| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206035 | Fuel | 2014 | 9 Pages |
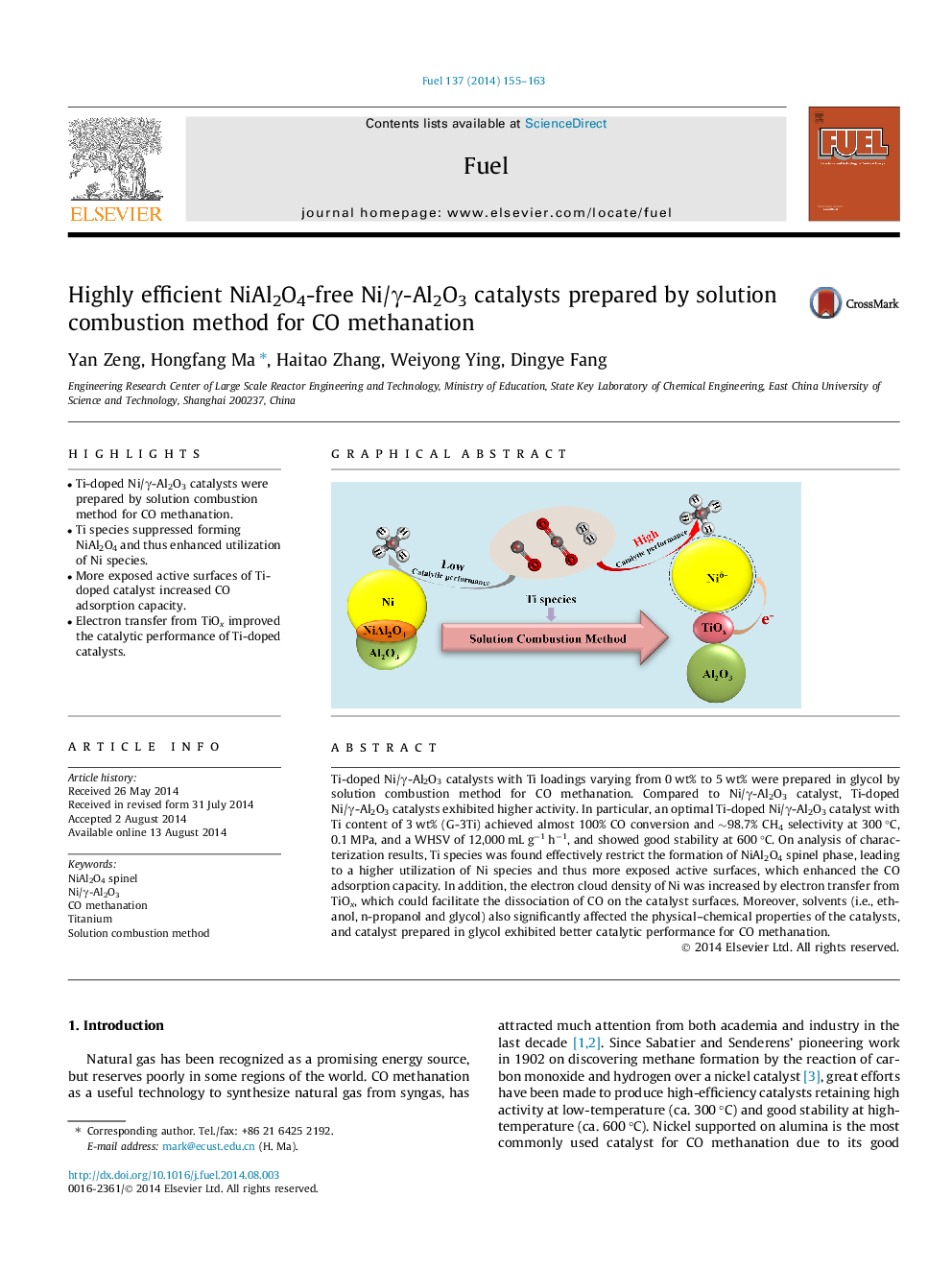
•Ti-doped Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalysts were prepared by solution combustion method for CO methanation.•Ti species suppressed forming NiAl2O4 and thus enhanced utilization of Ni species.•More exposed active surfaces of Ti-doped catalyst increased CO adsorption capacity.•Electron transfer from TiOx improved the catalytic performance of Ti-doped catalysts.
Ti-doped Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalysts with Ti loadings varying from 0 wt% to 5 wt% were prepared in glycol by solution combustion method for CO methanation. Compared to Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalyst, Ti-doped Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalysts exhibited higher activity. In particular, an optimal Ti-doped Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalyst with Ti content of 3 wt% (G-3Ti) achieved almost 100% CO conversion and ∼98.7% CH4 selectivity at 300 °C, 0.1 MPa, and a WHSV of 12,000 mL g−1 h−1, and showed good stability at 600 °C. On analysis of characterization results, Ti species was found effectively restrict the formation of NiAl2O4 spinel phase, leading to a higher utilization of Ni species and thus more exposed active surfaces, which enhanced the CO adsorption capacity. In addition, the electron cloud density of Ni was increased by electron transfer from TiOx, which could facilitate the dissociation of CO on the catalyst surfaces. Moreover, solvents (i.e., ethanol, n-propanol and glycol) also significantly affected the physical–chemical properties of the catalysts, and catalyst prepared in glycol exhibited better catalytic performance for CO methanation.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide