| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1336173 | Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects | 2015 | 7 Pages |
•Deposition of ruthenium nanoparticles (Ru-NPs) on graphene material.•Propylene carbonate as non-toxic and biodegradable solvent for the synthesis of Ru-NPs.•Quick and easy method for the preparation of Ru-NPs by microwave irradiation.•Synthesis of stable, small (∼4nm diameter) and catalytic active Ru-NPs.•Hydrogenation catalysis of benzene under solvent-free conditions.
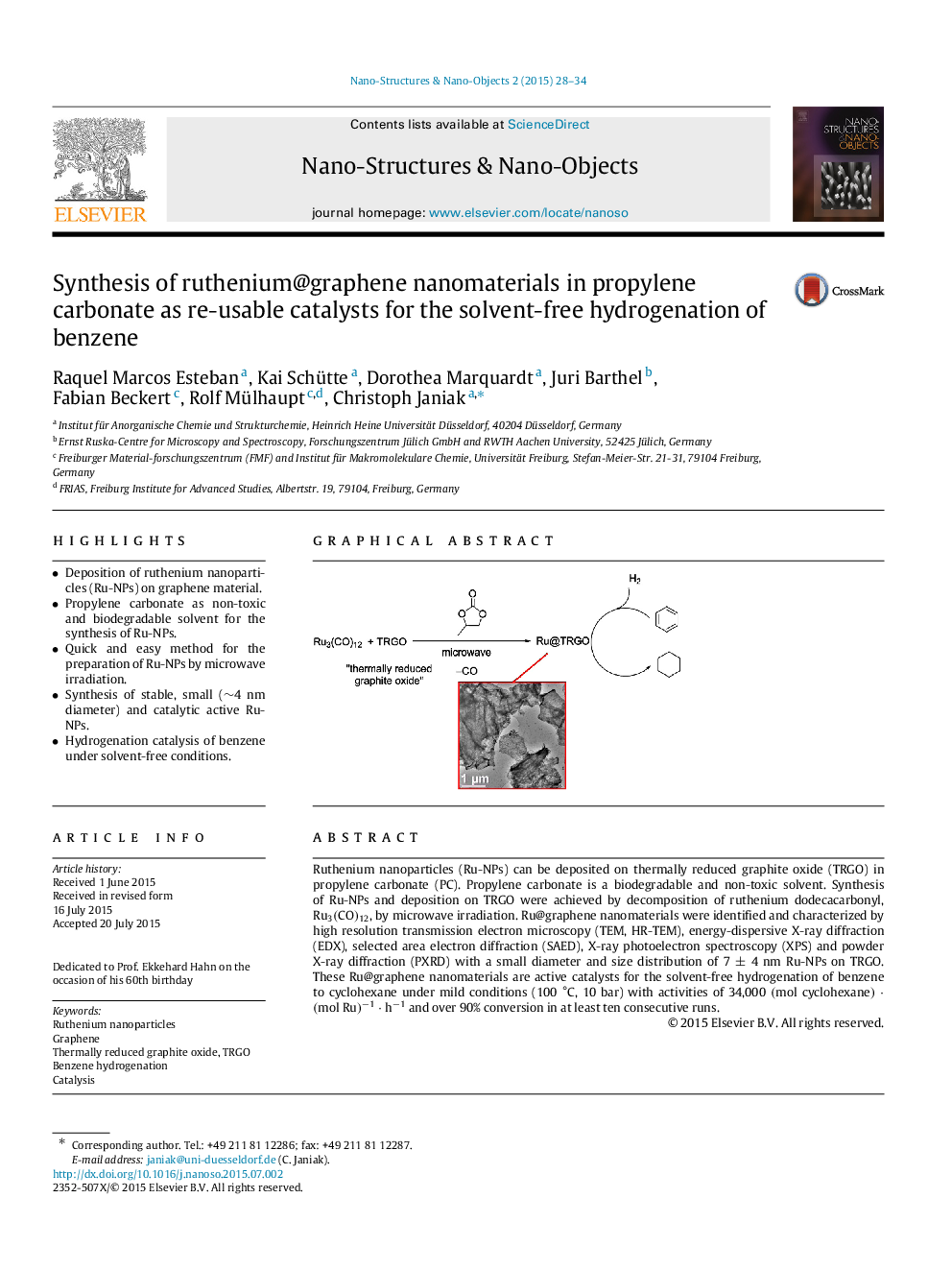
Ruthenium nanoparticles (Ru-NPs) can be deposited on thermally reduced graphite oxide (TRGO) in propylene carbonate (PC). Propylene carbonate is a biodegradable and non-toxic solvent. Synthesis of Ru-NPs and deposition on TRGO were achieved by decomposition of ruthenium dodecacarbonyl, Ru3(CO)12, by microwave irradiation. Ru@graphene nanomaterials were identified and characterized by high resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM, HR-TEM), energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction (EDX), selected area electron diffraction (SAED), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) with a small diameter and size distribution of 7±4nm Ru-NPs on TRGO. These Ru@graphene nanomaterials are active catalysts for the solvent-free hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexane under mild conditions (100 °C, 10 bar) with activities of 34,000(molcyclohexane)⋅(molRu)−1⋅h−1 and over 90% conversion in at least ten consecutive runs.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide