| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2743530 | Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine | 2008 | 4 Pages |
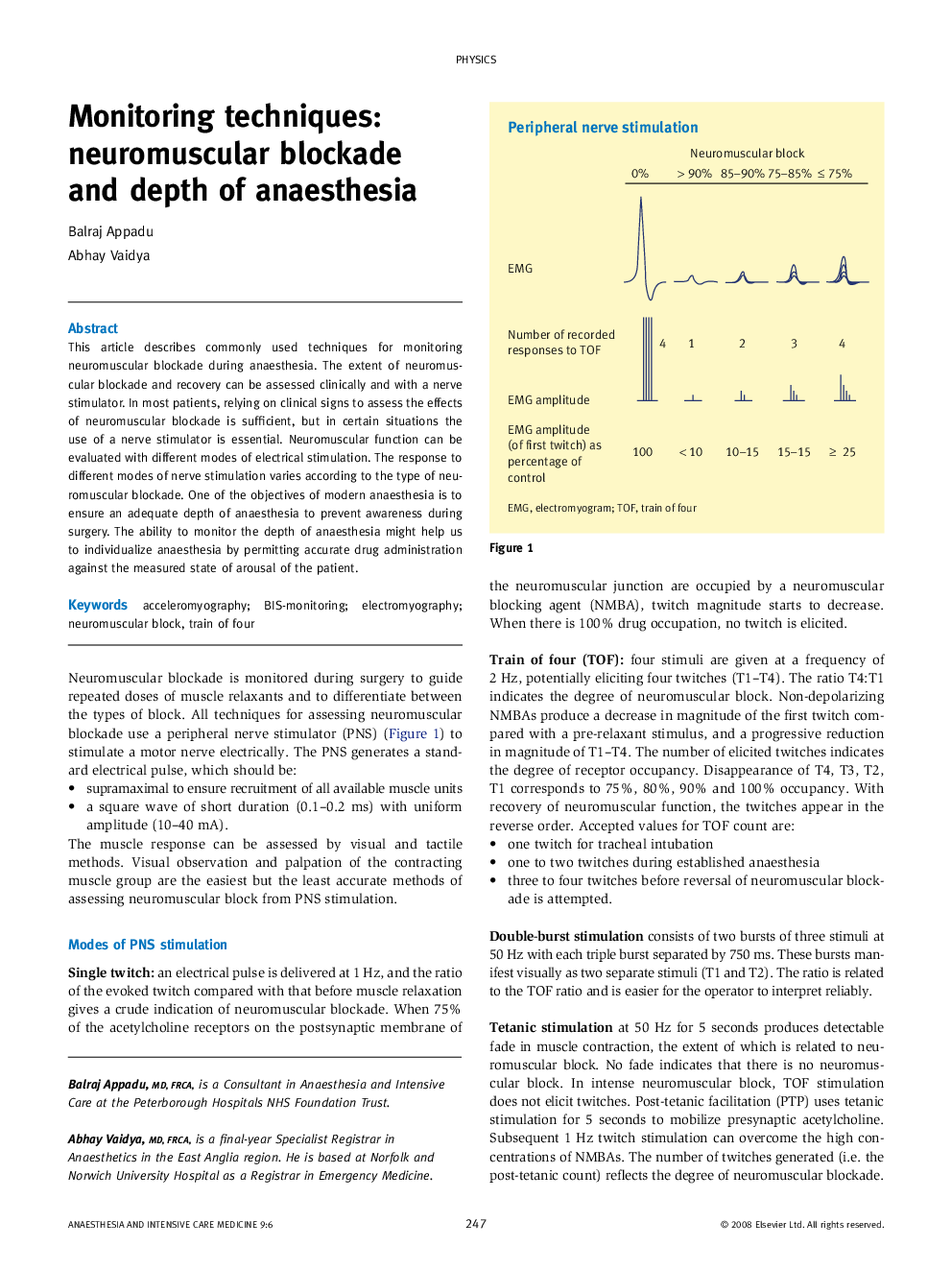
This article describes commonly used techniques for monitoring neuromuscular blockade during anaesthesia. The extent of neuromuscular blockade and recovery can be assessed clinically and with a nerve stimulator. In most patients, relying on clinical signs to assess the effects of neuromuscular blockade is sufficient, but in certain situations the use of a nerve stimulator is essential. Neuromuscular function can be evaluated with different modes of electrical stimulation. The response to different modes of nerve stimulation varies according to the type of neuromuscular blockade. One of the objectives of modern anaesthesia is to ensure an adequate depth of anaesthesia to prevent awareness during surgery. The ability to monitor the depth of anaesthesia might help us to individualize anaesthesia by permitting accurate drug administration against the measured state of arousal of the patient.