| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1235364 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2012 | 7 Pages |
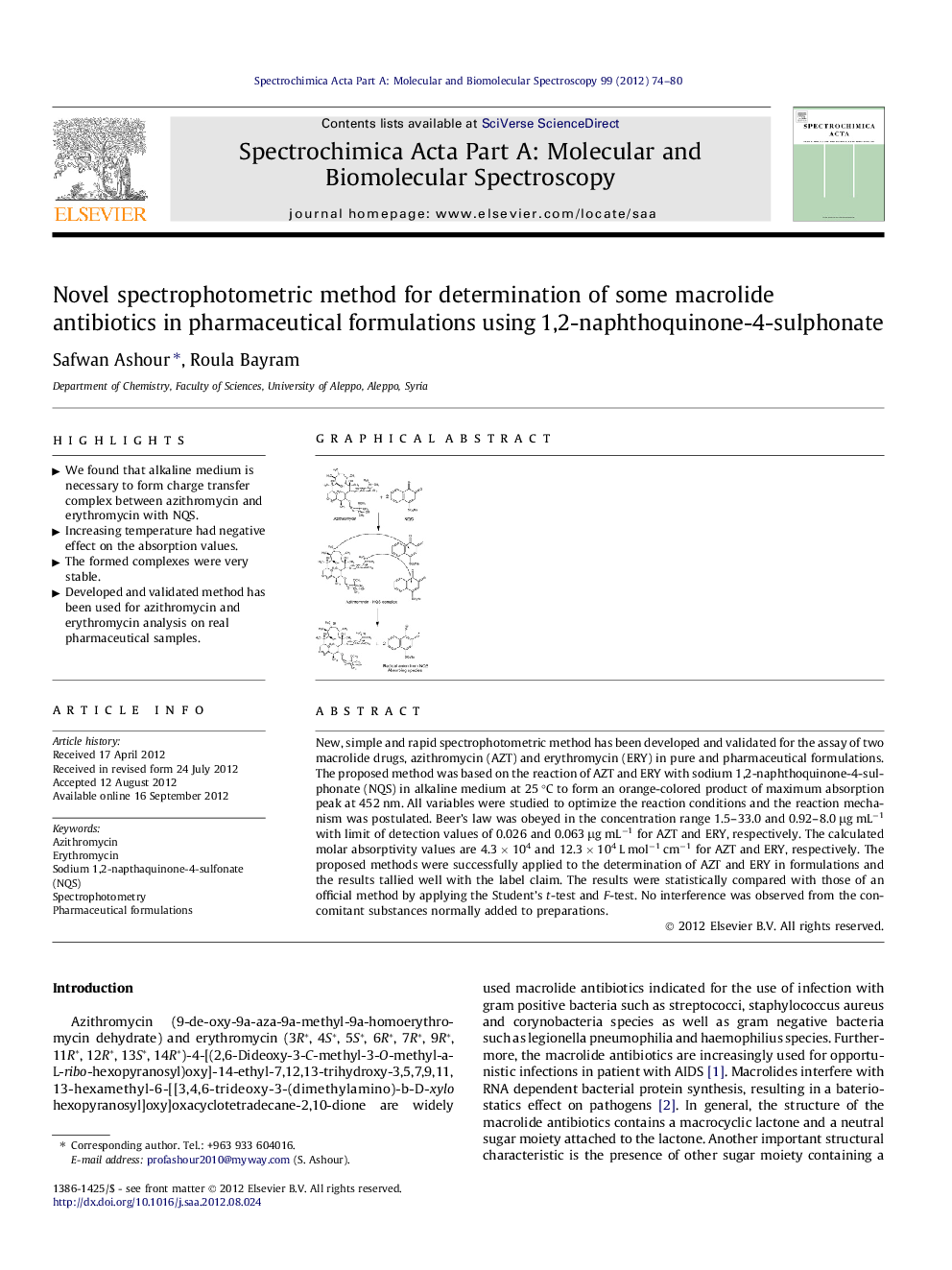
New, simple and rapid spectrophotometric method has been developed and validated for the assay of two macrolide drugs, azithromycin (AZT) and erythromycin (ERY) in pure and pharmaceutical formulations. The proposed method was based on the reaction of AZT and ERY with sodium 1,2-naphthoquinone-4-sulphonate (NQS) in alkaline medium at 25 °C to form an orange-colored product of maximum absorption peak at 452 nm. All variables were studied to optimize the reaction conditions and the reaction mechanism was postulated. Beer’s law was obeyed in the concentration range 1.5–33.0 and 0.92–8.0 μg mL−1 with limit of detection values of 0.026 and 0.063 μg mL−1 for AZT and ERY, respectively. The calculated molar absorptivity values are 4.3 × 104 and 12.3 × 104 L mol−1 cm−1 for AZT and ERY, respectively. The proposed methods were successfully applied to the determination of AZT and ERY in formulations and the results tallied well with the label claim. The results were statistically compared with those of an official method by applying the Student’s t-test and F-test. No interference was observed from the concomitant substances normally added to preparations.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► We found that alkaline medium is necessary to form charge transfer complex between azithromycin and erythromycin with NQS. ► Increasing temperature had negative effect on the absorption values. ► The formed complexes were very stable. ► Developed and validated method has been used for azithromycin and erythromycin analysis on real pharmaceutical samples.