| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2106707 | Cancer Cell | 2016 | 16 Pages |
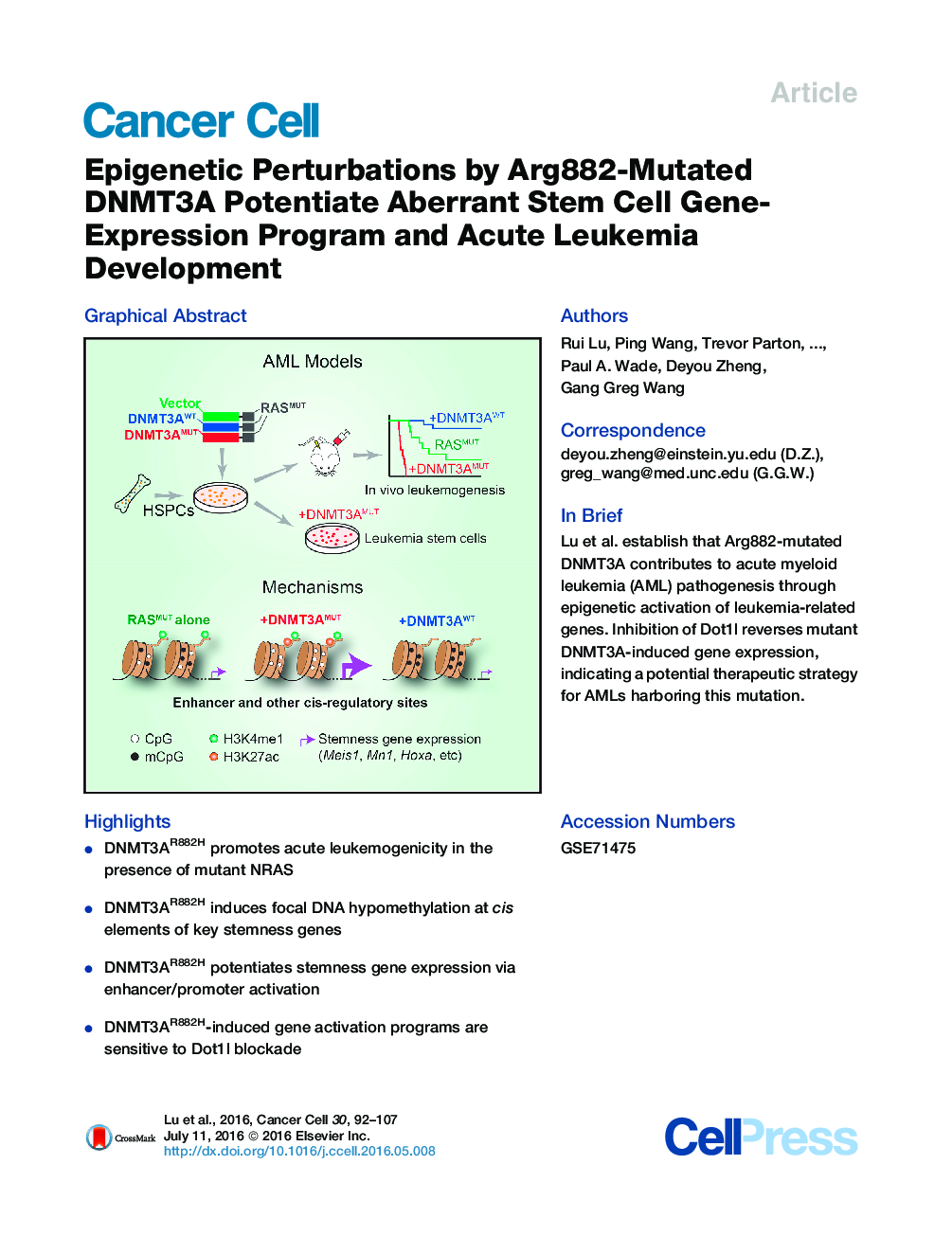
•DNMT3AR882H promotes acute leukemogenicity in the presence of mutant NRAS•DNMT3AR882H induces focal DNA hypomethylation at cis elements of key stemness genes•DNMT3AR882H potentiates stemness gene expression via enhancer/promoter activation•DNMT3AR882H-induced gene activation programs are sensitive to Dot1l blockade
SummaryDNA methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) is frequently mutated in hematological cancers; however, the underlying oncogenic mechanism remains elusive. Here, we report that the DNMT3A mutational hotspot at Arg882 (DNMT3AR882H) cooperates with NRAS mutation to transform hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and induce acute leukemia development. Mechanistically, DNMT3AR882H directly binds to and potentiates transactivation of stemness genes critical for leukemogenicity including Meis1, Mn1, and Hoxa gene cluster. DNMT3AR882H induces focal epigenetic alterations, including CpG hypomethylation and concurrent gain of active histone modifications, at cis-regulatory elements such as enhancers to facilitate gene transcription. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated ablation of a putative Meis1 enhancer carrying DNMT3AR882H-induced DNA hypomethylation impairs Meis1 expression. Importantly, DNMT3AR882H-induced gene-expression programs can be repressed through Dot1l inhibition, providing an attractive therapeutic strategy for DNMT3A-mutated leukemias.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (235 K)Download as PowerPoint slide