| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201373 | Fluid Phase Equilibria | 2016 | 8 Pages |
•The molar heat capacities of methyl α-d-glucopyranoside were measured by DSC.•Thermal decomposition of α-MeG was investigated by TGA.•The solubility of α-MeG in methanol was experimentally determined.•The solubility was correlated by modified Apelblat, λh, Wilson and NRTL models.•Solution thermodynamic properties of α-MeG in methanol were calculated.
Heat capacity of methyl α-d-glucopyranoside (α-MeG) was measured by differential scanning calorimetry at the temperatures ranging from 298.15 to 513.15 K. Melting point, enthalpy and entropy of fusion, enthalpy HT–H298.15 K, and entropy ST-S298.15 K were determined. Thermal decomposition of α-MeG was investigated using thermogravimetric analysis under pure nitrogen atmosphere. Ozawa-Flynn-Wall and ASTM models were used to calculate the activation energy and pre-exponential factor. Solubilities of α-MeG in methanol were measured within the temperature range of 293.15–318.15 K by using a synthetic method under atmospheric pressure. The modified Apelblat, λh, Wilson and NRTL models were applied to correlate the experimental data. The calculated results show good agreement with the experimental data and Wilson model is slightly more accurate than modified Apelblat, λh and NRTL models. The dissolution enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy were calculated by the Van't Hoff equation. The excess enthalpy of the solution can be evaluated by the λh model.
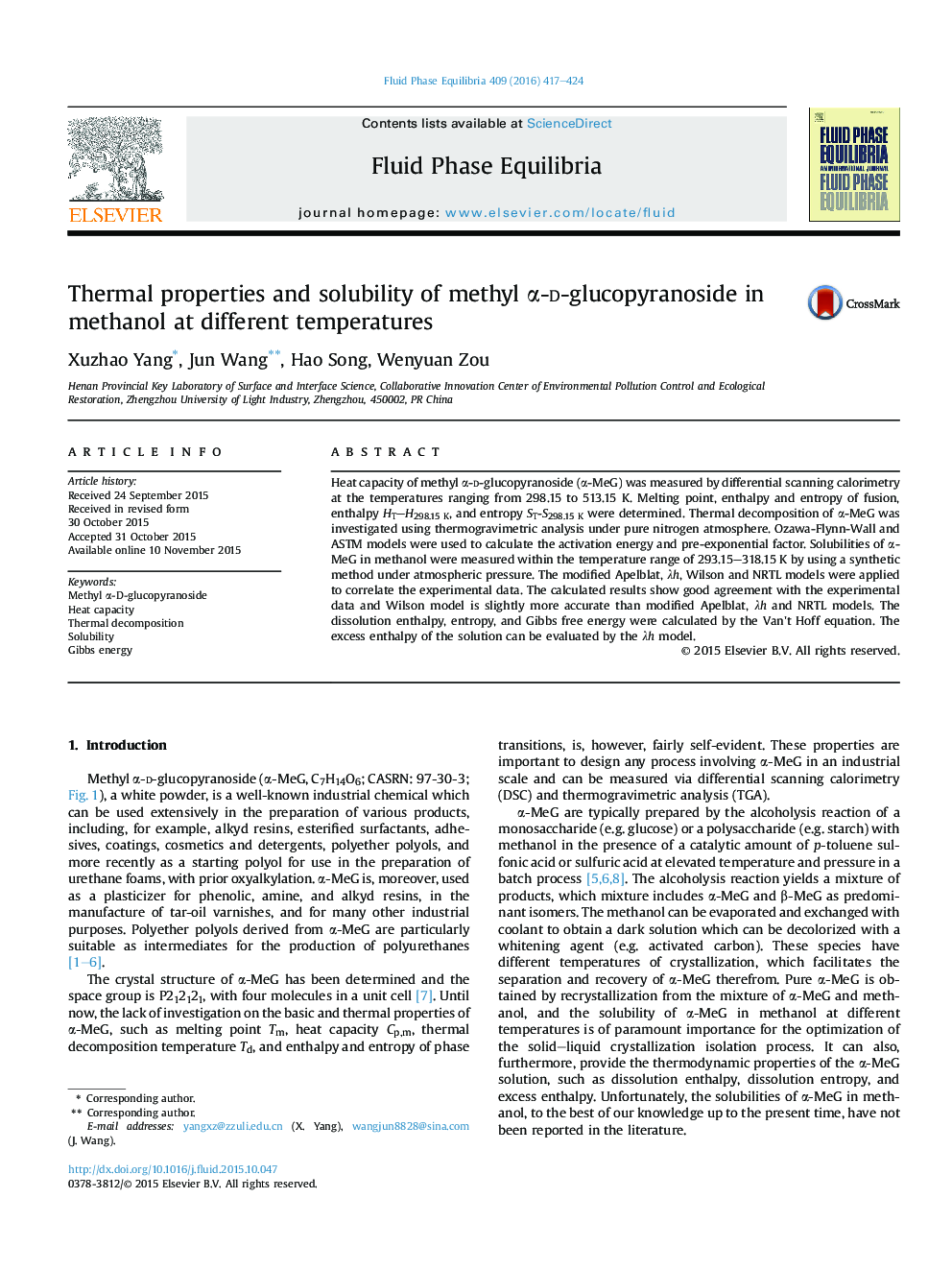
Graphical abstractMole fraction solubility (x) of α-MeG versus absolute temperature (T) in methanol: , experimental data; —, calculated by modified Apelblat equation.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide