| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1522901 | Materials Chemistry and Physics | 2013 | 8 Pages |
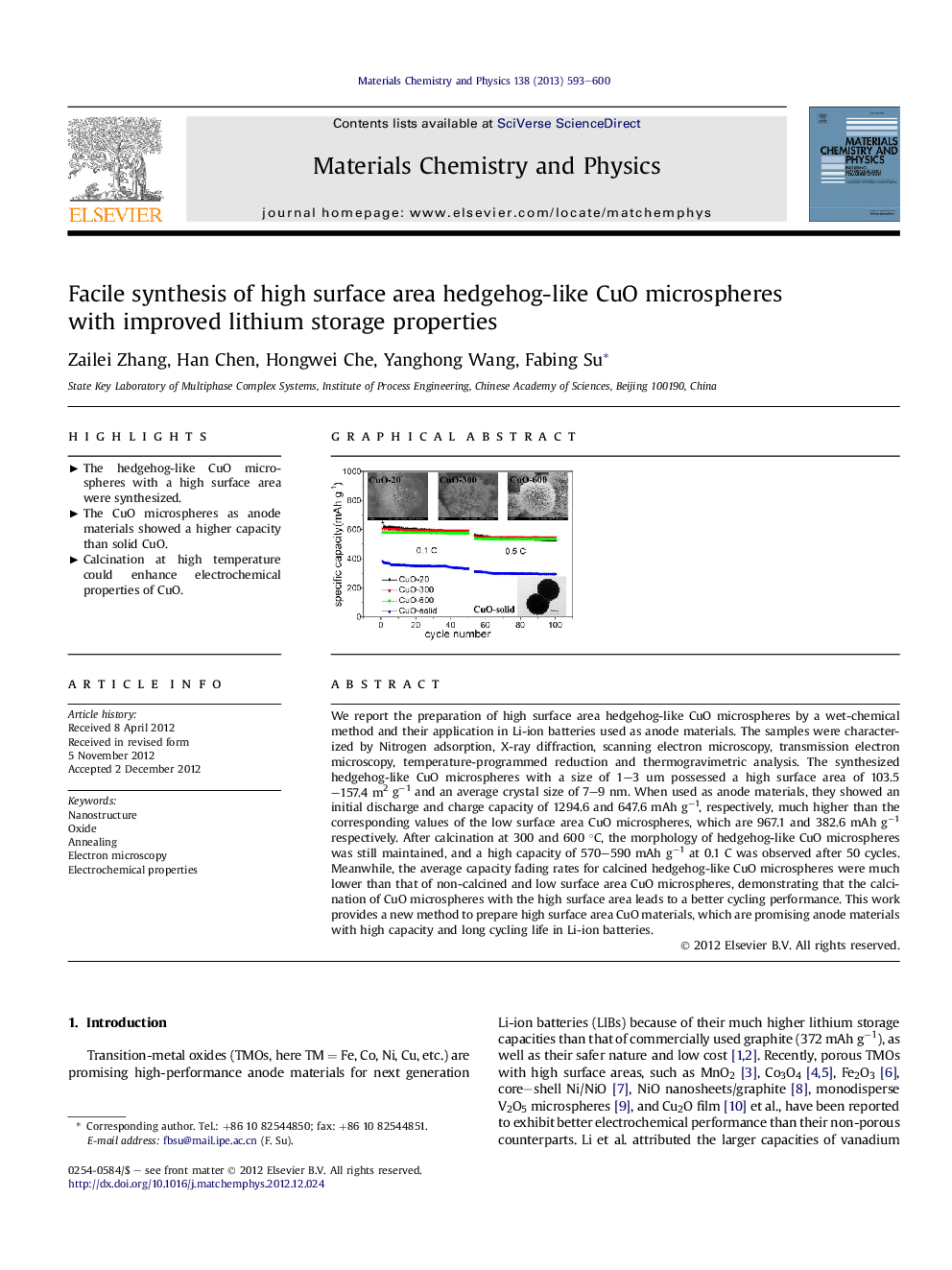
We report the preparation of high surface area hedgehog-like CuO microspheres by a wet-chemical method and their application in Li-ion batteries used as anode materials. The samples were characterized by Nitrogen adsorption, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, temperature-programmed reduction and thermogravimetric analysis. The synthesized hedgehog-like CuO microspheres with a size of 1–3 um possessed a high surface area of 103.5–157.4 m2 g−1 and an average crystal size of 7–9 nm. When used as anode materials, they showed an initial discharge and charge capacity of 1294.6 and 647.6 mAh g−1, respectively, much higher than the corresponding values of the low surface area CuO microspheres, which are 967.1 and 382.6 mAh g−1 respectively. After calcination at 300 and 600 °C, the morphology of hedgehog-like CuO microspheres was still maintained, and a high capacity of 570–590 mAh g−1 at 0.1 C was observed after 50 cycles. Meanwhile, the average capacity fading rates for calcined hedgehog-like CuO microspheres were much lower than that of non-calcined and low surface area CuO microspheres, demonstrating that the calcination of CuO microspheres with the high surface area leads to a better cycling performance. This work provides a new method to prepare high surface area CuO materials, which are promising anode materials with high capacity and long cycling life in Li-ion batteries.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The hedgehog-like CuO microspheres with a high surface area were synthesized. ► The CuO microspheres as anode materials showed a higher capacity than solid CuO. ► Calcination at high temperature could enhance electrochemical properties of CuO.