| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1544024 | Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures | 2015 | 6 Pages |
•ZnS:Fe nanoparticles were synthesized at 80 °C through chemical route.•Structural, band gap, PL and magnetization studies were carried out.•All the doped samples exhibited defect induced room temperature paramagnetism.•EPR signal characteristic of Fe3+ was observed in all the doped samples.
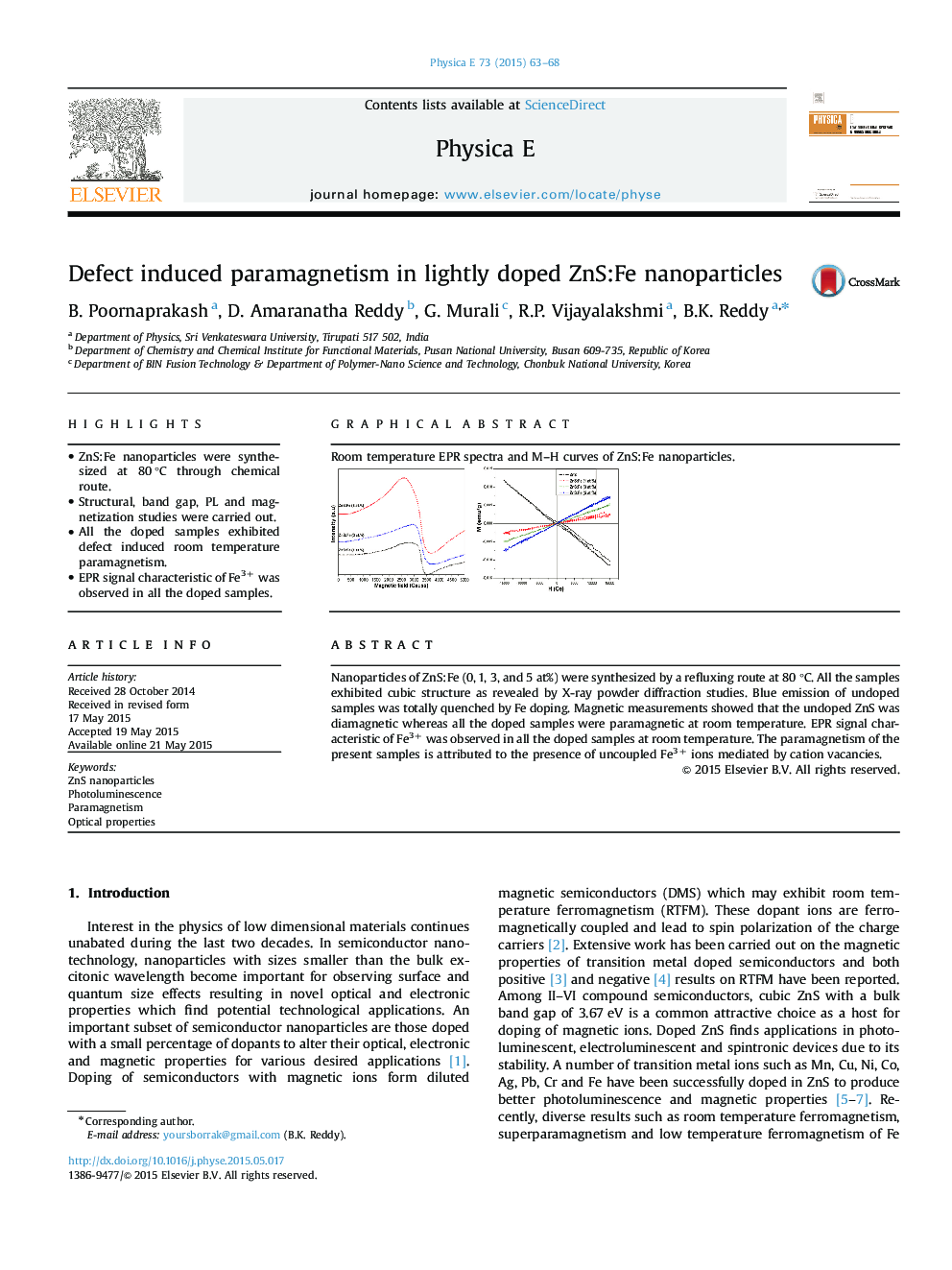
Nanoparticles of ZnS:Fe (0, 1, 3, and 5 at%) were synthesized by a refluxing route at 80 °C. All the samples exhibited cubic structure as revealed by X-ray powder diffraction studies. Blue emission of undoped samples was totally quenched by Fe doping. Magnetic measurements showed that the undoped ZnS was diamagnetic whereas all the doped samples were paramagnetic at room temperature. EPR signal characteristic of Fe3+ was observed in all the doped samples at room temperature. The paramagnetism of the present samples is attributed to the presence of uncoupled Fe3+ ions mediated by cation vacancies.
Graphical abstractRoom temperature EPR spectra and M–H curves of ZnS:Fe nanoparticles.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide