| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1389067 | Carbohydrate Research | 2011 | 8 Pages |
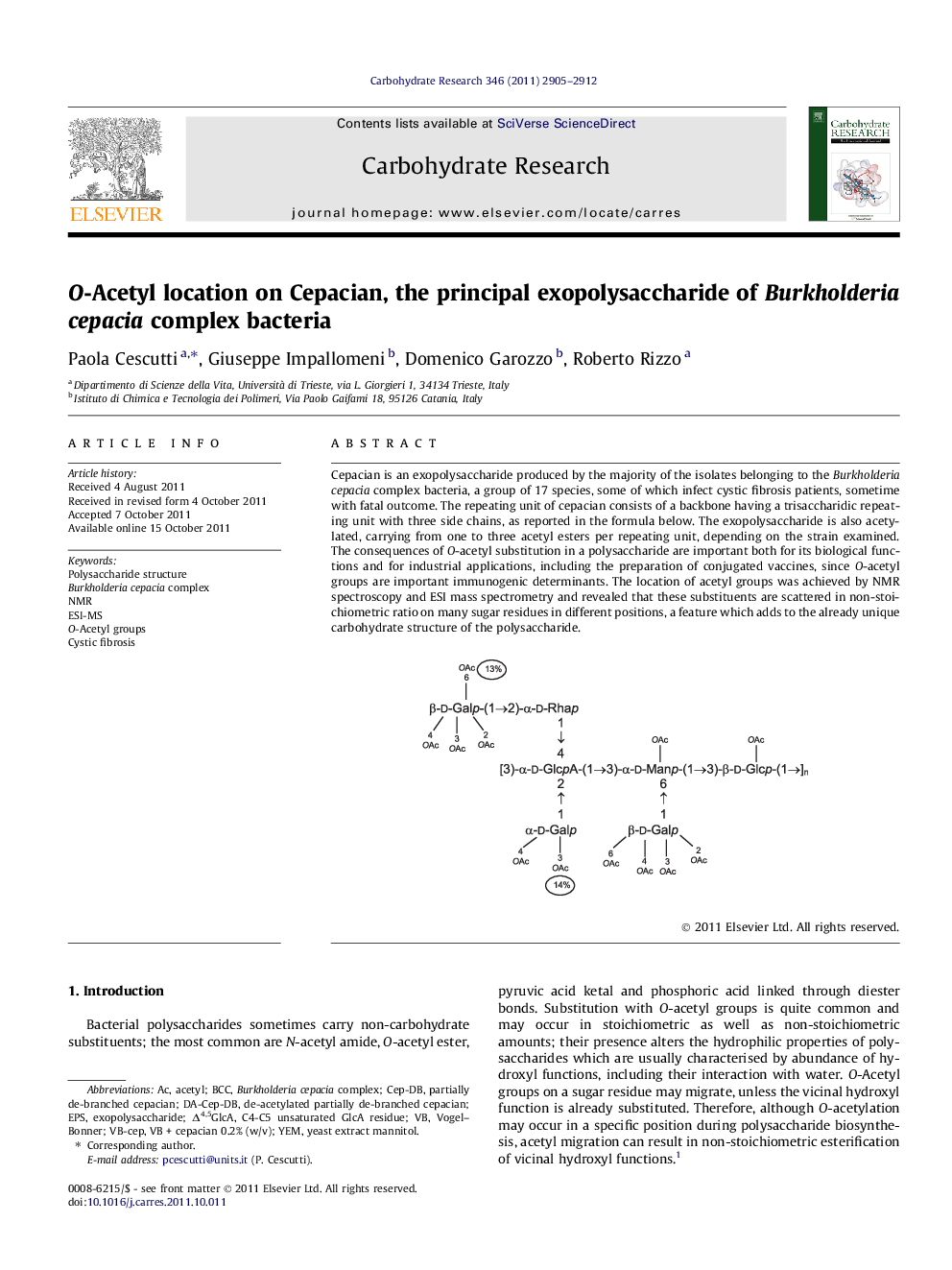
Cepacian is an exopolysaccharide produced by the majority of the isolates belonging to the Burkholderia cepacia complex bacteria, a group of 17 species, some of which infect cystic fibrosis patients, sometime with fatal outcome. The repeating unit of cepacian consists of a backbone having a trisaccharidic repeating unit with three side chains, as reported in the formula below. The exopolysaccharide is also acetylated, carrying from one to three acetyl esters per repeating unit, depending on the strain examined. The consequences of O-acetyl substitution in a polysaccharide are important both for its biological functions and for industrial applications, including the preparation of conjugated vaccines, since O-acetyl groups are important immunogenic determinants. The location of acetyl groups was achieved by NMR spectroscopy and ESI mass spectrometry and revealed that these substituents are scattered in non-stoichiometric ratio on many sugar residues in different positions, a feature which adds to the already unique carbohydrate structure of the polysaccharide.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Burkholderia cepacia complex bacteria are opportunistic pathogens for CF patients. ► Cepacian is the exopolysaccharide characteristic of the complex. ► First structural definition of acetylation in cepacian. ► Acetyl groups scattered on several sugar units in non-stoichiometric amounts. ► Use of exopolysaccharide biological repeating unit for structural studies.