| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2743686 | Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine | 2008 | 5 Pages |
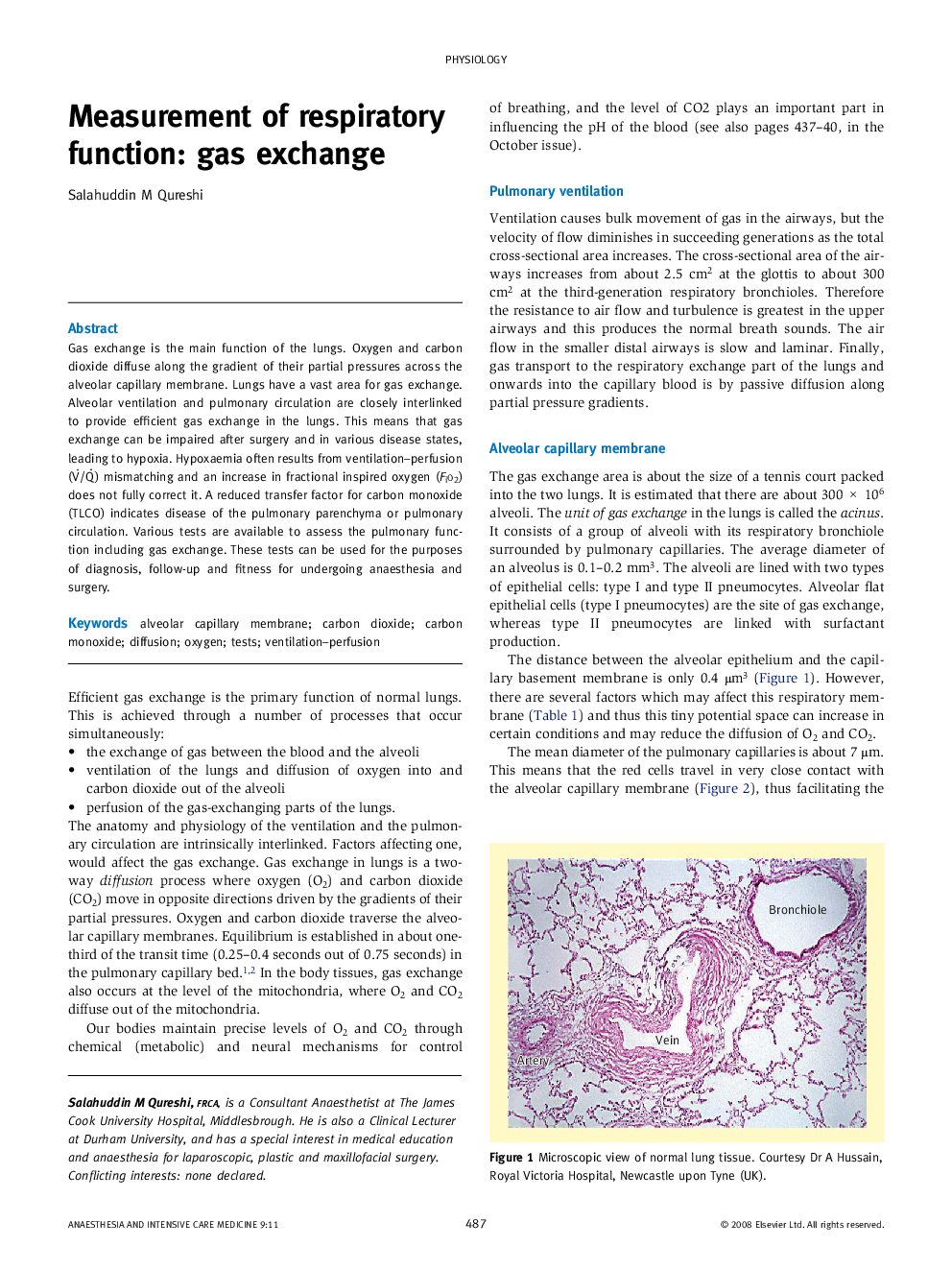
Gas exchange is the main function of the lungs. Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse along the gradient of their partial pressures across the alveolar capillary membrane. Lungs have a vast area for gas exchange. Alveolar ventilation and pulmonary circulation are closely interlinked to provide efficient gas exchange in the lungs. This means that gas exchange can be impaired after surgery and in various disease states, leading to hypoxia. Hypoxaemia often results from ventilation–perfusion (V⋅/Q⋅) mismatching and an increase in fractional inspired oxygen (Fio2) does not fully correct it. A reduced transfer factor for carbon monoxide (TLCO) indicates disease of the pulmonary parenchyma or pulmonary circulation. Various tests are available to assess the pulmonary function including gas exchange. These tests can be used for the purposes of diagnosis, follow-up and fitness for undergoing anaesthesia and surgery.