| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1544200 | Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures | 2015 | 7 Pages |
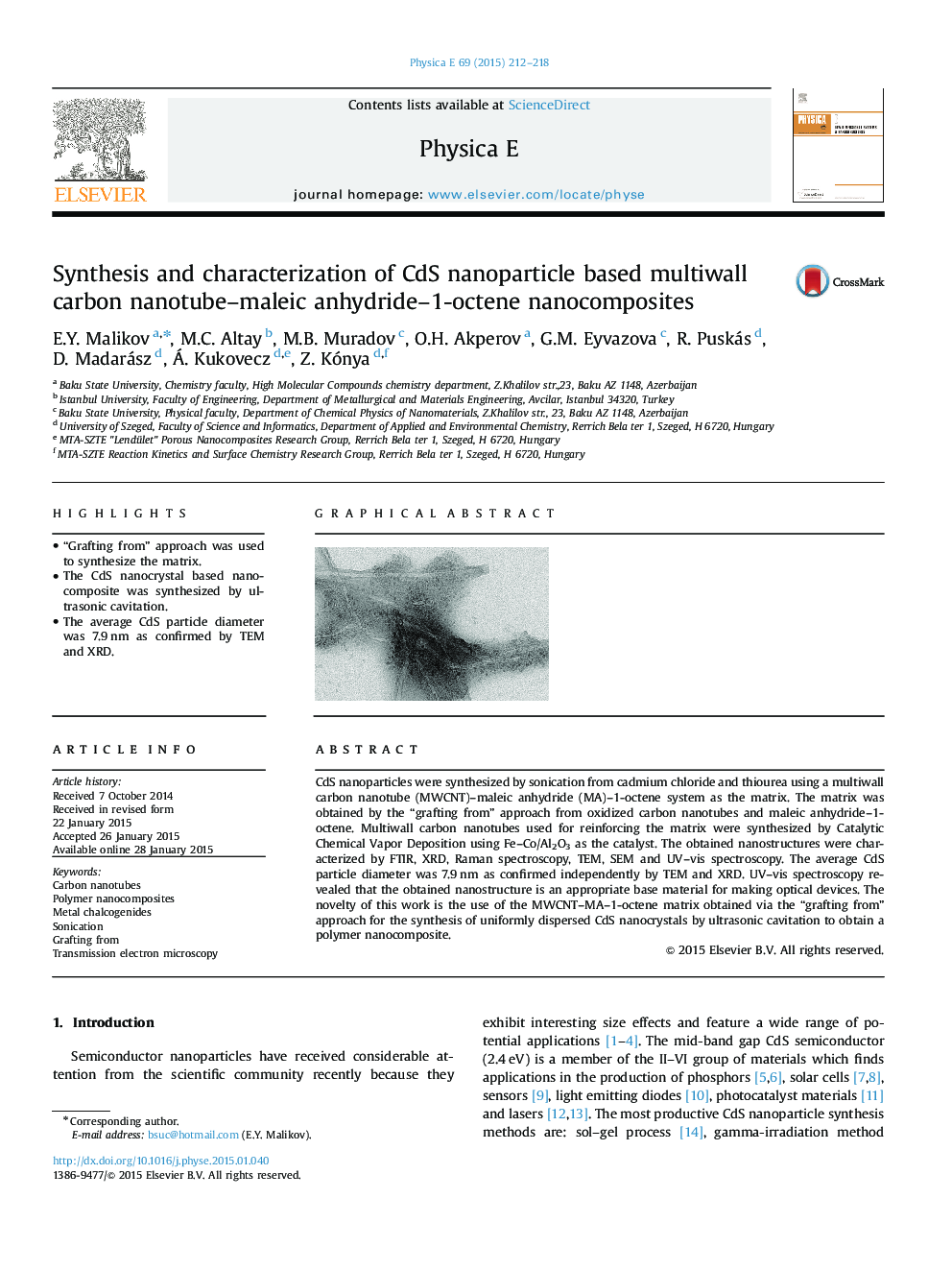
•“Grafting from” approach was used to synthesize the matrix.•The CdS nanocrystal based nanocomposite was synthesized by ultrasonic cavitation.•The average CdS particle diameter was 7.9 nm as confirmed by TEM and XRD.
CdS nanoparticles were synthesized by sonication from cadmium chloride and thiourea using a multiwall carbon nanotube (MWCNT)–maleic anhydride (MA)–1-octene system as the matrix. The matrix was obtained by the “grafting from” approach from oxidized carbon nanotubes and maleic anhydride–1-octene. Multiwall carbon nanotubes used for reinforcing the matrix were synthesized by Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition using Fe–Co/Al2O3 as the catalyst. The obtained nanostructures were characterized by FTIR, XRD, Raman spectroscopy, TEM, SEM and UV–vis spectroscopy. The average CdS particle diameter was 7.9 nm as confirmed independently by TEM and XRD. UV–vis spectroscopy revealed that the obtained nanostructure is an appropriate base material for making optical devices. The novelty of this work is the use of the MWCNT–MA–1-octene matrix obtained via the “grafting from” approach for the synthesis of uniformly dispersed CdS nanocrystals by ultrasonic cavitation to obtain a polymer nanocomposite.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide