| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1662018 | Surface and Coatings Technology | 2007 | 7 Pages |
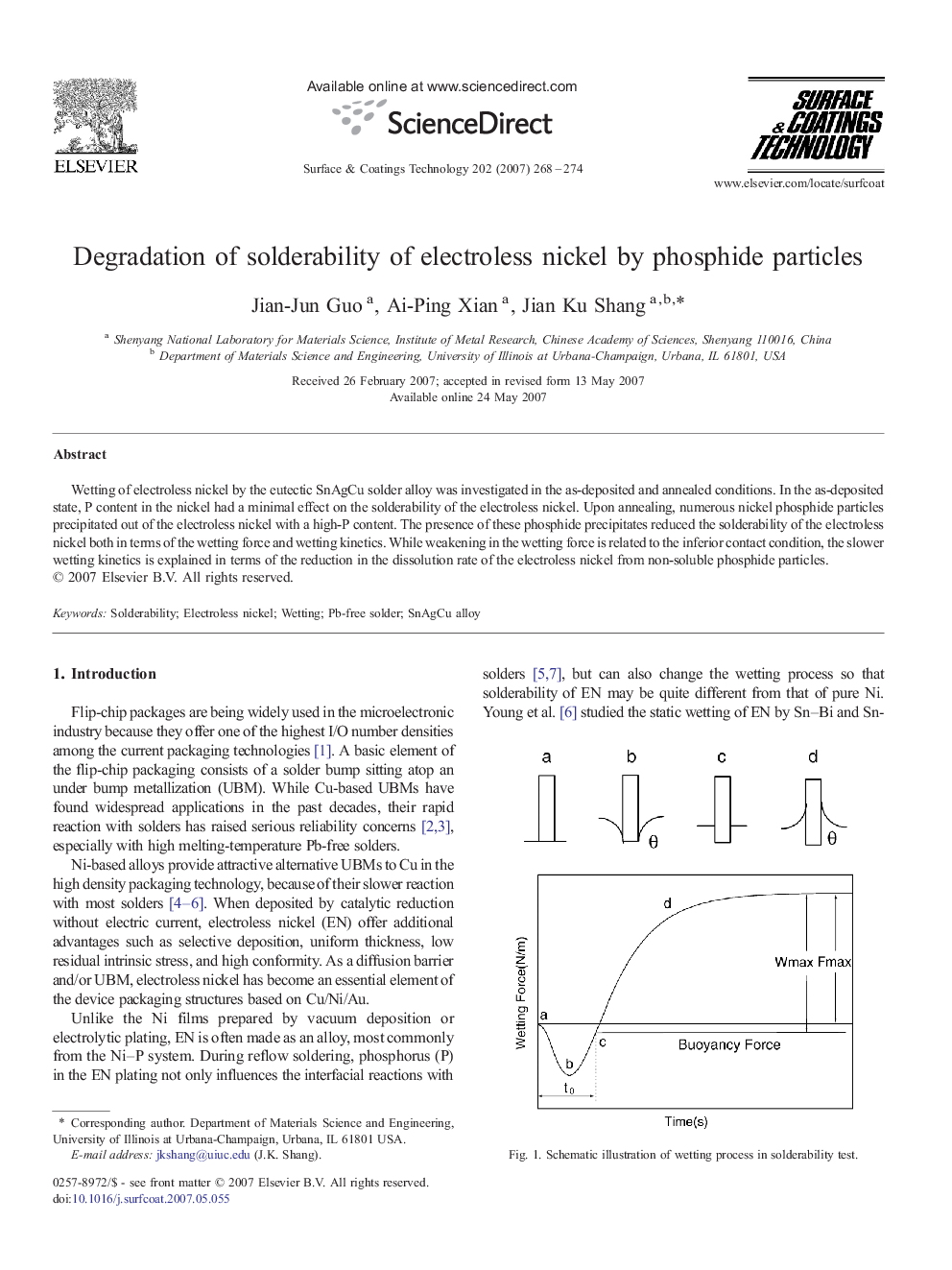
Wetting of electroless nickel by the eutectic SnAgCu solder alloy was investigated in the as-deposited and annealed conditions. In the as-deposited state, P content in the nickel had a minimal effect on the solderability of the electroless nickel. Upon annealing, numerous nickel phosphide particles precipitated out of the electroless nickel with a high-P content. The presence of these phosphide precipitates reduced the solderability of the electroless nickel both in terms of the wetting force and wetting kinetics. While weakening in the wetting force is related to the inferior contact condition, the slower wetting kinetics is explained in terms of the reduction in the dissolution rate of the electroless nickel from non-soluble phosphide particles.