| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 205083 | Fuel | 2016 | 6 Pages |
•A multi-day experimental simulation of UCG using large bulk samples of ortho-lignite was conducted.•The average moisture content of the coal was 46.5 wt%, and its calorific value was 12.6 MJ/kg.•The overall process energy efficiency was estimated at 59%, and the average gas calorific value was approximately 7.2 MJ/N m3.•The study demonstrated that oxygen-blown UCG of high moisture lignites may be a feasible option.
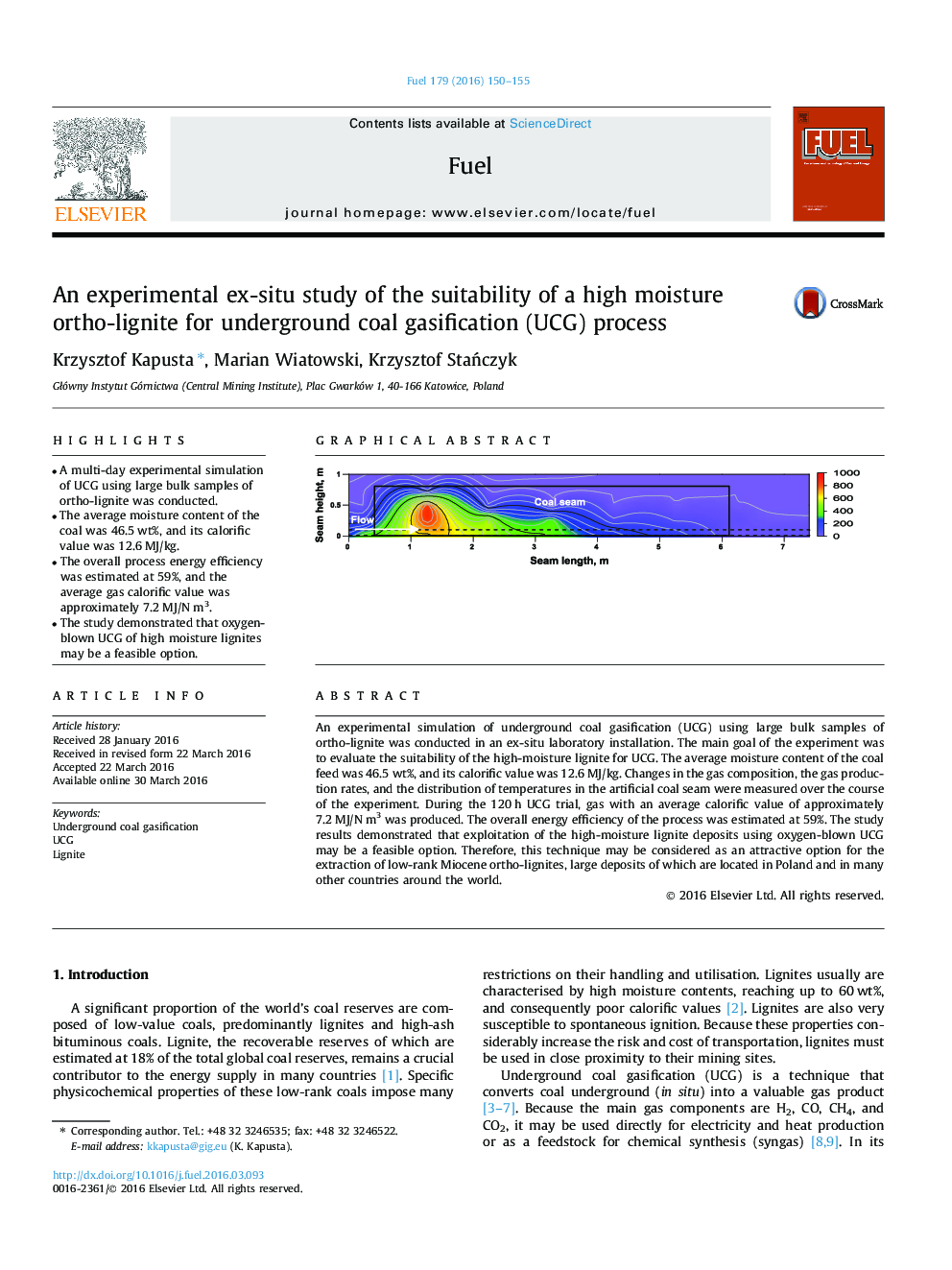
An experimental simulation of underground coal gasification (UCG) using large bulk samples of ortho-lignite was conducted in an ex-situ laboratory installation. The main goal of the experiment was to evaluate the suitability of the high-moisture lignite for UCG. The average moisture content of the coal feed was 46.5 wt%, and its calorific value was 12.6 MJ/kg. Changes in the gas composition, the gas production rates, and the distribution of temperatures in the artificial coal seam were measured over the course of the experiment. During the 120 h UCG trial, gas with an average calorific value of approximately 7.2 MJ/N m3 was produced. The overall energy efficiency of the process was estimated at 59%. The study results demonstrated that exploitation of the high-moisture lignite deposits using oxygen-blown UCG may be a feasible option. Therefore, this technique may be considered as an attractive option for the extraction of low-rank Miocene ortho-lignites, large deposits of which are located in Poland and in many other countries around the world.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide