| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2106708 | Cancer Cell | 2016 | 12 Pages |
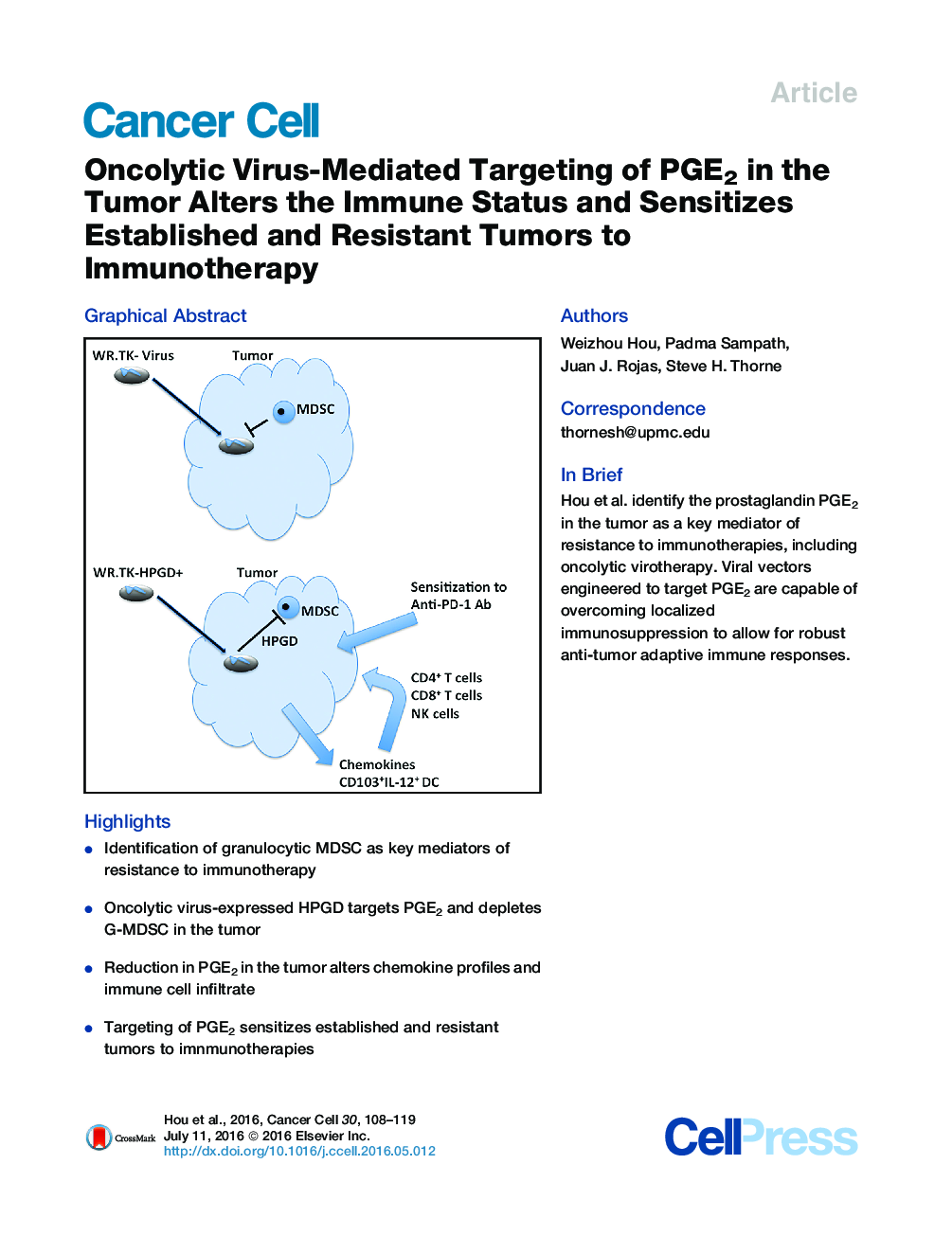
•Identification of granulocytic MDSC as key mediators of resistance to immunotherapy•Oncolytic virus-expressed HPGD targets PGE2 and depletes G-MDSC in the tumor•Reduction in PGE2 in the tumor alters chemokine profiles and immune cell infiltrate•Targeting of PGE2 sensitizes established and resistant tumors to imnmunotherapies
SummaryImmunotherapies are highly promising cancer treatments, but understanding the factors mediating their resistance remains critical. Successes in randomized clinical testing have supported the growing appreciation that oncolytic virotherapies primarily act as immunotherapies. Here we identified prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in the tumor as a key mediator of resistance to immunotherapies, including oncolytic vaccinia virotherapy. Elevated levels of PGE2 coupled to suppressive chemokine profiles and high levels of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells resulted in loss of immunotherapeutic potential. Viral vectors engineered to target PGE2 were capable of overcoming localized immunosuppression leading to profound changes in the tumor's immune status. This allowed the viral vectors to raise robust anti-tumor adaptive immune responses and sensitized established and previously resistant tumors to immunotherapies.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (127 K)Download as PowerPoint slide