| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1520908 | Materials Chemistry and Physics | 2016 | 9 Pages |
•Environmentally-friendly INT-WS2 is used to produce advanced PHBV NCPs.•Novel INT-WS2 improve the thermal stability of PHBV.•INT-WS2 is effective to accelerate the crystallization of PHBV.•Ring-banded spherulites of PHBV are observed at low INT-WS2 contents.•The benefits of using INTs compared to other nanoscale fillers are highlighted.
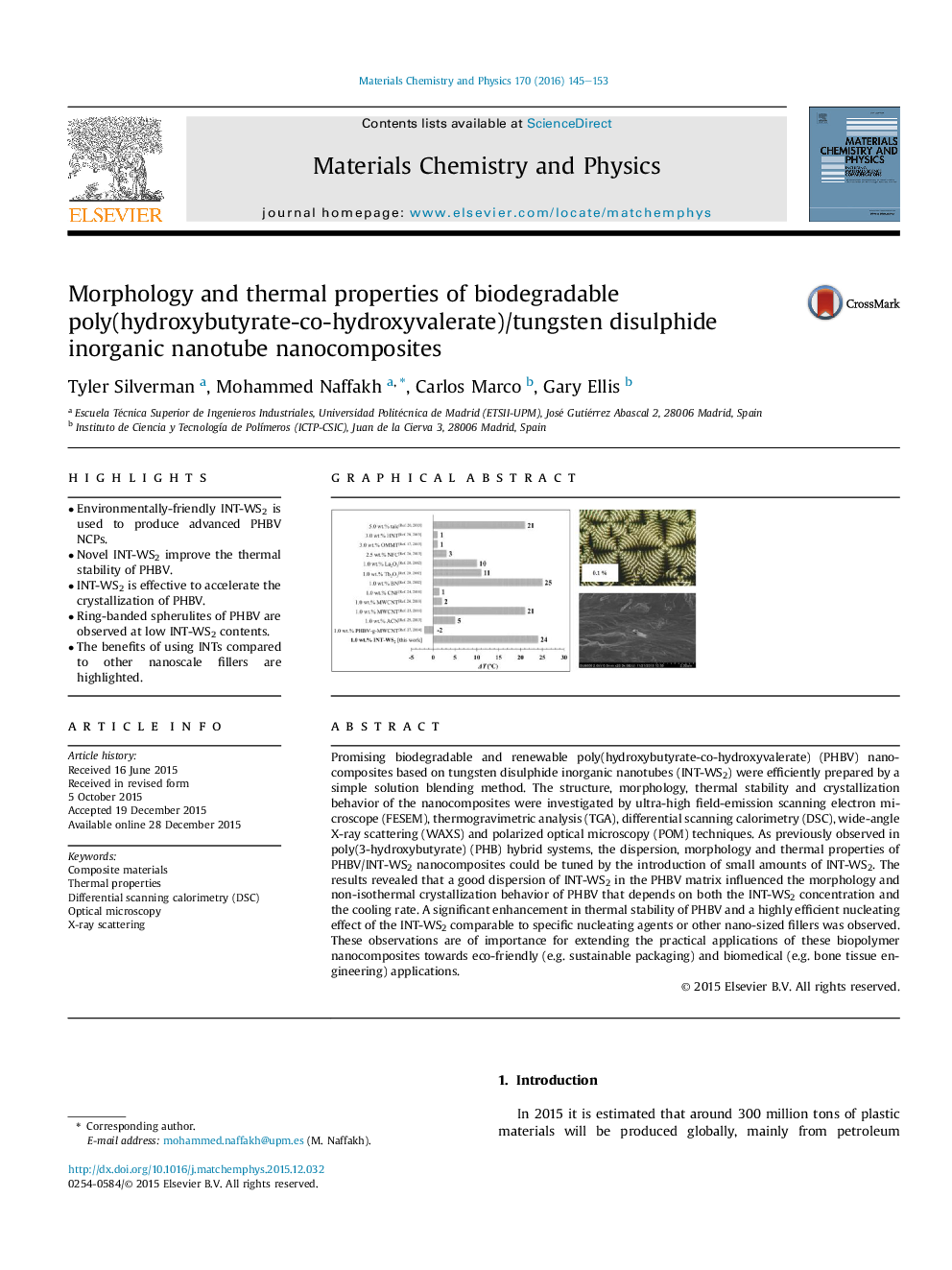
Promising biodegradable and renewable poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) nanocomposites based on tungsten disulphide inorganic nanotubes (INT-WS2) were efficiently prepared by a simple solution blending method. The structure, morphology, thermal stability and crystallization behavior of the nanocomposites were investigated by ultra-high field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) and polarized optical microscopy (POM) techniques. As previously observed in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) hybrid systems, the dispersion, morphology and thermal properties of PHBV/INT-WS2 nanocomposites could be tuned by the introduction of small amounts of INT-WS2. The results revealed that a good dispersion of INT-WS2 in the PHBV matrix influenced the morphology and non-isothermal crystallization behavior of PHBV that depends on both the INT-WS2 concentration and the cooling rate. A significant enhancement in thermal stability of PHBV and a highly efficient nucleating effect of the INT-WS2 comparable to specific nucleating agents or other nano-sized fillers was observed. These observations are of importance for extending the practical applications of these biopolymer nanocomposites towards eco-friendly (e.g. sustainable packaging) and biomedical (e.g. bone tissue engineering) applications.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide