| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1653621 | Materials Letters | 2006 | 4 Pages |
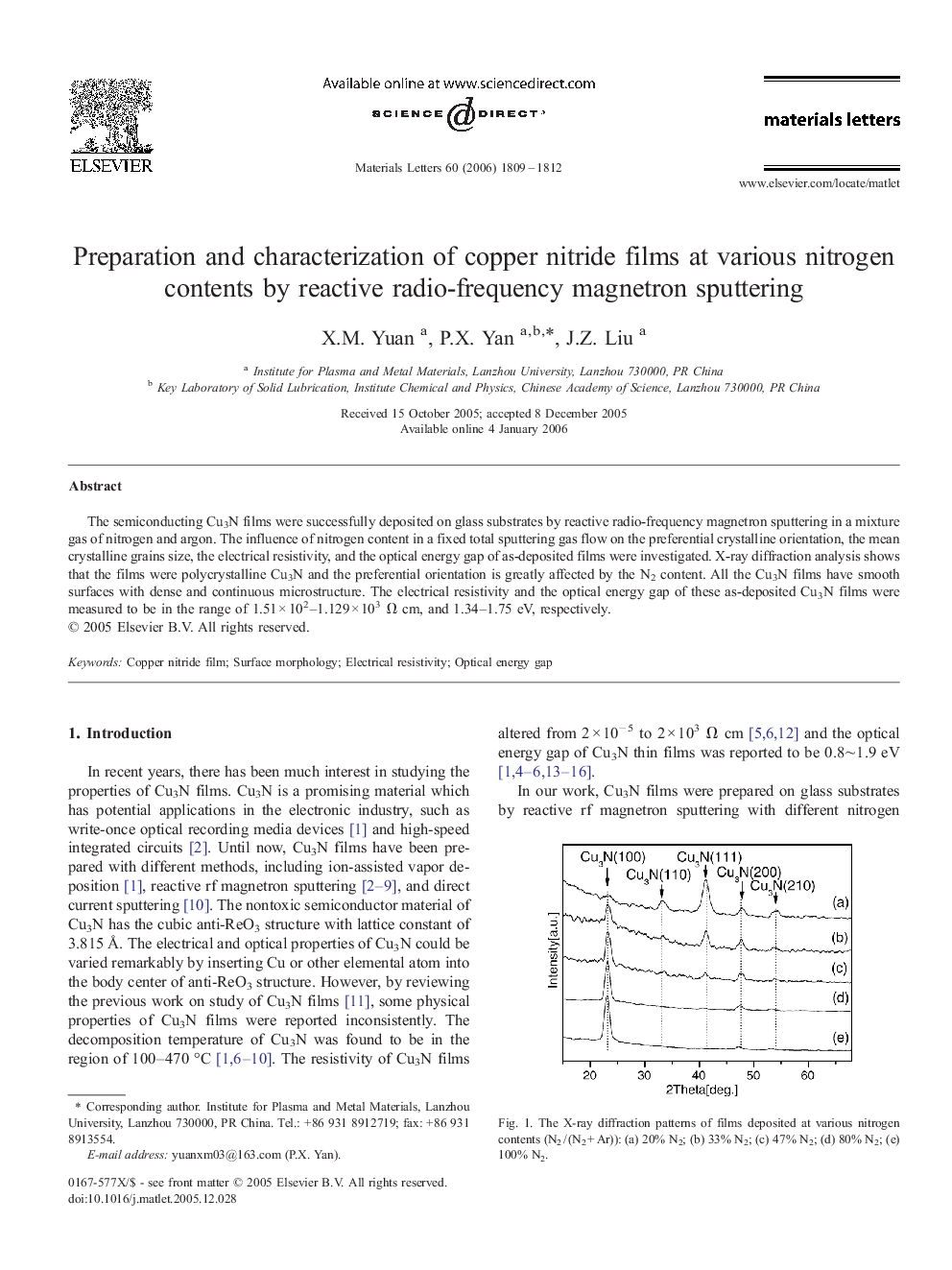
The semiconducting Cu3N films were successfully deposited on glass substrates by reactive radio-frequency magnetron sputtering in a mixture gas of nitrogen and argon. The influence of nitrogen content in a fixed total sputtering gas flow on the preferential crystalline orientation, the mean crystalline grains size, the electrical resistivity, and the optical energy gap of as-deposited films were investigated. X-ray diffraction analysis shows that the films were polycrystalline Cu3N and the preferential orientation is greatly affected by the N2 content. All the Cu3N films have smooth surfaces with dense and continuous microstructure. The electrical resistivity and the optical energy gap of these as-deposited Cu3N films were measured to be in the range of 1.51 × 102–1.129 × 103 Ω cm, and 1.34–1.75 eV, respectively.