| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1388941 | Carbohydrate Research | 2009 | 6 Pages |
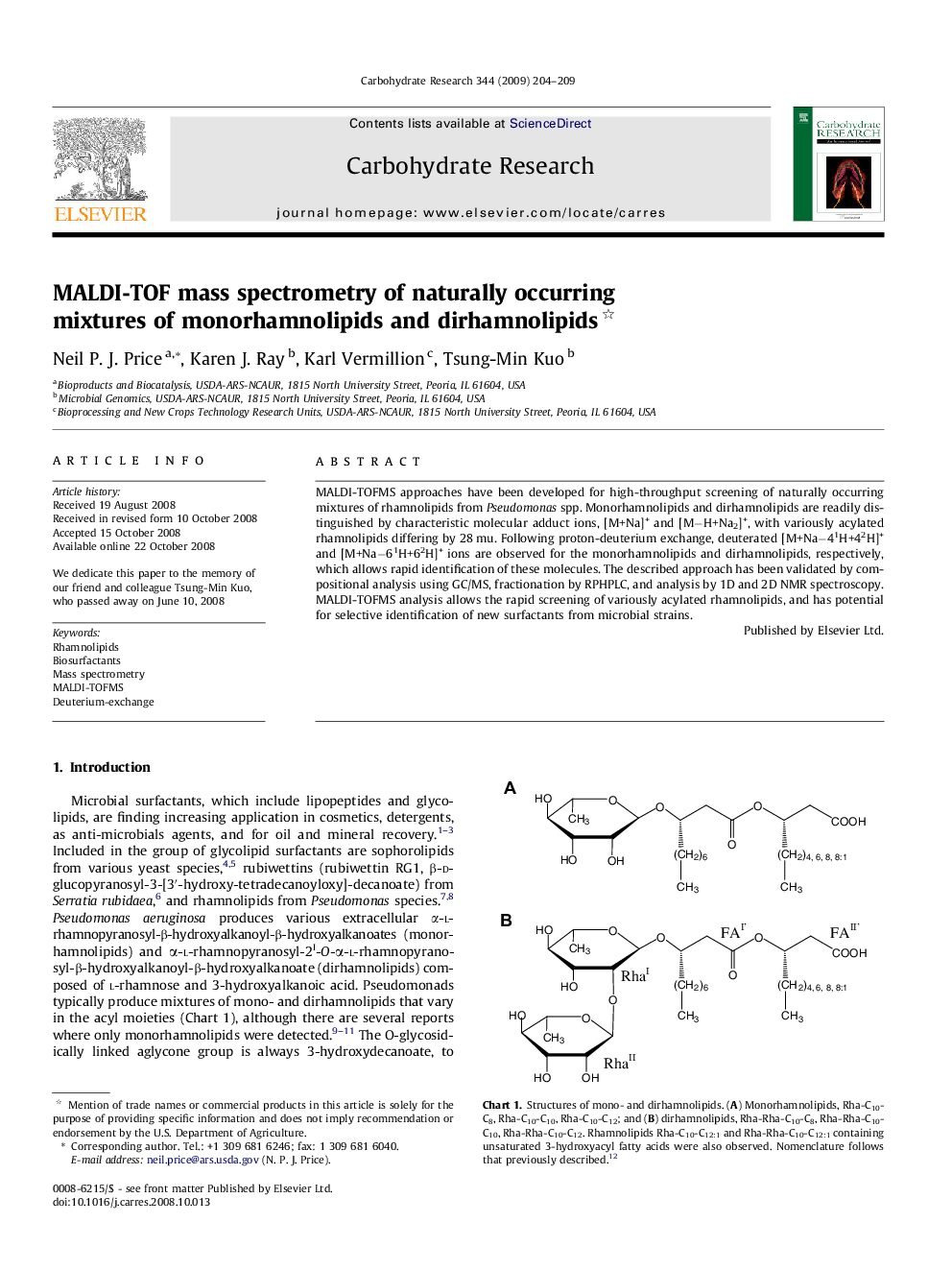
MALDI-TOFMS approaches have been developed for high-throughput screening of naturally occurring mixtures of rhamnolipids from Pseudomonas spp. Monorhamnolipids and dirhamnolipids are readily distinguished by characteristic molecular adduct ions, [M+Na]+ and [M−H+Na2]+, with variously acylated rhamnolipids differing by 28 mu. Following proton-deuterium exchange, deuterated [M+Na−41H+42H]+ and [M+Na−61H+62H]+ ions are observed for the monorhamnolipids and dirhamnolipids, respectively, which allows rapid identification of these molecules. The described approach has been validated by compositional analysis using GC/MS, fractionation by RPHPLC, and analysis by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy. MALDI-TOFMS analysis allows the rapid screening of variously acylated rhamnolipids, and has potential for selective identification of new surfactants from microbial strains.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide