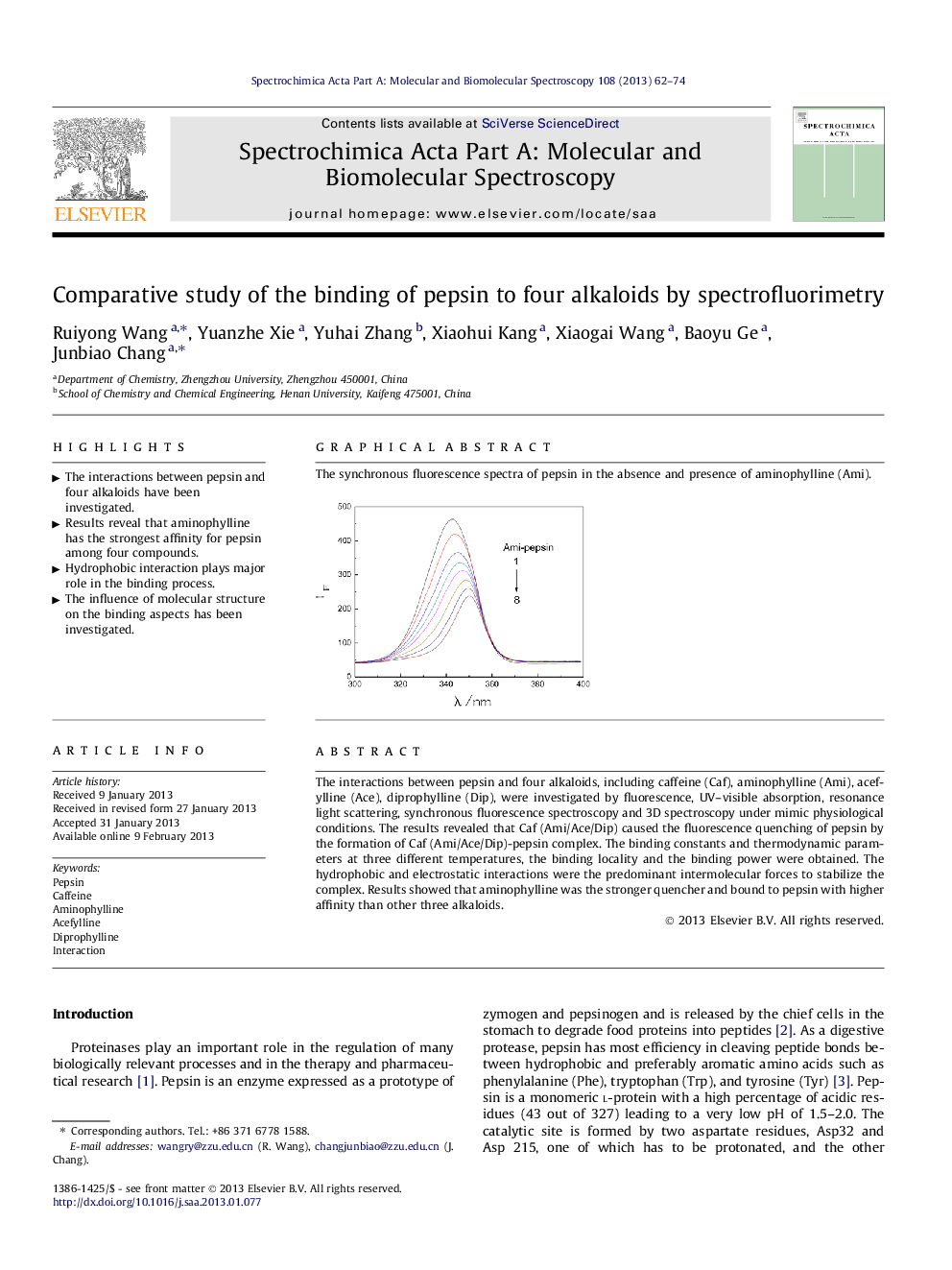
The interactions between pepsin and four alkaloids, including caffeine (Caf), aminophylline (Ami), acefylline (Ace), diprophylline (Dip), were investigated by fluorescence, UV–visible absorption, resonance light scattering, synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy and 3D spectroscopy under mimic physiological conditions. The results revealed that Caf (Ami/Ace/Dip) caused the fluorescence quenching of pepsin by the formation of Caf (Ami/Ace/Dip)-pepsin complex. The binding constants and thermodynamic parameters at three different temperatures, the binding locality and the binding power were obtained. The hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions were the predominant intermolecular forces to stabilize the complex. Results showed that aminophylline was the stronger quencher and bound to pepsin with higher affinity than other three alkaloids.
Graphical abstractThe synchronous fluorescence spectra of pepsin in the absence and presence of aminophylline (Ami).Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The interactions between pepsin and four alkaloids have been investigated. ► Results reveal that aminophylline has the strongest affinity for pepsin among four compounds. ► Hydrophobic interaction plays major role in the binding process. ► The influence of molecular structure on the binding aspects has been investigated.