| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1675876 | Thin Solid Films | 2007 | 4 Pages |
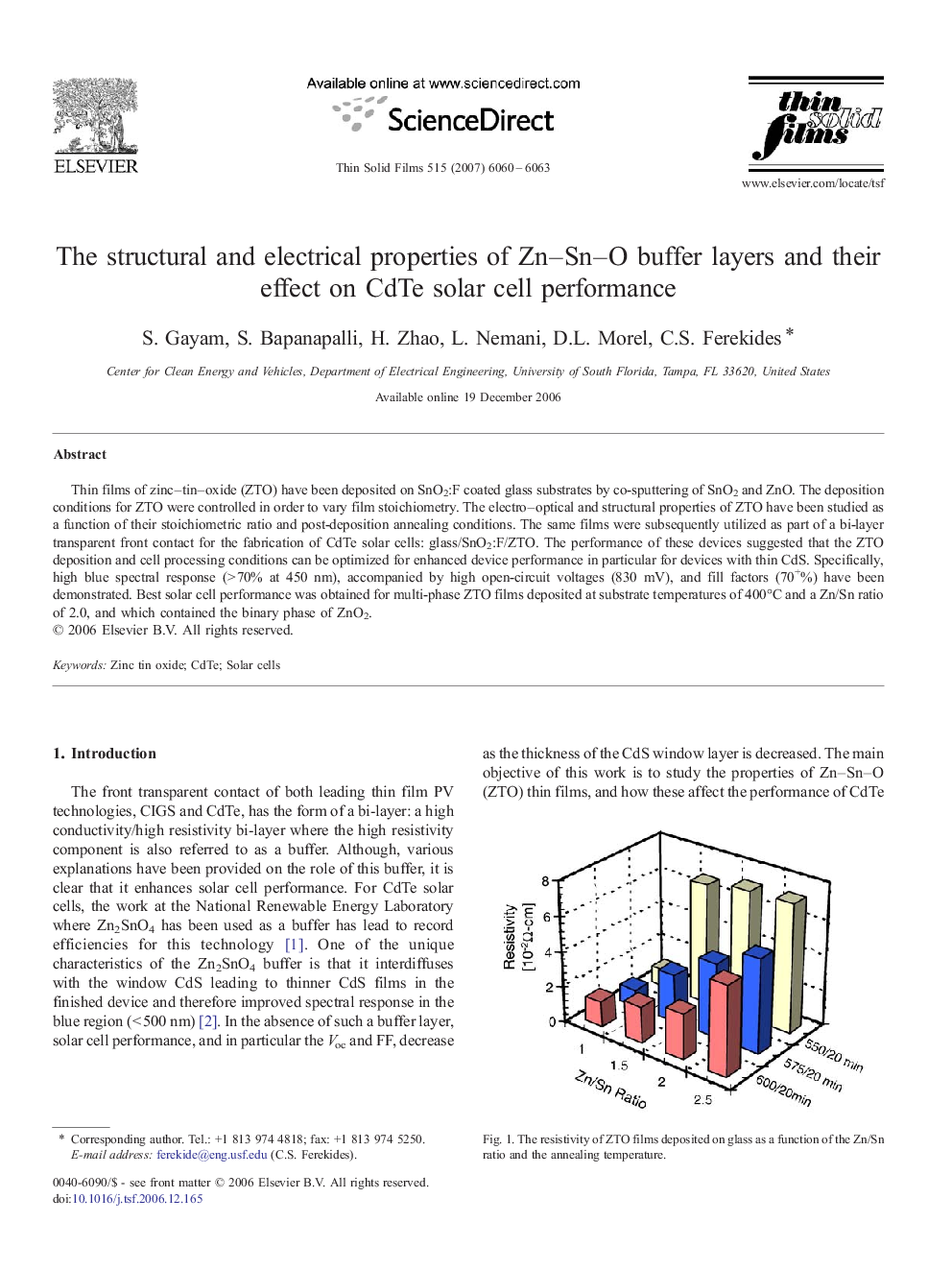
Thin films of zinc–tin–oxide (ZTO) have been deposited on SnO2:F coated glass substrates by co-sputtering of SnO2 and ZnO. The deposition conditions for ZTO were controlled in order to vary film stoichiometry. The electro–optical and structural properties of ZTO have been studied as a function of their stoichiometric ratio and post-deposition annealing conditions. The same films were subsequently utilized as part of a bi-layer transparent front contact for the fabrication of CdTe solar cells: glass/SnO2:F/ZTO. The performance of these devices suggested that the ZTO deposition and cell processing conditions can be optimized for enhanced device performance in particular for devices with thin CdS. Specifically, high blue spectral response (> 70% at 450 nm), accompanied by high open-circuit voltages (830 mV), and fill factors (70+%) have been demonstrated. Best solar cell performance was obtained for multi-phase ZTO films deposited at substrate temperatures of 400°C and a Zn/Sn ratio of 2.0, and which contained the binary phase of ZnO2.