| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1647751 | Materials Letters | 2012 | 5 Pages |
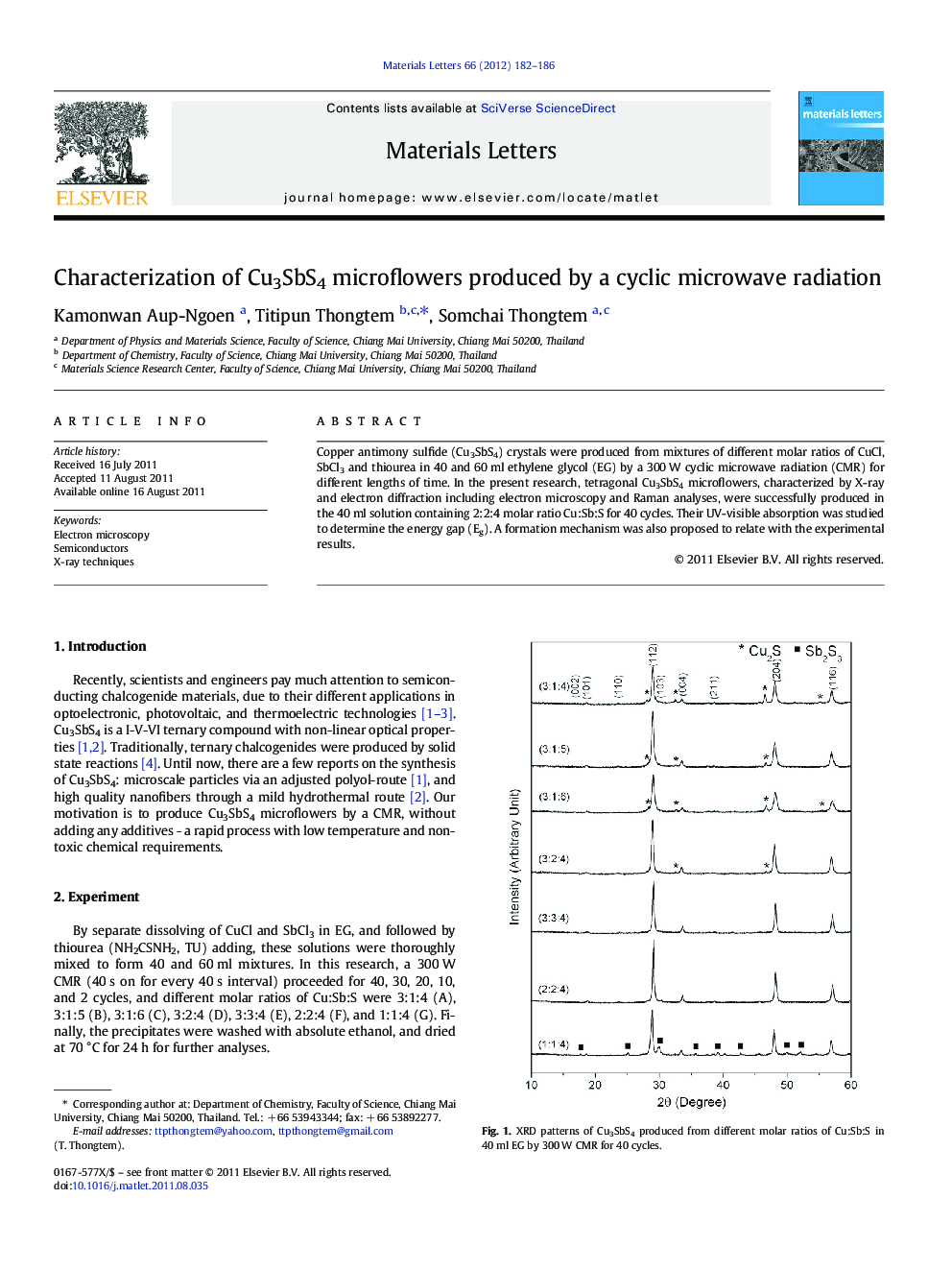
Copper antimony sulfide (Cu3SbS4) crystals were produced from mixtures of different molar ratios of CuCl, SbCl3 and thiourea in 40 and 60 ml ethylene glycol (EG) by a 300 W cyclic microwave radiation (CMR) for different lengths of time. In the present research, tetragonal Cu3SbS4 microflowers, characterized by X-ray and electron diffraction including electron microscopy and Raman analyses, were successfully produced in the 40 ml solution containing 2:2:4 molar ratio Cu:Sb:S for 40 cycles. Their UV-visible absorption was studied to determine the energy gap (Eg). A formation mechanism was also proposed to relate with the experimental results.
► Cu3SbS4 as one of semiconducting chalcogenide materials. ► Cyclic microwave radiation was used to form Cu3SbS4 microflowers. ► Upon processing 2:2:4 molar ratio Cu:Sb:S in EG, Cu3SbS4 microflowers were produced. ► A promising material for multiple potential applications.