| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1679582 | CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology | 2006 | 4 Pages |
Abstract
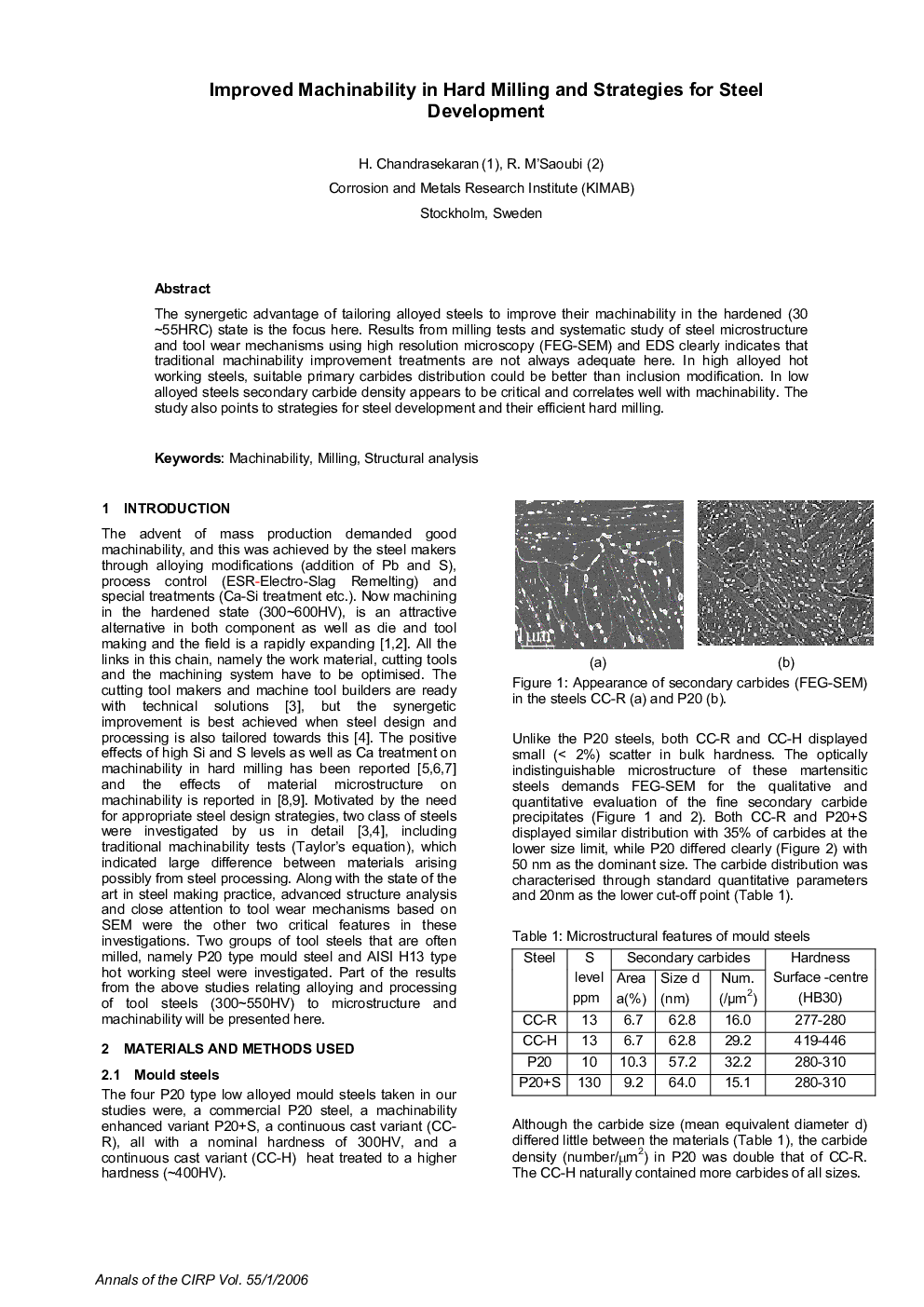
The synergetic advantage of tailoring alloyed steels to improve their machinability in the hardened (30 ∼55HRC) state is the focus here. Results from milling tests and systematic study of steel microstructure and tool wear mechanisms using high resolution microscopy (FEG-SEM) and EDS clearly indicates that traditional machinability improvement treatments are not always adequate here. In high alloyed hot working steels, suitable primary carbides distribution could be better than inclusion modification. In low alloyed steels secondary carbide density appears to be critical and correlates well with machinability. The study also points to strategies for steel development and their efficient hard milling.
Related Topics
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Engineering
Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering