| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2792389 | Cell Metabolism | 2015 | 15 Pages |
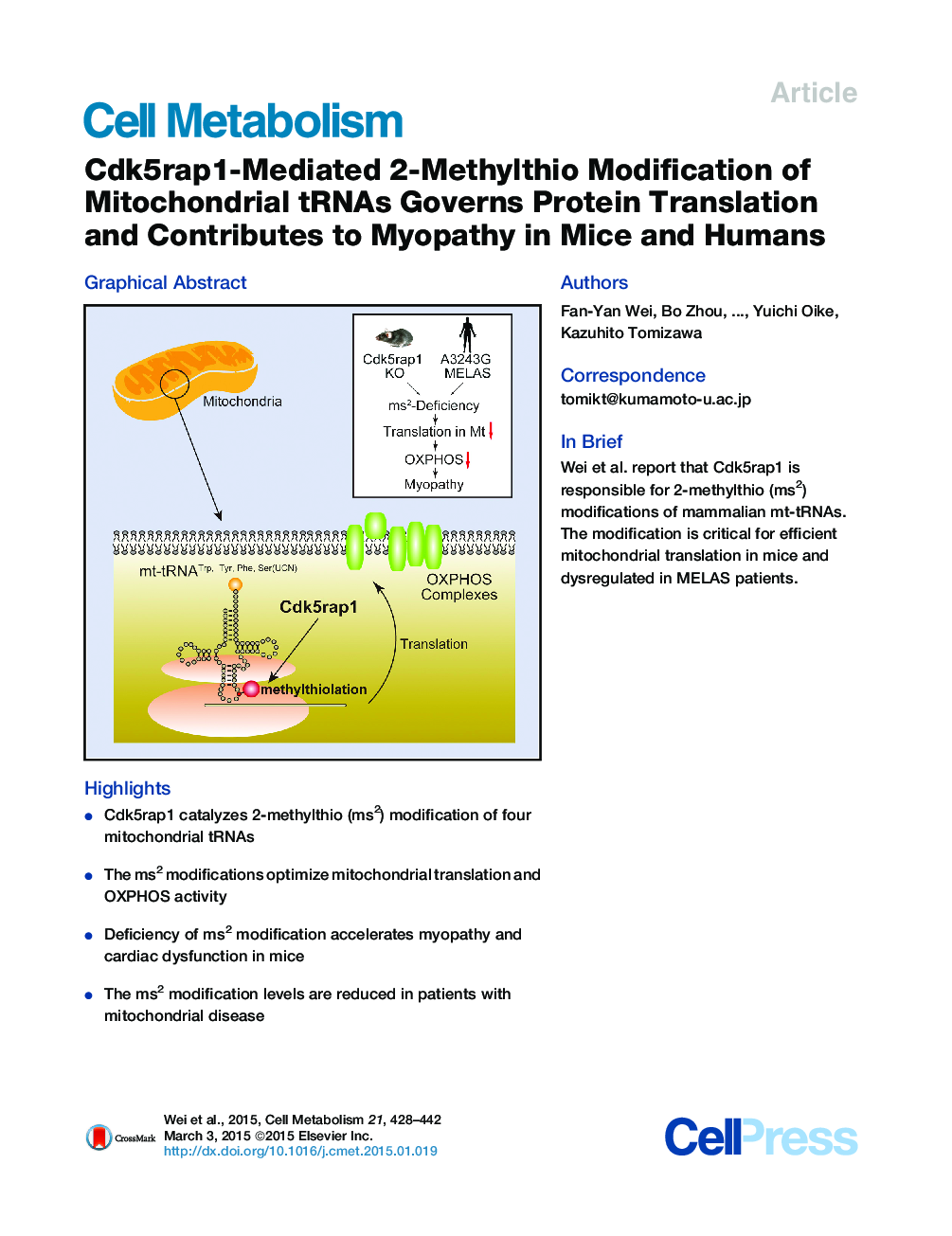
•Cdk5rap1 catalyzes 2-methylthio (ms2) modification of four mitochondrial tRNAs•The ms2 modifications optimize mitochondrial translation and OXPHOS activity•Deficiency of ms2 modification accelerates myopathy and cardiac dysfunction in mice•The ms2 modification levels are reduced in patients with mitochondrial disease
SummaryTransfer RNAs (tRNAs) contain a wide variety of posttranscriptional modifications that are important for accurate decoding. Mammalian mitochondrial tRNAs (mt-tRNAs) are modified by nuclear-encoded tRNA-modifying enzymes; however, the physiological roles of these modifications remain largely unknown. In this study, we report that Cdk5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 1 (Cdk5rap1) is responsible for 2-methylthio (ms2) modifications of mammalian mt-tRNAs for Ser(UCN), Phe, Tyr, and Trp codons. Deficiency in ms2 modification markedly impaired mitochondrial protein synthesis, which resulted in respiratory defects in Cdk5rap1 knockout (KO) mice. The KO mice were highly susceptive to stress-induced mitochondrial remodeling and exhibited accelerated myopathy and cardiac dysfunction under stressed conditions. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the ms2 modifications of mt-tRNAs were sensitive to oxidative stress and were reduced in patients with mitochondrial disease. These findings highlight the fundamental role of ms2 modifications of mt-tRNAs in mitochondrial protein synthesis and their pathological consequences in mitochondrial disease.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (212 K)Download as PowerPoint slide