| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1544637 | Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures | 2014 | 4 Pages |
•C–C bond lengths decrease (increase) with increasing compressive (tensile) strain.•The lowest average energy corresponds to the unstrained state.•Band gap undergoes the direct-to-indirect transition by applying compressive strains.•Band gap increases slightly by applying tensile strains.
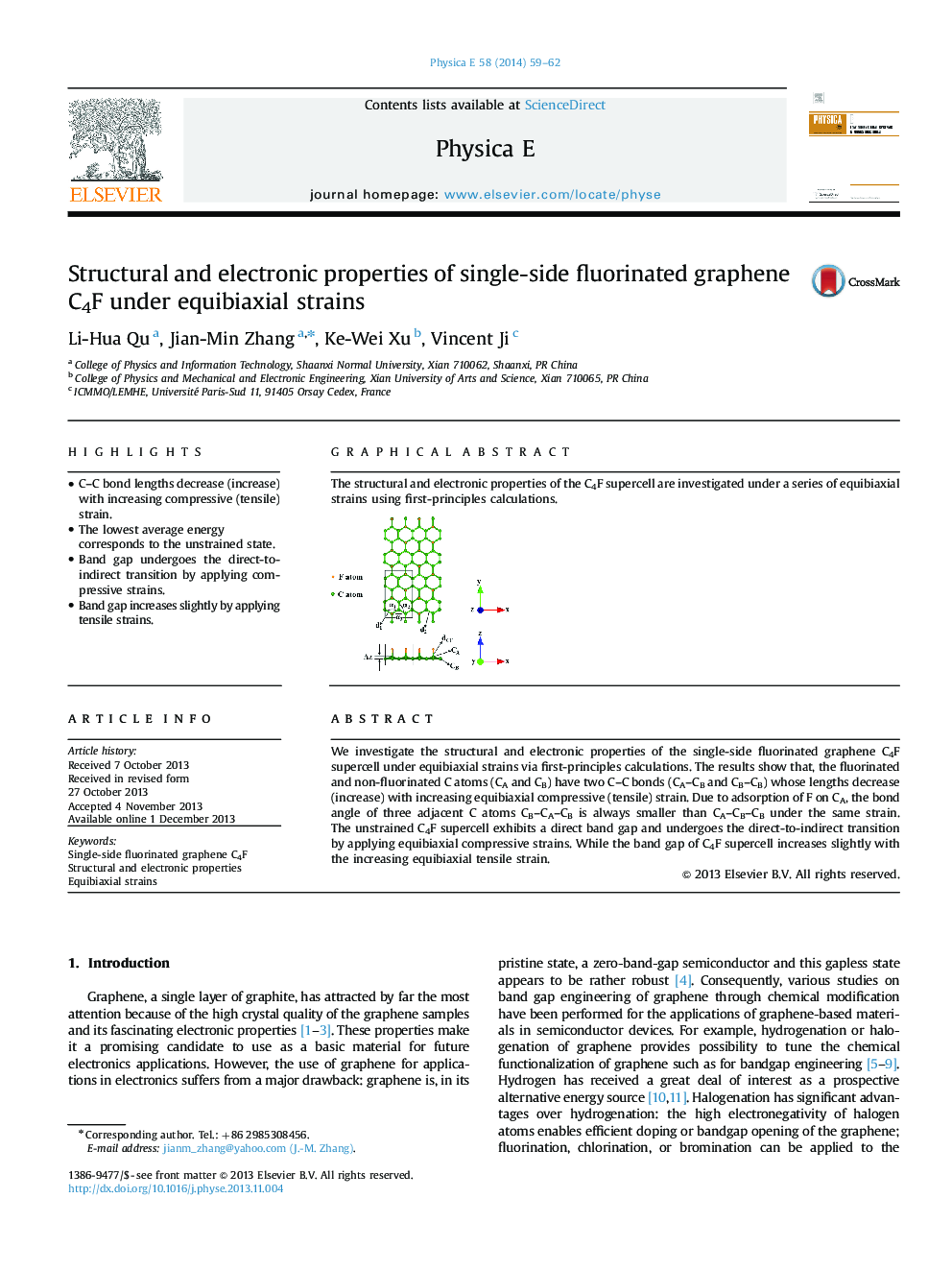
We investigate the structural and electronic properties of the single-side fluorinated graphene C4F supercell under equibiaxial strains via first-principles calculations. The results show that, the fluorinated and non-fluorinated C atoms (CA and CB) have two C–C bonds (CA–CB and CB–CB) whose lengths decrease (increase) with increasing equibiaxial compressive (tensile) strain. Due to adsorption of F on CA, the bond angle of three adjacent C atoms CB–CA–CB is always smaller than CA–CB–CB under the same strain. The unstrained C4F supercell exhibits a direct band gap and undergoes the direct-to-indirect transition by applying equibiaxial compressive strains. While the band gap of C4F supercell increases slightly with the increasing equibiaxial tensile strain.
Graphical abstractThe structural and electronic properties of the C4F supercell are investigated under a series of equibiaxial strains using first-principles calculations.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide