| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1543663 | Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures | 2016 | 5 Pages |
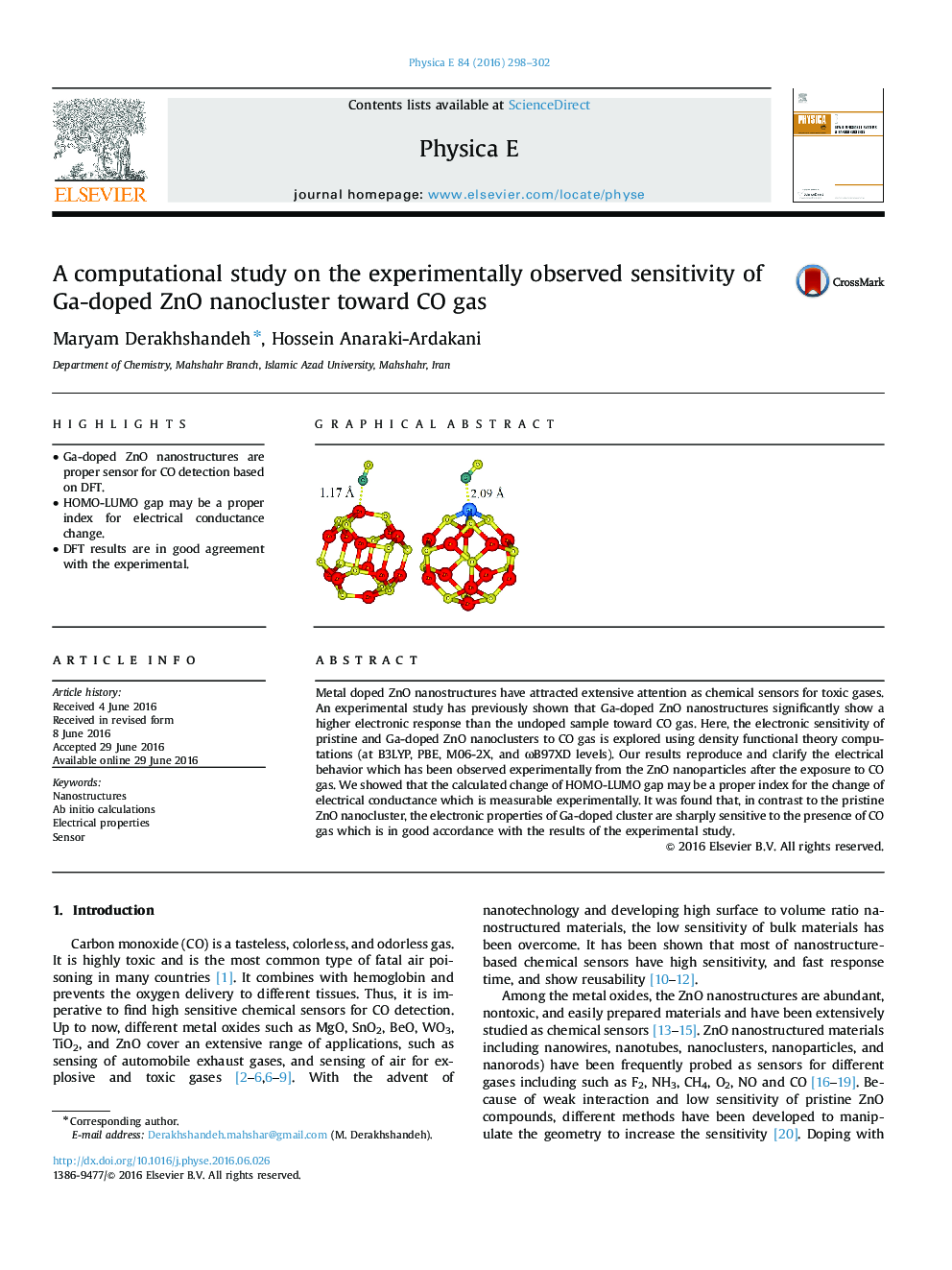
•Ga-doped ZnO nanostructures are proper sensor for CO detection based on DFT.•HOMO-LUMO gap may be a proper index for electrical conductance change.•DFT results are in good agreement with the experimental.
Metal doped ZnO nanostructures have attracted extensive attention as chemical sensors for toxic gases. An experimental study has previously shown that Ga-doped ZnO nanostructures significantly show a higher electronic response than the undoped sample toward CO gas. Here, the electronic sensitivity of pristine and Ga-doped ZnO nanoclusters to CO gas is explored using density functional theory computations (at B3LYP, PBE, M06-2X, and ωB97XD levels). Our results reproduce and clarify the electrical behavior which has been observed experimentally from the ZnO nanoparticles after the exposure to CO gas. We showed that the calculated change of HOMO-LUMO gap may be a proper index for the change of electrical conductance which is measurable experimentally. It was found that, in contrast to the pristine ZnO nanocluster, the electronic properties of Ga-doped cluster are sharply sensitive to the presence of CO gas which is in good accordance with the results of the experimental study.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide