| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 155451 | Chemical Engineering Science | 2013 | 9 Pages |
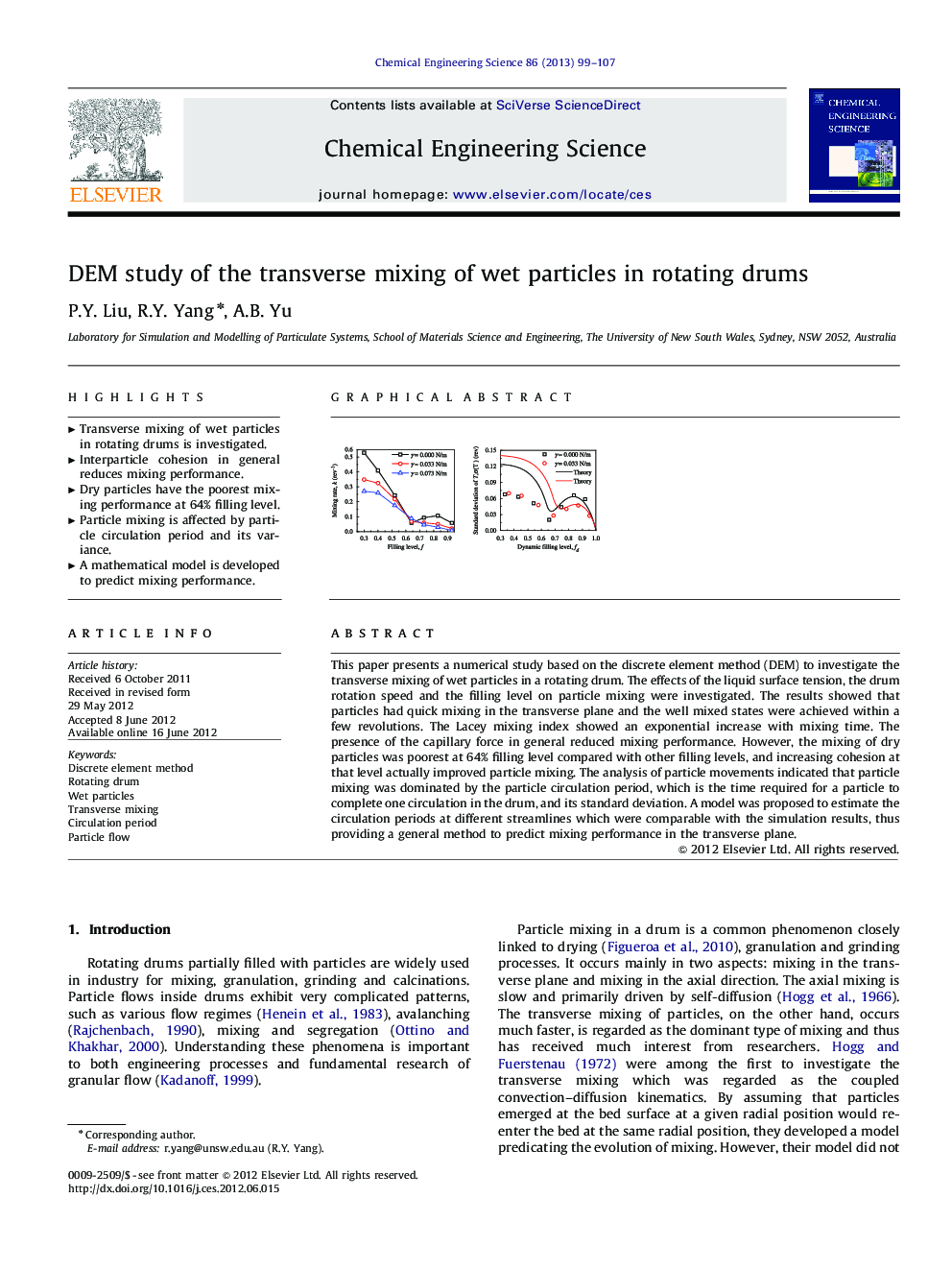
This paper presents a numerical study based on the discrete element method (DEM) to investigate the transverse mixing of wet particles in a rotating drum. The effects of the liquid surface tension, the drum rotation speed and the filling level on particle mixing were investigated. The results showed that particles had quick mixing in the transverse plane and the well mixed states were achieved within a few revolutions. The Lacey mixing index showed an exponential increase with mixing time. The presence of the capillary force in general reduced mixing performance. However, the mixing of dry particles was poorest at 64% filling level compared with other filling levels, and increasing cohesion at that level actually improved particle mixing. The analysis of particle movements indicated that particle mixing was dominated by the particle circulation period, which is the time required for a particle to complete one circulation in the drum, and its standard deviation. A model was proposed to estimate the circulation periods at different streamlines which were comparable with the simulation results, thus providing a general method to predict mixing performance in the transverse plane.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (221 K)Download as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Transverse mixing of wet particles in rotating drums is investigated. ► Interparticle cohesion in general reduces mixing performance. ► Dry particles have the poorest mixing performance at 64% filling level. ► Particle mixing is affected by particle circulation period and its variance. ► A mathematical model is developed to predict mixing performance.