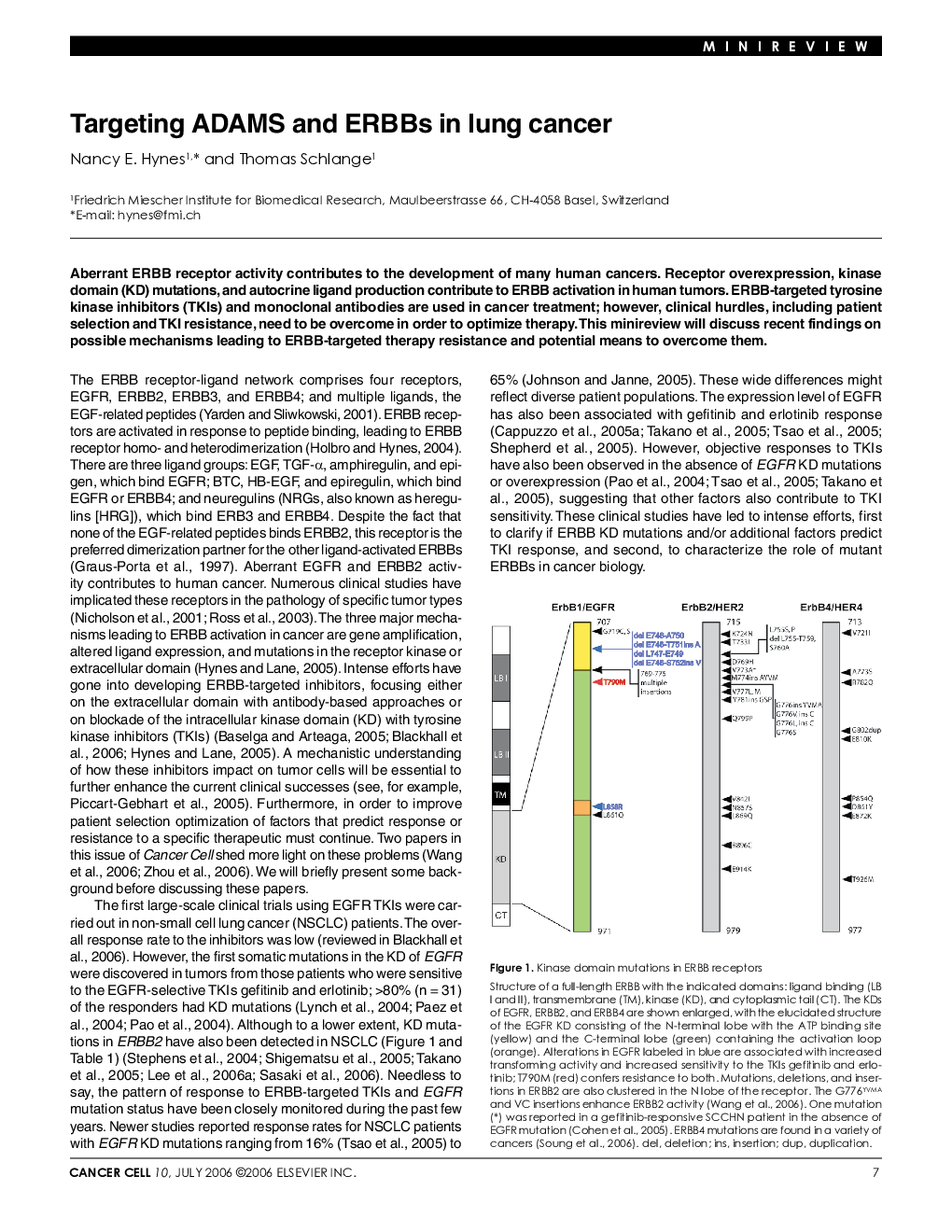
| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2108198 | Cancer Cell | 2006 | 5 Pages |
Abstract
Aberrant ERBB receptor activity contributes to the development of many human cancers. Receptor overexpression, kinase domain (KD) mutations, and autocrine ligand production contribute to ERBB activation in human tumors. ERBB-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and monoclonal antibodies are used in cancer treatment; however, clinical hurdles, including patient selection and TKI resistance, need to be overcome in order to optimize therapy. This minireview will discuss recent findings on possible mechanisms leading to ERBB-targeted therapy resistance and potential means to overcome them.
Related Topics
Life Sciences
Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology
Cancer Research
Authors
Nancy E. Hynes, Thomas Schlange,