| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1674888 | Thin Solid Films | 2005 | 7 Pages |
Abstract
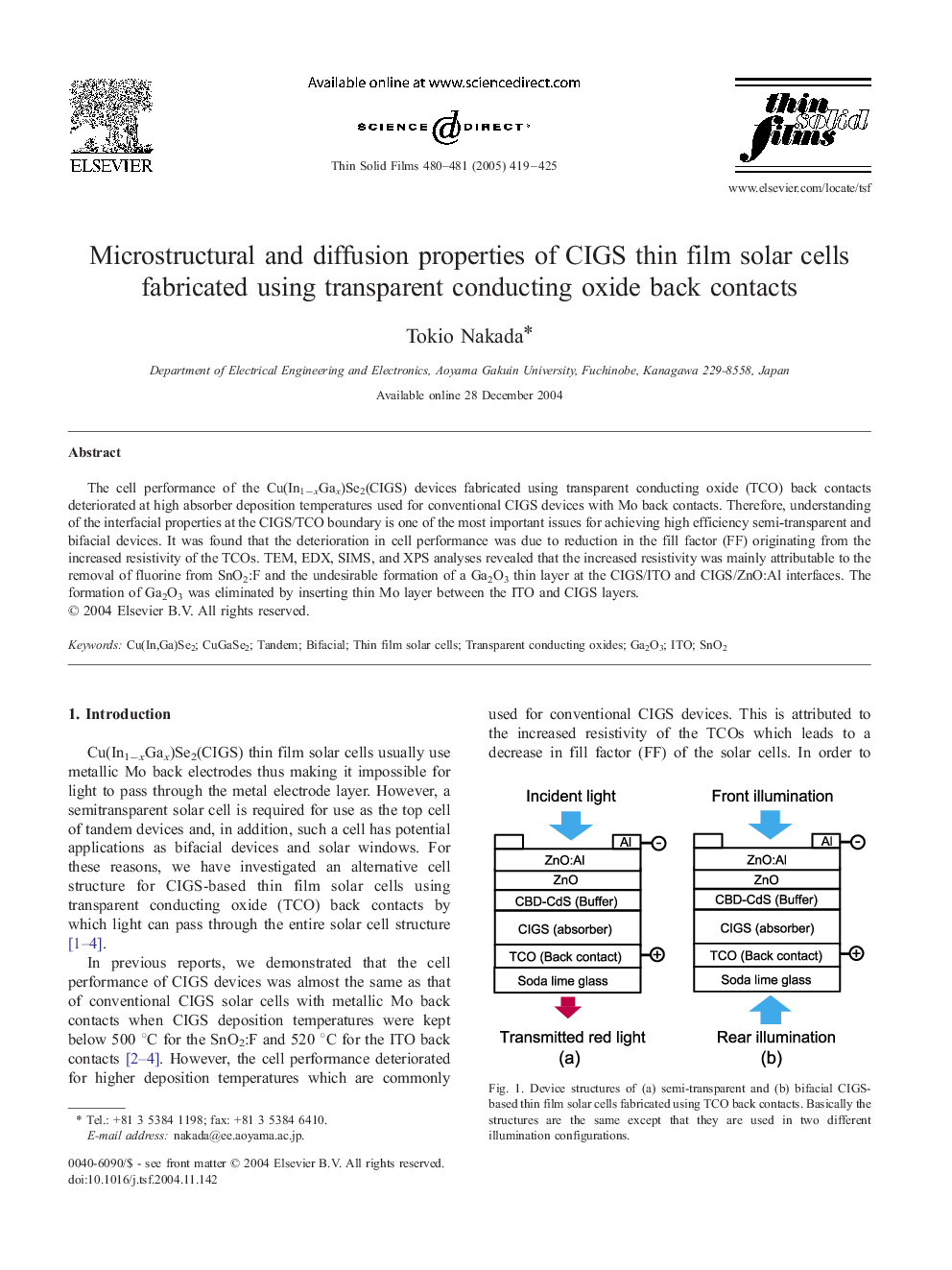
The cell performance of the Cu(In1âxGax)Se2(CIGS) devices fabricated using transparent conducting oxide (TCO) back contacts deteriorated at high absorber deposition temperatures used for conventional CIGS devices with Mo back contacts. Therefore, understanding of the interfacial properties at the CIGS/TCO boundary is one of the most important issues for achieving high efficiency semi-transparent and bifacial devices. It was found that the deterioration in cell performance was due to reduction in the fill factor (FF) originating from the increased resistivity of the TCOs. TEM, EDX, SIMS, and XPS analyses revealed that the increased resistivity was mainly attributable to the removal of fluorine from SnO2:F and the undesirable formation of a Ga2O3 thin layer at the CIGS/ITO and CIGS/ZnO:Al interfaces. The formation of Ga2O3 was eliminated by inserting thin Mo layer between the ITO and CIGS layers.
Keywords
Related Topics
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Materials Science
Nanotechnology
Authors
Tokio Nakada,