| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 257560 | Construction and Building Materials | 2014 | 9 Pages |
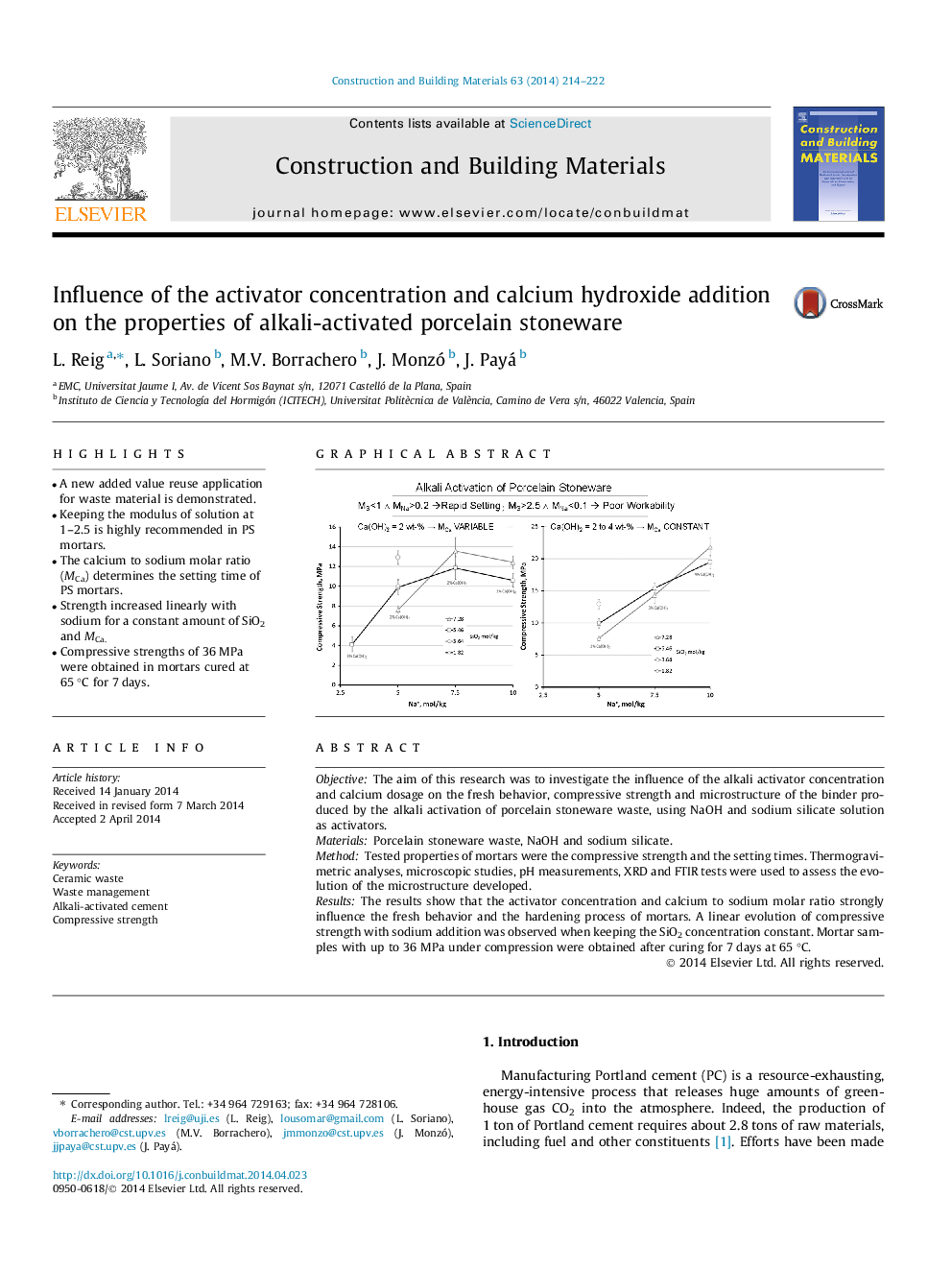
•A new added value reuse application for waste material is demonstrated.•Keeping the modulus of solution at 1–2.5 is highly recommended in PS mortars.•The calcium to sodium molar ratio (MCa) determines the setting time of PS mortars.•Strength increased linearly with sodium for a constant amount of SiO2 and MCa.•Compressive strengths of 36 MPa were obtained in mortars cured at 65 °C for 7 days.
ObjectiveThe aim of this research was to investigate the influence of the alkali activator concentration and calcium dosage on the fresh behavior, compressive strength and microstructure of the binder produced by the alkali activation of porcelain stoneware waste, using NaOH and sodium silicate solution as activators.MaterialsPorcelain stoneware waste, NaOH and sodium silicate.MethodTested properties of mortars were the compressive strength and the setting times. Thermogravimetric analyses, microscopic studies, pH measurements, XRD and FTIR tests were used to assess the evolution of the microstructure developed.ResultsThe results show that the activator concentration and calcium to sodium molar ratio strongly influence the fresh behavior and the hardening process of mortars. A linear evolution of compressive strength with sodium addition was observed when keeping the SiO2 concentration constant. Mortar samples with up to 36 MPa under compression were obtained after curing for 7 days at 65 °C.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide