| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 154644 | Chemical Engineering Science | 2015 | 18 Pages |
•The integration of heat and work is studied.•Expanders are integrated with sub-ambient heat exchanger networks.•Pinch Expansion is proven to be preferred.•The exergy consumption is minimized.
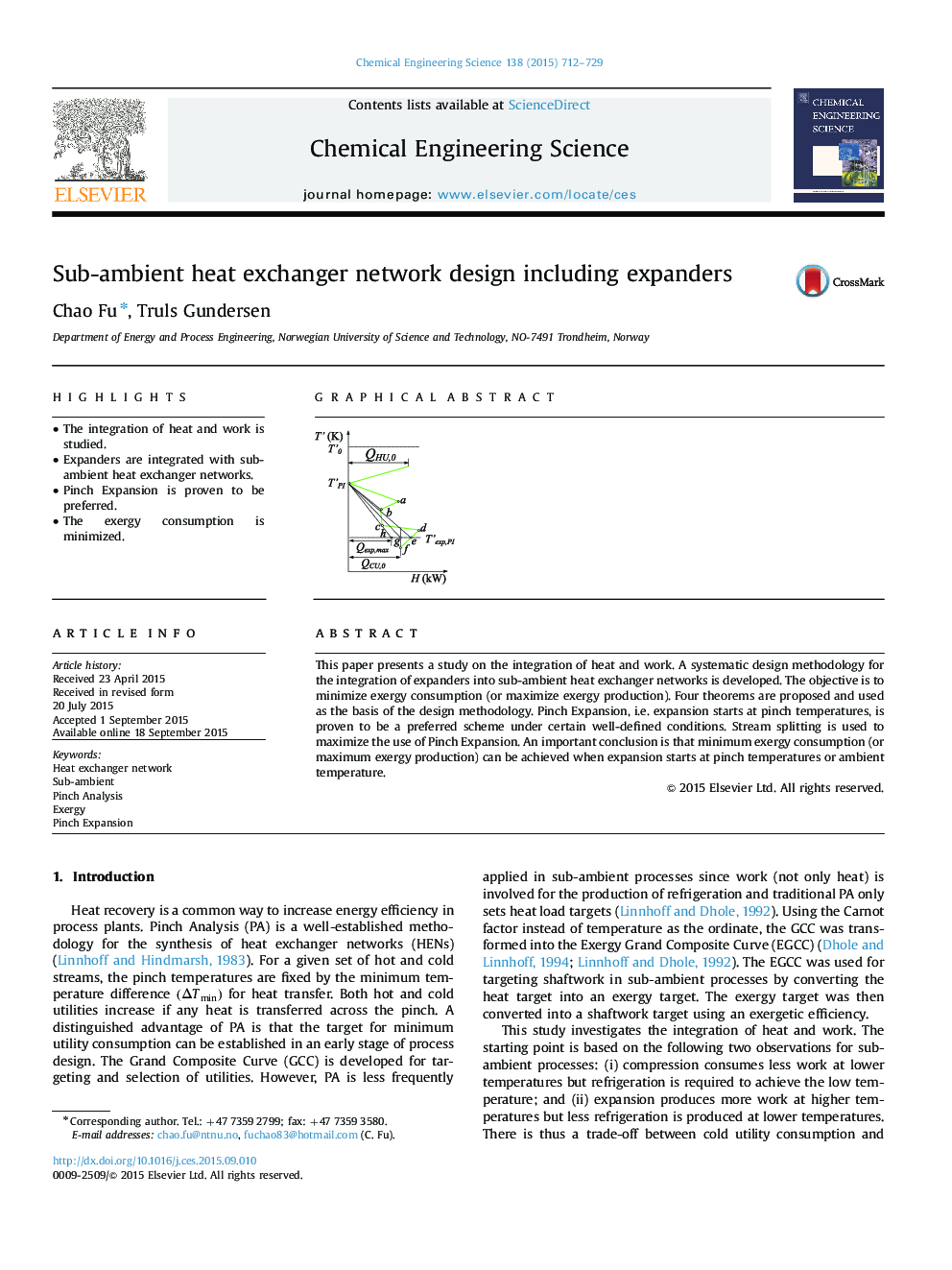
This paper presents a study on the integration of heat and work. A systematic design methodology for the integration of expanders into sub-ambient heat exchanger networks is developed. The objective is to minimize exergy consumption (or maximize exergy production). Four theorems are proposed and used as the basis of the design methodology. Pinch Expansion, i.e. expansion starts at pinch temperatures, is proven to be a preferred scheme under certain well-defined conditions. Stream splitting is used to maximize the use of Pinch Expansion. An important conclusion is that minimum exergy consumption (or maximum exergy production) can be achieved when expansion starts at pinch temperatures or ambient temperature.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (101 K)Download as PowerPoint slide