| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1521675 | Materials Chemistry and Physics | 2014 | 6 Pages |
•Fe–Ti-MCM-48 mesoporous molecular sieves were successfully synthesized.•Bimetallic Fe–Ti-MCM-48 with 0.01Fe/Si and 0.01Ti/Si ratio had highly hydrothermal stability.•The higher titanium content led to the lower specific surface area and hydrothermal stability.
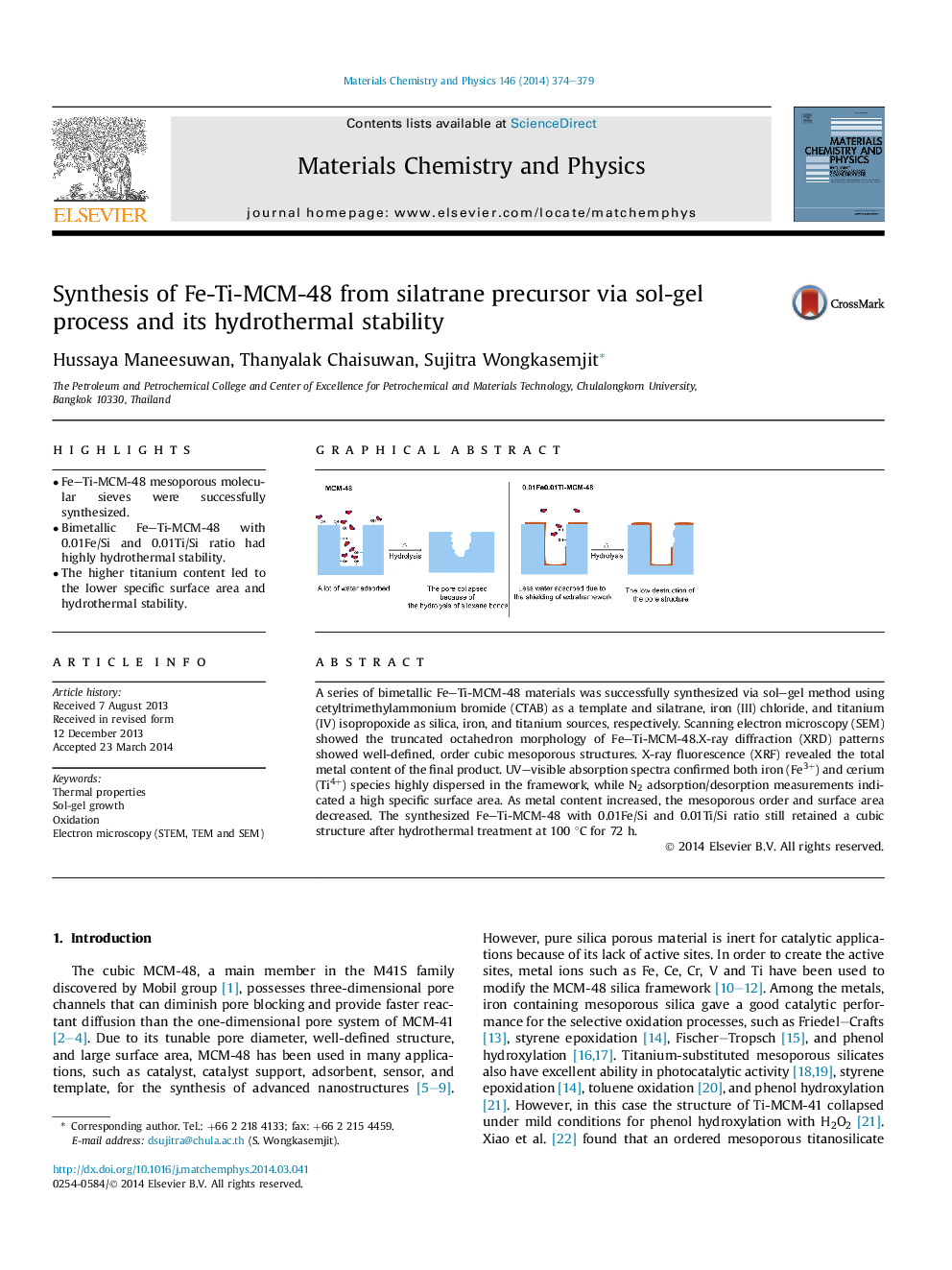
A series of bimetallic Fe–Ti-MCM-48 materials was successfully synthesized via sol–gel method using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) as a template and silatrane, iron (III) chloride, and titanium (IV) isopropoxide as silica, iron, and titanium sources, respectively. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed the truncated octahedron morphology of Fe–Ti-MCM-48.X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns showed well-defined, order cubic mesoporous structures. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) revealed the total metal content of the final product. UV–visible absorption spectra confirmed both iron (Fe3+) and cerium (Ti4+) species highly dispersed in the framework, while N2 adsorption/desorption measurements indicated a high specific surface area. As metal content increased, the mesoporous order and surface area decreased. The synthesized Fe–Ti-MCM-48 with 0.01Fe/Si and 0.01Ti/Si ratio still retained a cubic structure after hydrothermal treatment at 100 °C for 72 h.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide