| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1348327 | Tetrahedron: Asymmetry | 2007 | 6 Pages |
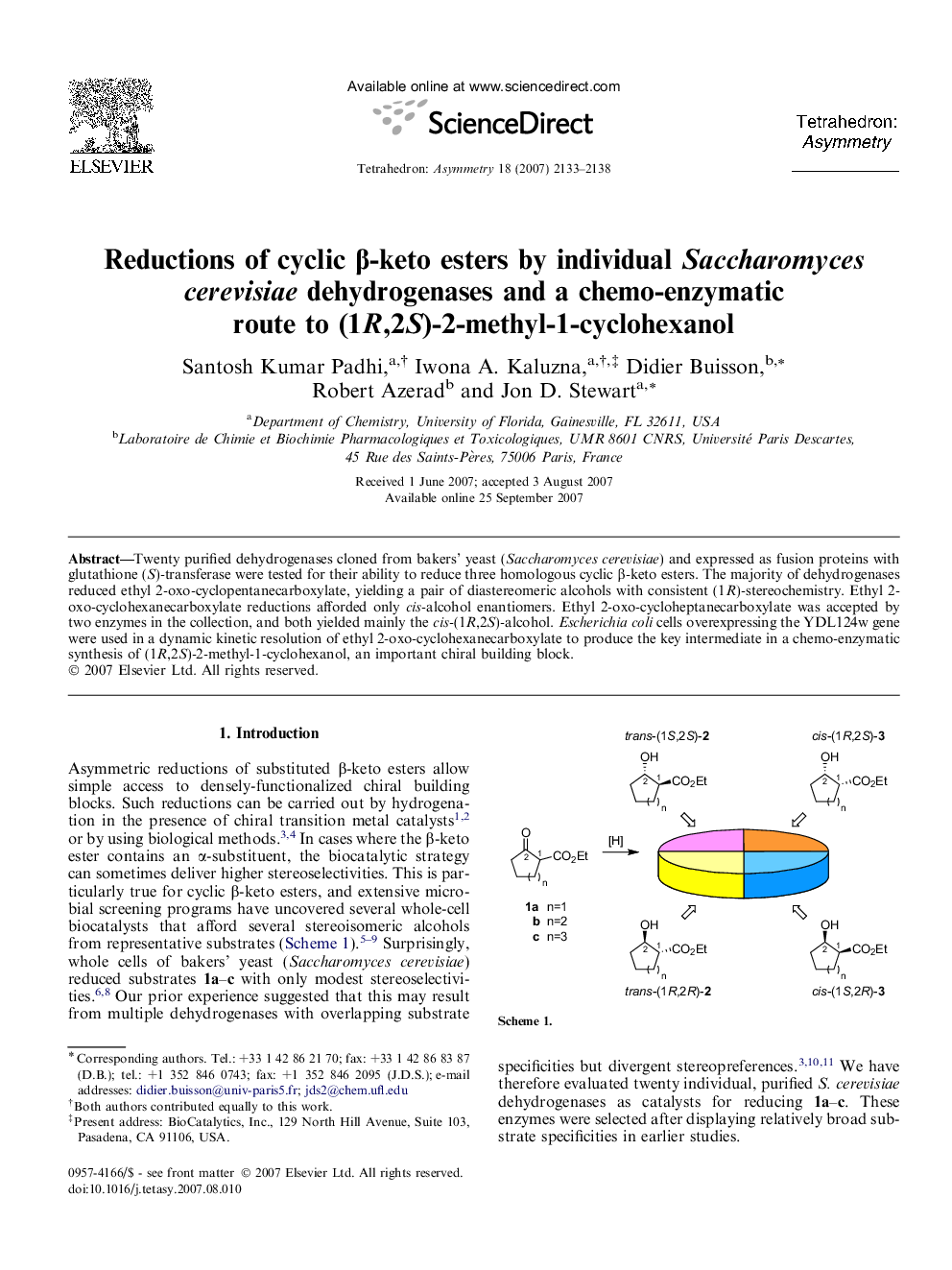
Twenty purified dehydrogenases cloned from bakers’ yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and expressed as fusion proteins with glutathione (S)-transferase were tested for their ability to reduce three homologous cyclic β-keto esters. The majority of dehydrogenases reduced ethyl 2-oxo-cyclopentanecarboxylate, yielding a pair of diastereomeric alcohols with consistent (1R)-stereochemistry. Ethyl 2-oxo-cyclohexanecarboxylate reductions afforded only cis-alcohol enantiomers. Ethyl 2-oxo-cycloheptanecarboxylate was accepted by two enzymes in the collection, and both yielded mainly the cis-(1R,2S)-alcohol. Escherichia coli cells overexpressing the YDL124w gene were used in a dynamic kinetic resolution of ethyl 2-oxo-cyclohexanecarboxylate to produce the key intermediate in a chemo-enzymatic synthesis of (1R,2S)-2-methyl-1-cyclohexanol, an important chiral building block.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide
cis-(1S,2R) Ethyl 2-hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylateC9H16O3Ee = 80%[α]D = −27.5 (c 0.6, CHCl3)Source of chirality: enzymatic reductionAbsolute configuration: (1S,2R)
(1R,2R)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-cyclohexanolC7H14O2Ee = 80%[α]D = −32.1 (c 0.24, H2O)Source of chirality: prior enzymatic reductionAbsolute configuration: (1R,2R)
((1R,2R)-2-Hydroxycyclohexyl)methyl 2,4,6-trimethyl-benzenesulfonateC16H24O4SEe = 80%[α]D = −9.5 (c 1.0, CHCl3)Source of chirality: prior enzymatic reductionAbsolute configuration: (1R,2R)
(1R,2S)-2-Methyl-cyclohexanolC7H14OEe = 80%[α]D = −16.2 (c 2.12, CHCl3)Source of chirality: prior enzymatic reductionAbsolute configuration: (1R,2S)