| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1389790 | Carbohydrate Research | 2008 | 8 Pages |
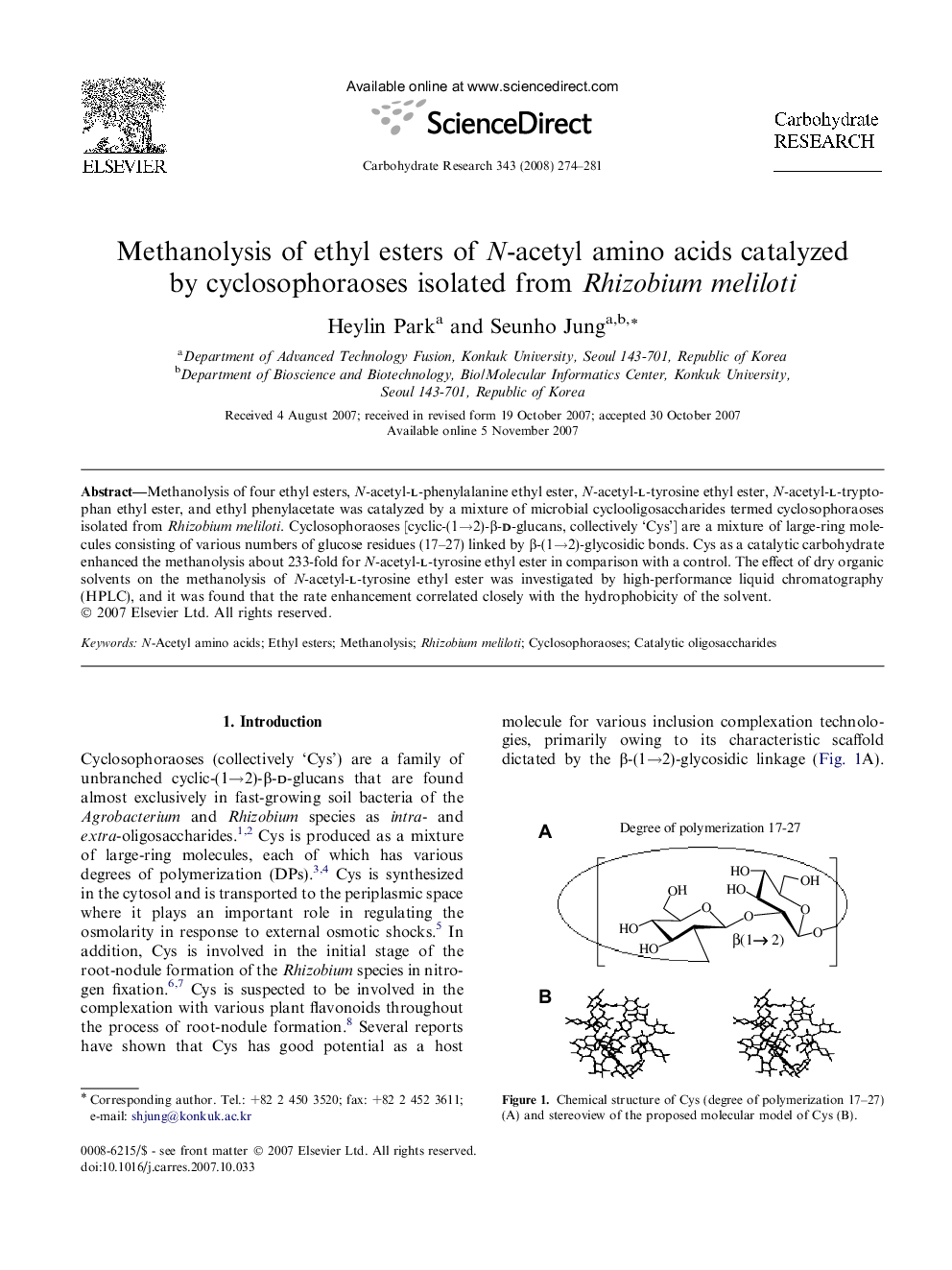
Methanolysis of four ethyl esters, N-acetyl-l-phenylalanine ethyl ester, N-acetyl-l-tyrosine ethyl ester, N-acetyl-l-tryptophan ethyl ester, and ethyl phenylacetate was catalyzed by a mixture of microbial cyclooligosaccharides termed cyclosophoraoses isolated from Rhizobium meliloti. Cyclosophoraoses [cyclic-(1→2)-β-d-glucans, collectively ‘Cys’] are a mixture of large-ring molecules consisting of various numbers of glucose residues (17–27) linked by β-(1→2)-glycosidic bonds. Cys as a catalytic carbohydrate enhanced the methanolysis about 233-fold for N-acetyl-l-tyrosine ethyl ester in comparison with a control. The effect of dry organic solvents on the methanolysis of N-acetyl-l-tyrosine ethyl ester was investigated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and it was found that the rate enhancement correlated closely with the hydrophobicity of the solvent.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide