| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2743683 | Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine | 2008 | 5 Pages |
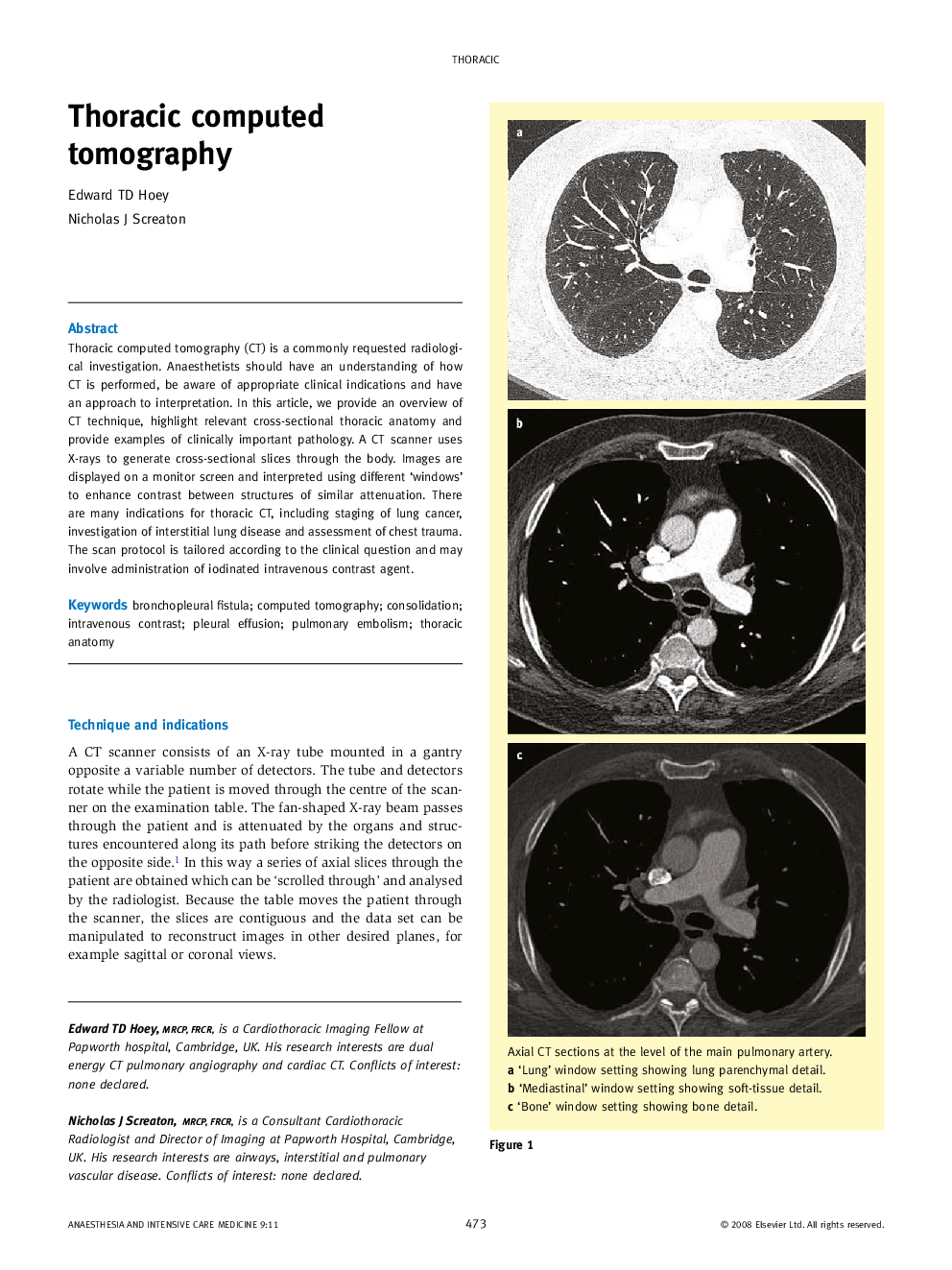
Thoracic computed tomography (CT) is a commonly requested radiological investigation. Anaesthetists should have an understanding of how CT is performed, be aware of appropriate clinical indications and have an approach to interpretation. In this article, we provide an overview of CT technique, highlight relevant cross-sectional thoracic anatomy and provide examples of clinically important pathology. A CT scanner uses X-rays to generate cross-sectional slices through the body. Images are displayed on a monitor screen and interpreted using different ‘windows’ to enhance contrast between structures of similar attenuation. There are many indications for thoracic CT, including staging of lung cancer, investigation of interstitial lung disease and assessment of chest trauma. The scan protocol is tailored according to the clinical question and may involve administration of iodinated intravenous contrast agent.