| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1544798 | Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures | 2013 | 4 Pages |
•Au:VO2 thin film was fabricated by NSL method and rf-magnetron sputtering method.•The surface morphology, crystal structure and composition, electrical and optical properties were studied.•Au doping in VO2 thin films could reduce the transition temperature, which is better than that reported in reference.•Au doping synchronizes influences the extent of transmittance is discussed.
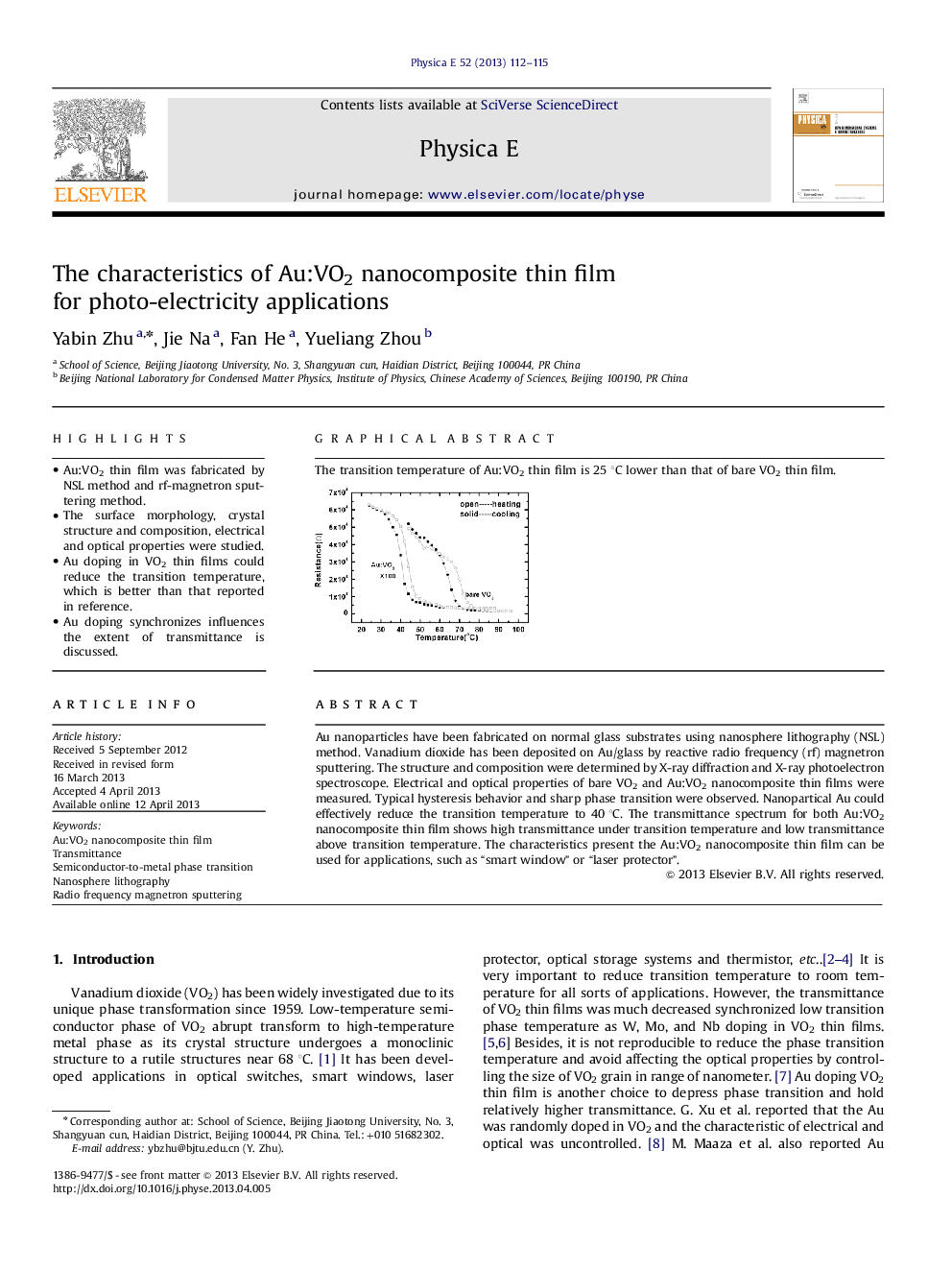
Au nanoparticles have been fabricated on normal glass substrates using nanosphere lithography (NSL) method. Vanadium dioxide has been deposited on Au/glass by reactive radio frequency (rf) magnetron sputtering. The structure and composition were determined by X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope. Electrical and optical properties of bare VO2 and Au:VO2 nanocomposite thin films were measured. Typical hysteresis behavior and sharp phase transition were observed. Nanopartical Au could effectively reduce the transition temperature to 40 °C. The transmittance spectrum for both Au:VO2 nanocomposite thin film shows high transmittance under transition temperature and low transmittance above transition temperature. The characteristics present the Au:VO2 nanocomposite thin film can be used for applications, such as “smart window” or “laser protector”.
Graphical abstractThe transition temperature of Au:VO2 thin film is 25 °C lower than that of bare VO2 thin film.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide