| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 155259 | Chemical Engineering Science | 2013 | 5 Pages |
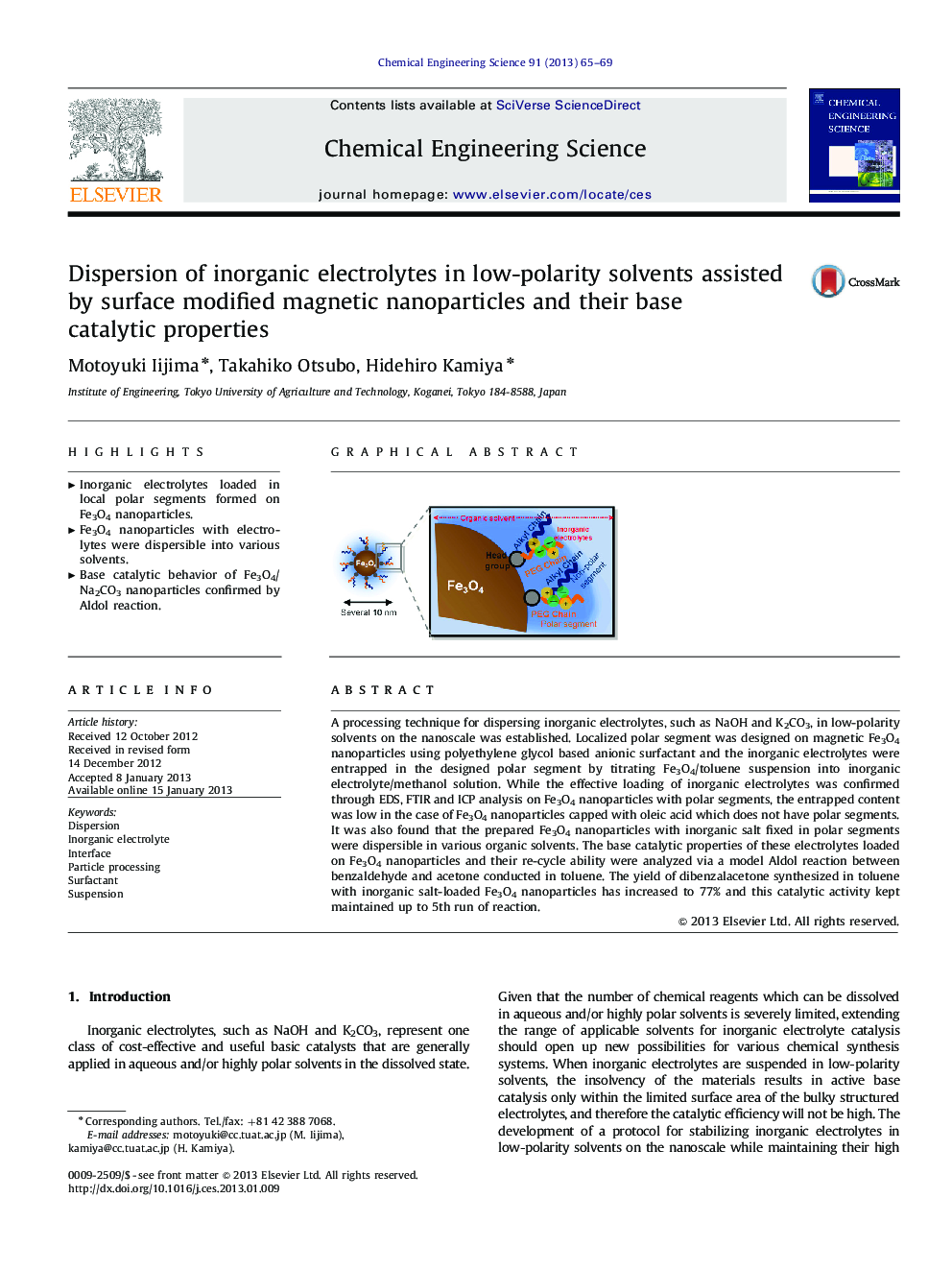
A processing technique for dispersing inorganic electrolytes, such as NaOH and K2CO3, in low-polarity solvents on the nanoscale was established. Localized polar segment was designed on magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles using polyethylene glycol based anionic surfactant and the inorganic electrolytes were entrapped in the designed polar segment by titrating Fe3O4/toluene suspension into inorganic electrolyte/methanol solution. While the effective loading of inorganic electrolytes was confirmed through EDS, FTIR and ICP analysis on Fe3O4 nanoparticles with polar segments, the entrapped content was low in the case of Fe3O4 nanoparticles capped with oleic acid which does not have polar segments. It was also found that the prepared Fe3O4 nanoparticles with inorganic salt fixed in polar segments were dispersible in various organic solvents. The base catalytic properties of these electrolytes loaded on Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their re-cycle ability were analyzed via a model Aldol reaction between benzaldehyde and acetone conducted in toluene. The yield of dibenzalacetone synthesized in toluene with inorganic salt-loaded Fe3O4 nanoparticles has increased to 77% and this catalytic activity kept maintained up to 5th run of reaction.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (240 K)Download as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Inorganic electrolytes loaded in local polar segments formed on Fe3O4 nanoparticles. ► Fe3O4 nanoparticles with electrolytes were dispersible into various solvents. ► Base catalytic behavior of Fe3O4/Na2CO3 nanoparticles confirmed by Aldol reaction.