| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1521835 | Materials Chemistry and Physics | 2014 | 11 Pages |
•Synthesis of new imidazole derivatives-BIDM(bipodal) and TITM(tripodal) inhibitors.•Gravimetric analysis to investigate mild steel corrosion inhibition in ground water.•Electrochemical characterizations to substantiate results of weight loss method.•Quantum studies to analyse the chemical behavior, structure and substituent effect.
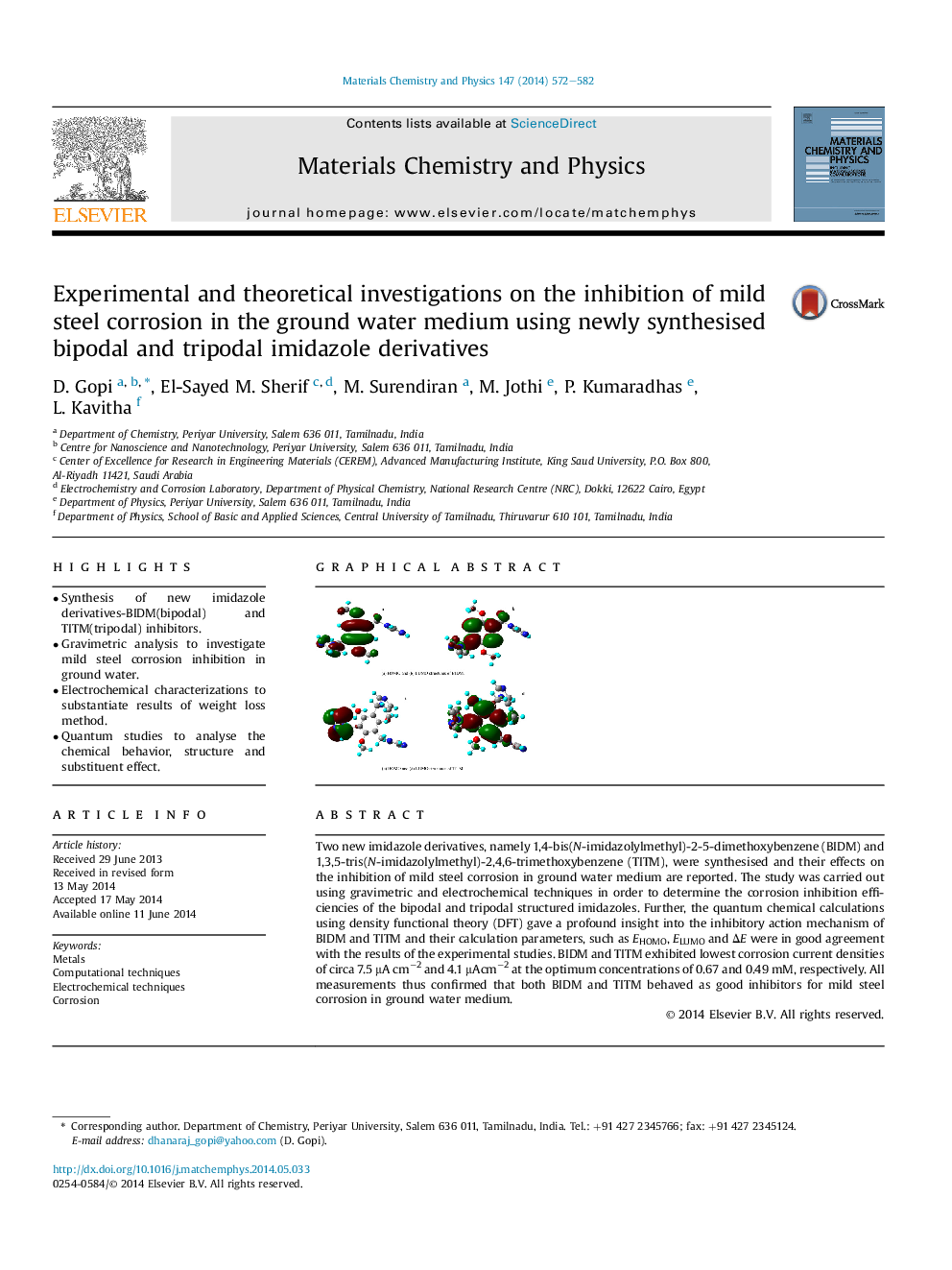
Two new imidazole derivatives, namely 1,4-bis(N-imidazolylmethyl)-2-5-dimethoxybenzene (BIDM) and 1,3,5-tris(N-imidazolylmethyl)-2,4,6-trimethoxybenzene (TITM), were synthesised and their effects on the inhibition of mild steel corrosion in ground water medium are reported. The study was carried out using gravimetric and electrochemical techniques in order to determine the corrosion inhibition efficiencies of the bipodal and tripodal structured imidazoles. Further, the quantum chemical calculations using density functional theory (DFT) gave a profound insight into the inhibitory action mechanism of BIDM and TITM and their calculation parameters, such as EHOMO, ELUMO and ΔE were in good agreement with the results of the experimental studies. BIDM and TITM exhibited lowest corrosion current densities of circa 7.5 μA cm−2 and 4.1 μAcm−2 at the optimum concentrations of 0.67 and 0.49 mM, respectively. All measurements thus confirmed that both BIDM and TITM behaved as good inhibitors for mild steel corrosion in ground water medium.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide