| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2058788 | MethodsX | 2015 | 8 Pages |
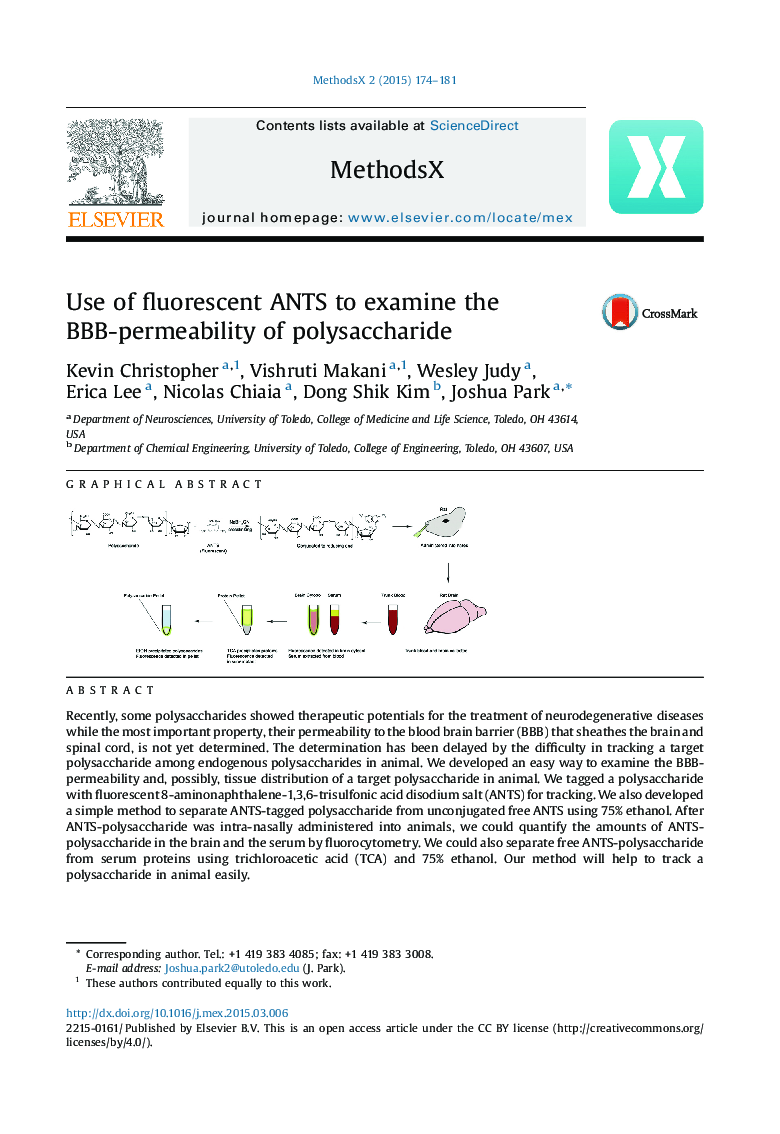
Recently, some polysaccharides showed therapeutic potentials for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases while the most important property, their permeability to the blood brain barrier (BBB) that sheathes the brain and spinal cord, is not yet determined. The determination has been delayed by the difficulty in tracking a target polysaccharide among endogenous polysaccharides in animal. We developed an easy way to examine the BBB-permeability and, possibly, tissue distribution of a target polysaccharide in animal. We tagged a polysaccharide with fluorescent 8-aminonaphthalene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid disodium salt (ANTS) for tracking. We also developed a simple method to separate ANTS-tagged polysaccharide from unconjugated free ANTS using 75% ethanol. After ANTS-polysaccharide was intra-nasally administered into animals, we could quantify the amounts of ANTS-polysaccharide in the brain and the serum by fluorocytometry. We could also separate free ANTS-polysaccharide from serum proteins using trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and 75% ethanol. Our method will help to track a polysaccharide in animal easily.•ANTS-labeling is less tedious than but as powerful as radiolabeling for tracking a target polysaccharide in animal.•Our simple method can separate structurally intact ANTS-polysaccharide from animal serum and tissues.•This method is good for the fluorometry-based measurement of ANTS-conjugated macromolecules in tissues.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide