| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1544020 | Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures | 2015 | 5 Pages |
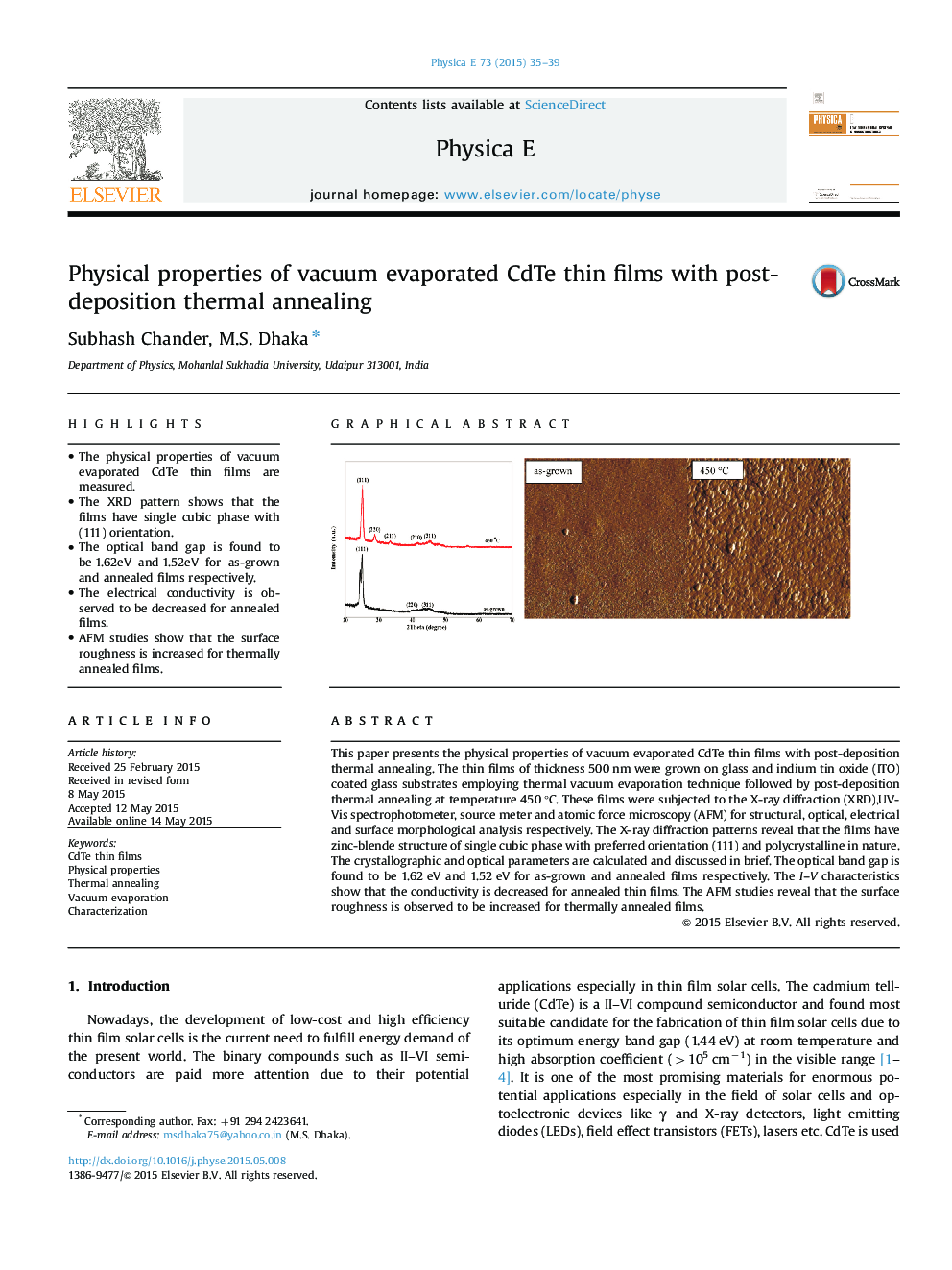
•The physical properties of vacuum evaporated CdTe thin films are measured.•The XRD pattern shows that the films have single cubic phase with (111) orientation.•The optical band gap is found to be 1.62eV and 1.52eV for as-grown and annealed films respectively.•The electrical conductivity is observed to be decreased for annealed films.•AFM studies show that the surface roughness is increased for thermally annealed films.
This paper presents the physical properties of vacuum evaporated CdTe thin films with post-deposition thermal annealing. The thin films of thickness 500 nm were grown on glass and indium tin oxide (ITO) coated glass substrates employing thermal vacuum evaporation technique followed by post-deposition thermal annealing at temperature 450 °C. These films were subjected to the X-ray diffraction (XRD),UV-Vis spectrophotometer, source meter and atomic force microscopy (AFM) for structural, optical, electrical and surface morphological analysis respectively. The X-ray diffraction patterns reveal that the films have zinc-blende structure of single cubic phase with preferred orientation (111) and polycrystalline in nature. The crystallographic and optical parameters are calculated and discussed in brief. The optical band gap is found to be 1.62 eV and 1.52 eV for as-grown and annealed films respectively. The I–V characteristics show that the conductivity is decreased for annealed thin films. The AFM studies reveal that the surface roughness is observed to be increased for thermally annealed films.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide