| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1521781 | Materials Chemistry and Physics | 2014 | 8 Pages |
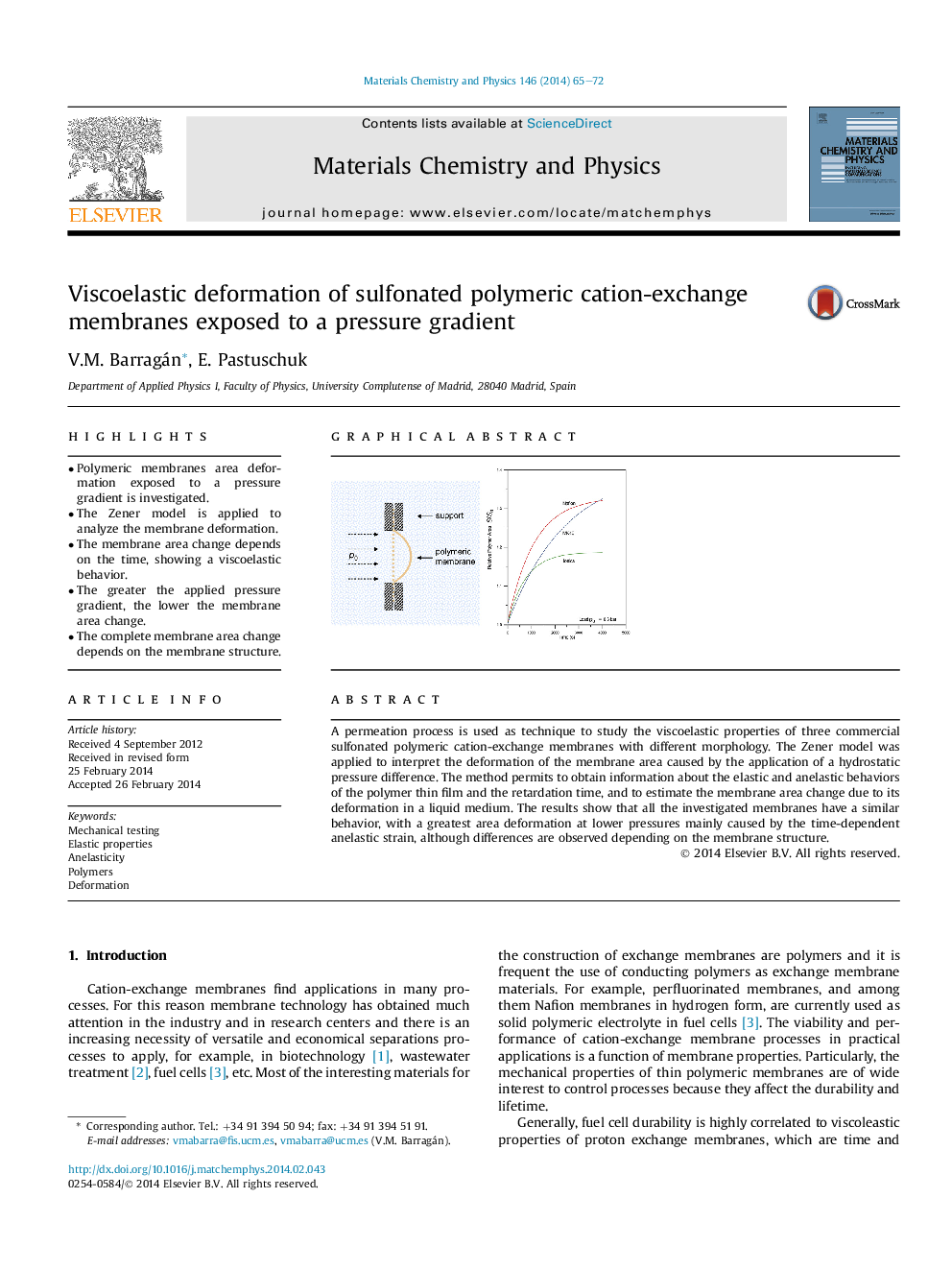
•Polymeric membranes area deformation exposed to a pressure gradient is investigated.•The Zener model is applied to analyze the membrane deformation.•The membrane area change depends on the time, showing a viscoelastic behavior.•The greater the applied pressure gradient, the lower the membrane area change.•The complete membrane area change depends on the membrane structure.
A permeation process is used as technique to study the viscoelastic properties of three commercial sulfonated polymeric cation-exchange membranes with different morphology. The Zener model was applied to interpret the deformation of the membrane area caused by the application of a hydrostatic pressure difference. The method permits to obtain information about the elastic and anelastic behaviors of the polymer thin film and the retardation time, and to estimate the membrane area change due to its deformation in a liquid medium. The results show that all the investigated membranes have a similar behavior, with a greatest area deformation at lower pressures mainly caused by the time-dependent anelastic strain, although differences are observed depending on the membrane structure.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide