| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2035353 | Cell | 2015 | 11 Pages |
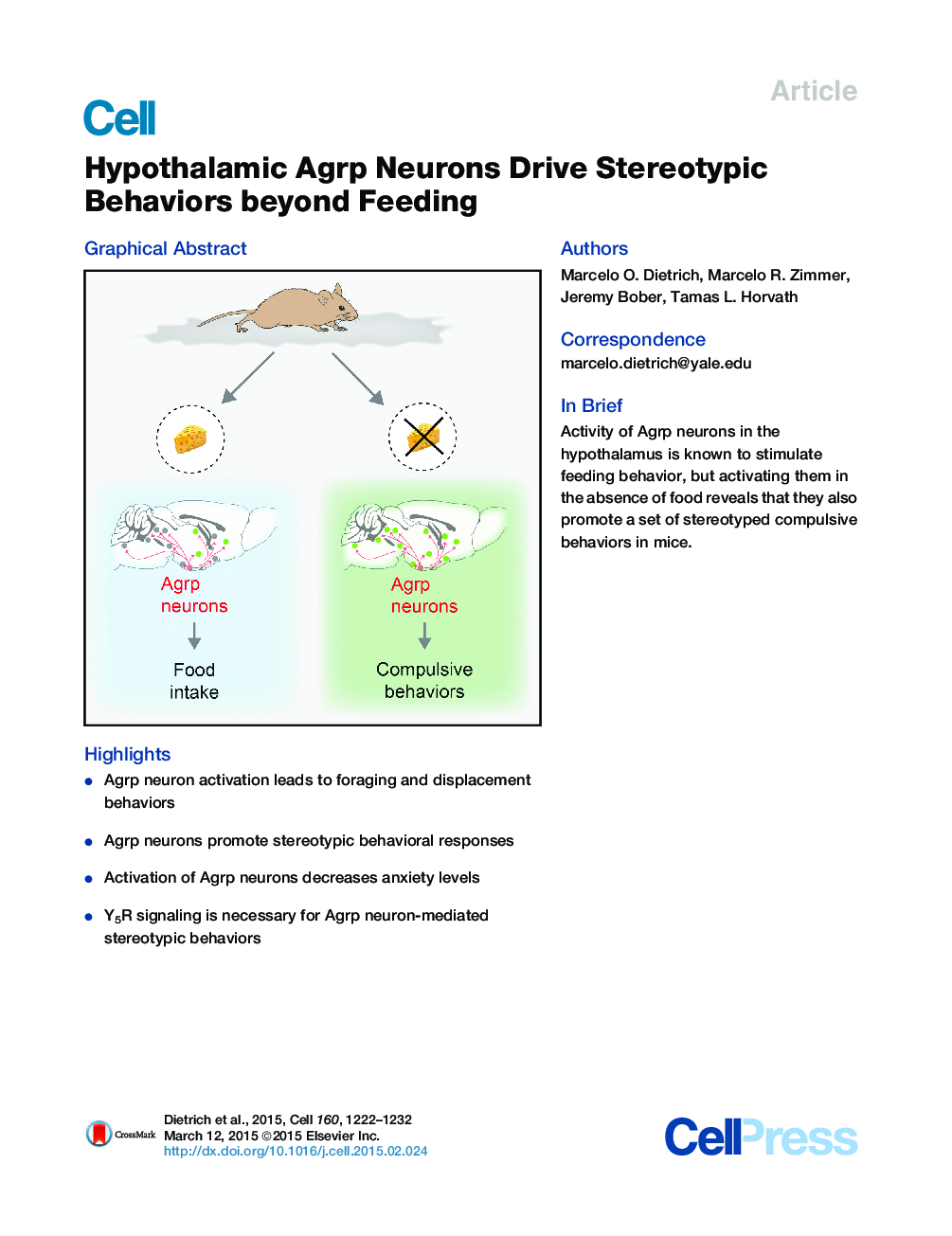
•Agrp neuron activation leads to foraging and displacement behaviors•Agrp neurons promote stereotypic behavioral responses•Activation of Agrp neurons decreases anxiety levels•Y5R signaling is necessary for Agrp neuron-mediated stereotypic behaviors
SummaryThe nervous system evolved to coordinate flexible goal-directed behaviors by integrating interoceptive and sensory information. Hypothalamic Agrp neurons are known to be crucial for feeding behavior. Here, however, we show that these neurons also orchestrate other complex behaviors in adult mice. Activation of Agrp neurons in the absence of food triggers foraging and repetitive behaviors, which are reverted by food consumption. These stereotypic behaviors that are triggered by Agrp neurons are coupled with decreased anxiety. NPY5 receptor signaling is necessary to mediate the repetitive behaviors after Agrp neuron activation while having minor effects on feeding. Thus, we have unmasked a functional role for Agrp neurons in controlling repetitive behaviors mediated, at least in part, by neuropeptidergic signaling. The findings reveal a new set of behaviors coupled to the energy homeostasis circuit and suggest potential therapeutic avenues for diseases with stereotypic behaviors.PaperClip To listen to this audio, enable JavaScript on your browser. However, you can download and play the audio by clicking on the icon belowHelp with MP3 filesOptionsDownload audio (3238 K)
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (169 K)Download as PowerPoint slide