| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2106771 | Cancer Cell | 2016 | 17 Pages |
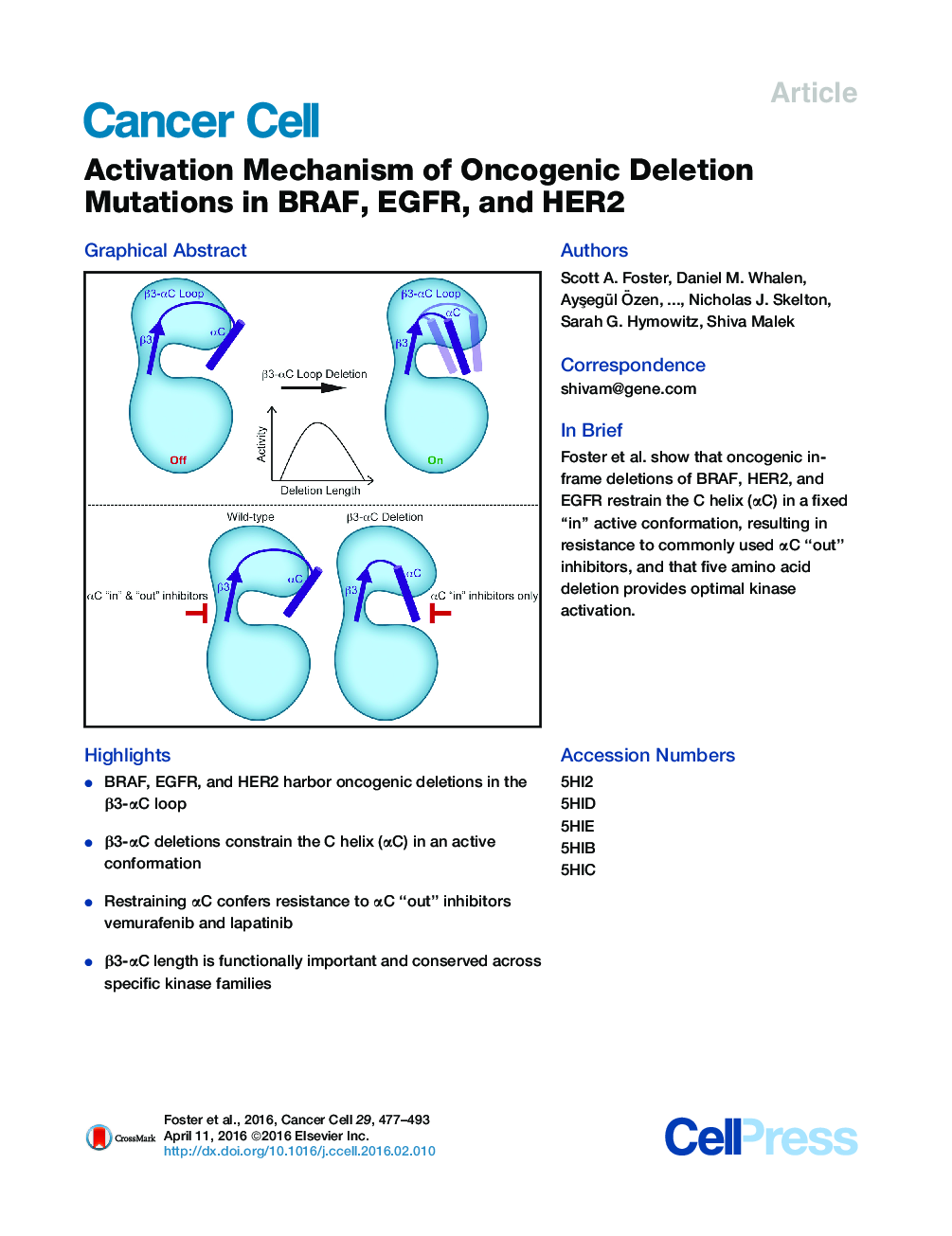
•BRAF, EGFR, and HER2 harbor oncogenic deletions in the β3-αC loop•β3-αC deletions constrain the C helix (αC) in an active conformation•Restraining αC confers resistance to αC “out” inhibitors vemurafenib and lapatinib•β3-αC length is functionally important and conserved across specific kinase families
SummaryActivating mutations in protein kinases drive many cancers. While how recurring point mutations affect kinase activity has been described, the effect of in-frame deletions is not well understood. We show that oncogenic deletions within the β3-αC loop of HER2 and BRAF are analogous to the recurrent EGFR exon 19 deletions. We identify pancreatic carcinomas with BRAF deletions mutually exclusive with KRAS mutations. Crystal structures of BRAF deletions reveal the truncated loop restrains αC in an active “in” conformation, imparting resistance to inhibitors like vemurafenib that bind the αC “out” conformation. Characterization of loop length explains the prevalence of five amino acid deletions in BRAF, EGFR, and HER2 and highlights the importance of this region for kinase activity and inhibitor efficacy.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (164 K)Download as PowerPoint slide