| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1235064 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 12 Pages |
Oxidation of propan-2-ol to acetone was carried out in aqueous media at room temperature. The effect of promoter (PA, bpy, phen), micellar catalyst (SDS, CPC, TX-100) and their combination has been studied. The reactions were performed under the condition [Propan-2-ol]T ≫ [Cr(VI)]T at 30 °C. Then kobs and half life of all the reaction were determined to identify which promoter and which combination are the most effective for this oxidation. Among the promoters phen accelerates the reaction most in aqueous media. In absence of promoters anionic surfactant SDS increases the rate more effectively than neutral surfactant TX-100. CPC retards the rate in comparison to aqueous media. The rate of the oxidation is highest in presence of the combination of bpy and SDS.
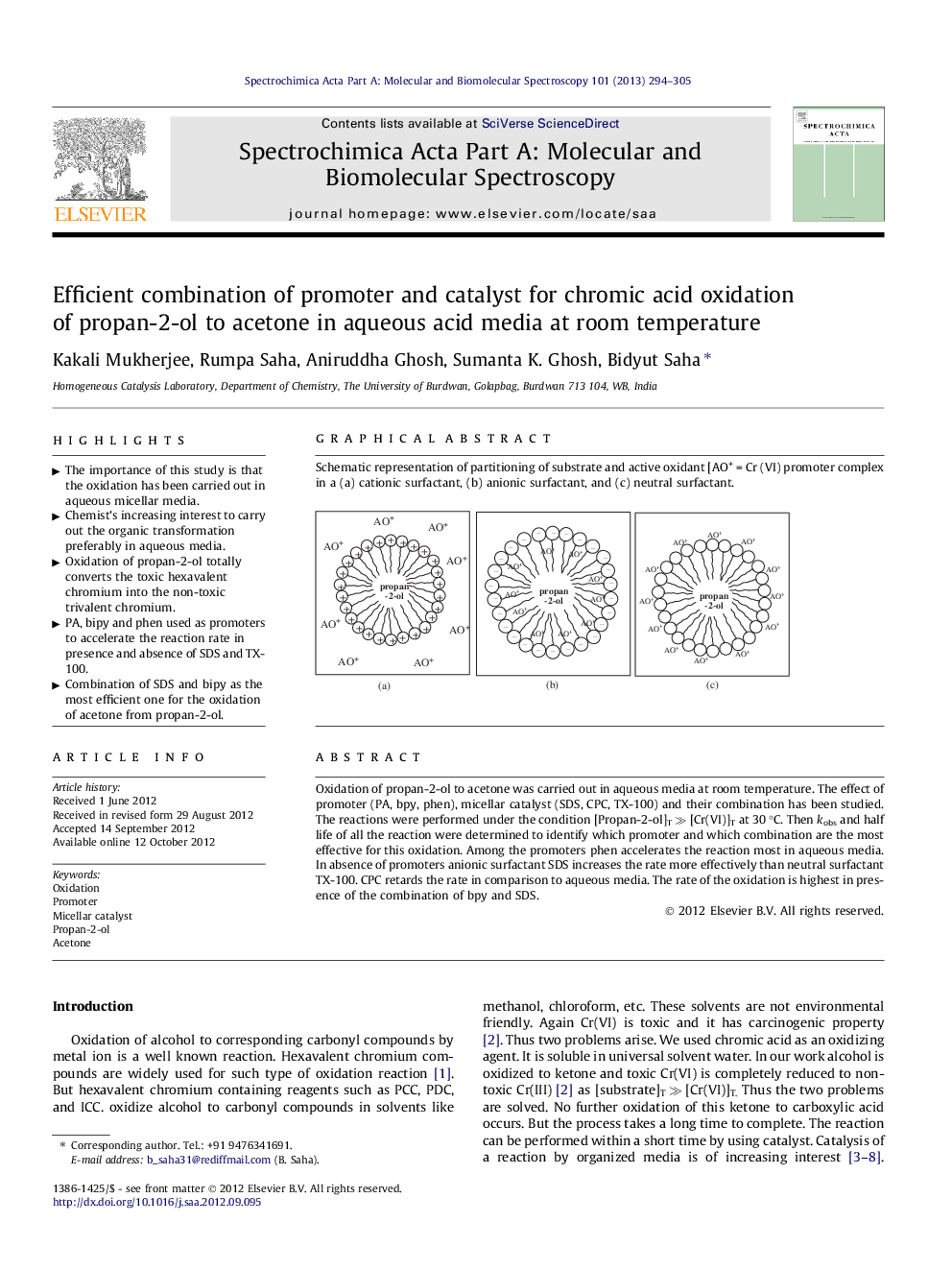
Graphical abstractSchematic representation of partitioning of substrate and active oxidant [AO+ = Cr (VI) promoter complex in a (a) cationic surfactant, (b) anionic surfactant, and (c) neutral surfactant.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The importance of this study is that the oxidation has been carried out in aqueous micellar media. ► Chemist’s increasing interest to carry out the organic transformation preferably in aqueous media. ► Oxidation of propan-2-ol totally converts the toxic hexavalent chromium into the non-toxic trivalent chromium. ► PA, bipy and phen used as promoters to accelerate the reaction rate in presence and absence of SDS and TX-100. ► Combination of SDS and bipy as the most efficient one for the oxidation of acetone from propan-2-ol.