| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1522860 | Materials Chemistry and Physics | 2013 | 7 Pages |
•Natural reductants were used as green electroless deposition reagents.•Room temperature synthesis of supported Ag and Pd nanoparticles was achieved.•Carbon porous microspheres were used as supports.•Synthesis via natural reductants yielded catalytically active nanoparticles.
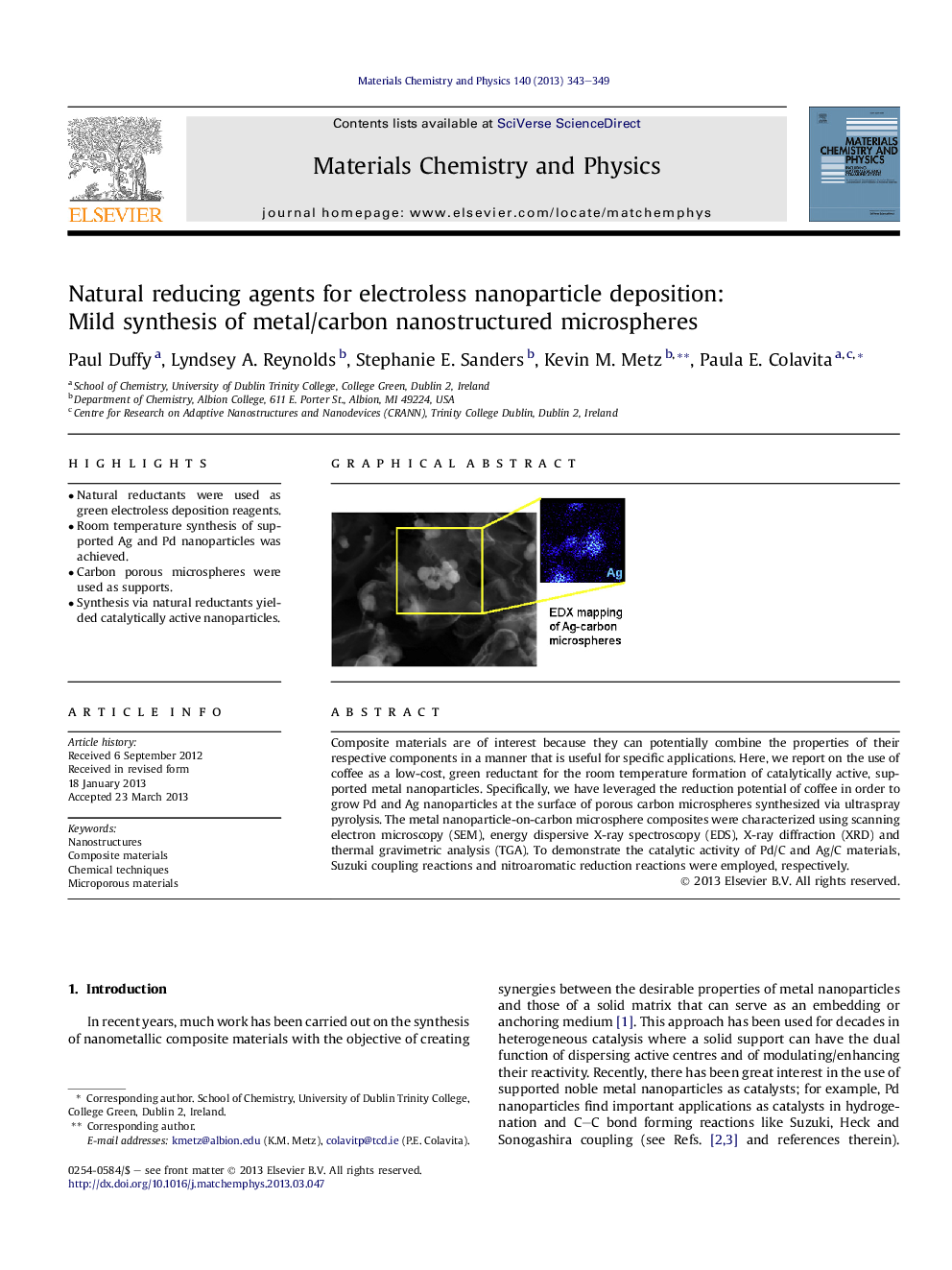
Composite materials are of interest because they can potentially combine the properties of their respective components in a manner that is useful for specific applications. Here, we report on the use of coffee as a low-cost, green reductant for the room temperature formation of catalytically active, supported metal nanoparticles. Specifically, we have leveraged the reduction potential of coffee in order to grow Pd and Ag nanoparticles at the surface of porous carbon microspheres synthesized via ultraspray pyrolysis. The metal nanoparticle-on-carbon microsphere composites were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA). To demonstrate the catalytic activity of Pd/C and Ag/C materials, Suzuki coupling reactions and nitroaromatic reduction reactions were employed, respectively.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide