| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1235647 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2012 | 7 Pages |
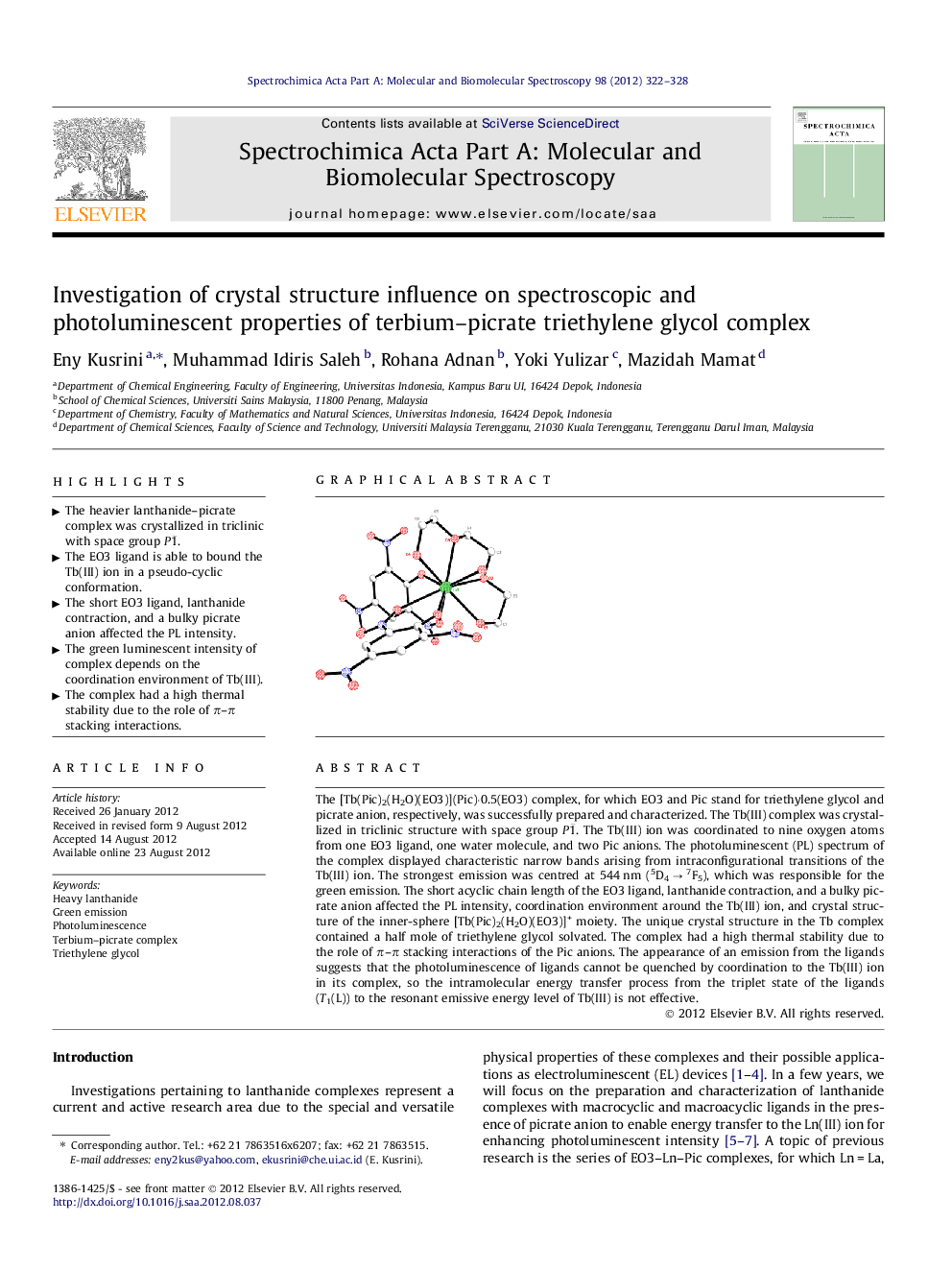
The [Tb(Pic)2(H2O)(EO3)](Pic)·0.5(EO3) complex, for which EO3 and Pic stand for triethylene glycol and picrate anion, respectively, was successfully prepared and characterized. The Tb(III) complex was crystallized in triclinic structure with space group P1¯. The Tb(III) ion was coordinated to nine oxygen atoms from one EO3 ligand, one water molecule, and two Pic anions. The photoluminescent (PL) spectrum of the complex displayed characteristic narrow bands arising from intraconfigurational transitions of the Tb(III) ion. The strongest emission was centred at 544 nm (5D4 → 7F5), which was responsible for the green emission. The short acyclic chain length of the EO3 ligand, lanthanide contraction, and a bulky picrate anion affected the PL intensity, coordination environment around the Tb(III) ion, and crystal structure of the inner-sphere [Tb(Pic)2(H2O)(EO3)]+ moiety. The unique crystal structure in the Tb complex contained a half mole of triethylene glycol solvated. The complex had a high thermal stability due to the role of π–π stacking interactions of the Pic anions. The appearance of an emission from the ligands suggests that the photoluminescence of ligands cannot be quenched by coordination to the Tb(III) ion in its complex, so the intramolecular energy transfer process from the triplet state of the ligands (T1(L)) to the resonant emissive energy level of Tb(III) is not effective.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The heavier lanthanide–picrate complex was crystallized in triclinic with space group P1¯. ► The EO3 ligand is able to bound the Tb(III) ion in a pseudo-cyclic conformation. ► The short EO3 ligand, lanthanide contraction, and a bulky picrate anion affected the PL intensity. ► The green luminescent intensity of complex depends on the coordination environment of Tb(III). ► The complex had a high thermal stability due to the role of π–π stacking interactions.