| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1296825 | Solid State Ionics | 2009 | 5 Pages |
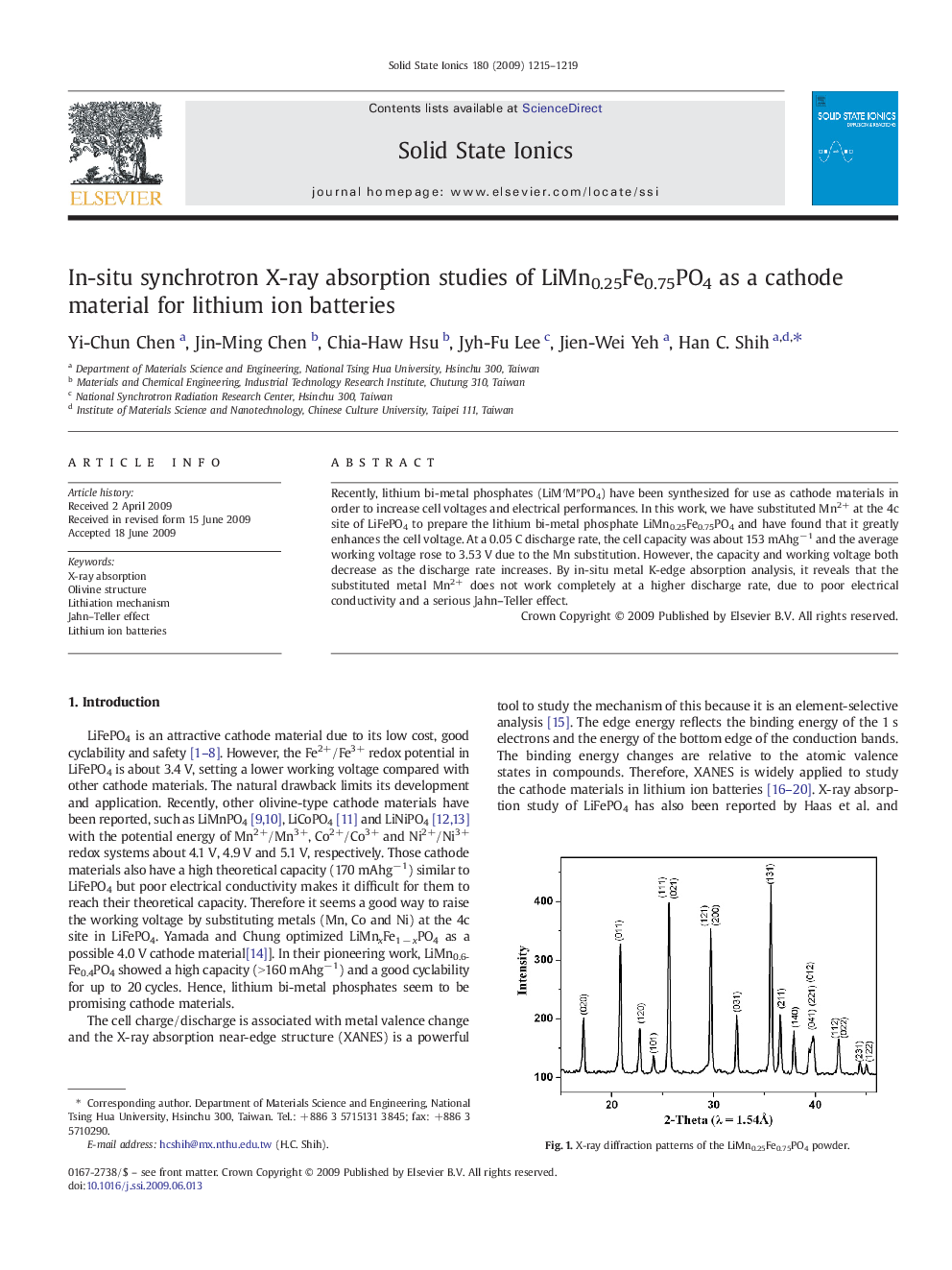
Recently, lithium bi-metal phosphates (LiM′M″PO4) have been synthesized for use as cathode materials in order to increase cell voltages and electrical performances. In this work, we have substituted Mn2+ at the 4c site of LiFePO4 to prepare the lithium bi-metal phosphate LiMn0.25Fe0.75PO4 and have found that it greatly enhances the cell voltage. At a 0.05 C discharge rate, the cell capacity was about 153 mAhg− 1 and the average working voltage rose to 3.53 V due to the Mn substitution. However, the capacity and working voltage both decrease as the discharge rate increases. By in-situ metal K-edge absorption analysis, it reveals that the substituted metal Mn2+ does not work completely at a higher discharge rate, due to poor electrical conductivity and a serious Jahn–Teller effect.