| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1521997 | Materials Chemistry and Physics | 2014 | 8 Pages |
•δ-MnO2 is prepared by one-step and energy-saving way using ascorbic acid.•δ-MnO2 nanoparticles with a large specific surface area have been obtained.•Pseudo maximum adsorption capacities for Pb2+ and Zn2+ are 3425 and 1789 mmol/kg.•97% and 68% of the MB were adsorbed and oxidized by δ-MnO2 respectively.
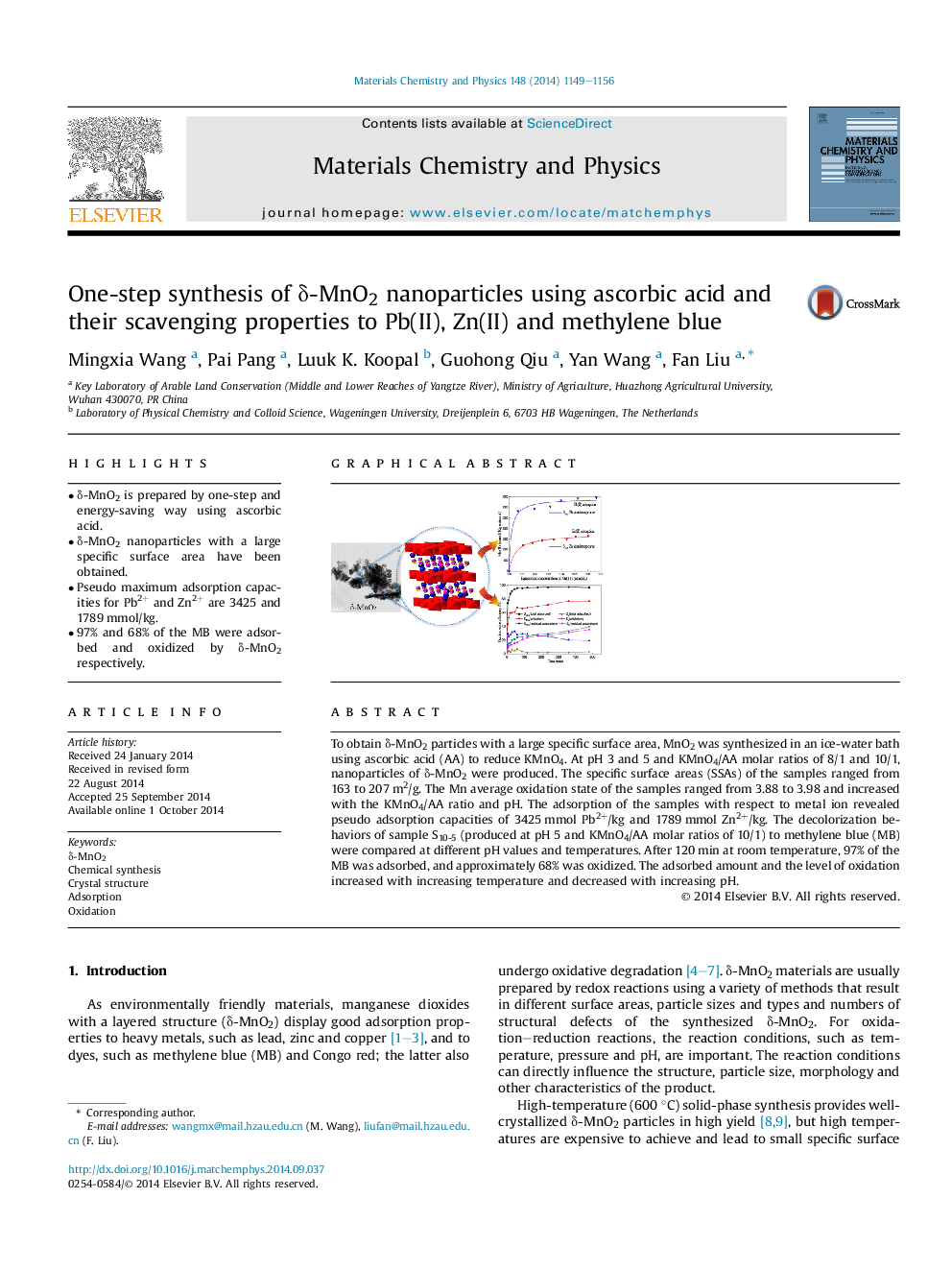
To obtain δ-MnO2 particles with a large specific surface area, MnO2 was synthesized in an ice-water bath using ascorbic acid (AA) to reduce KMnO4. At pH 3 and 5 and KMnO4/AA molar ratios of 8/1 and 10/1, nanoparticles of δ-MnO2 were produced. The specific surface areas (SSAs) of the samples ranged from 163 to 207 m2/g. The Mn average oxidation state of the samples ranged from 3.88 to 3.98 and increased with the KMnO4/AA ratio and pH. The adsorption of the samples with respect to metal ion revealed pseudo adsorption capacities of 3425 mmol Pb2+/kg and 1789 mmol Zn2+/kg. The decolorization behaviors of sample S10-5 (produced at pH 5 and KMnO4/AA molar ratios of 10/1) to methylene blue (MB) were compared at different pH values and temperatures. After 120 min at room temperature, 97% of the MB was adsorbed, and approximately 68% was oxidized. The adsorbed amount and the level of oxidation increased with increasing temperature and decreased with increasing pH.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide