| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2792513 | Cell Metabolism | 2015 | 9 Pages |
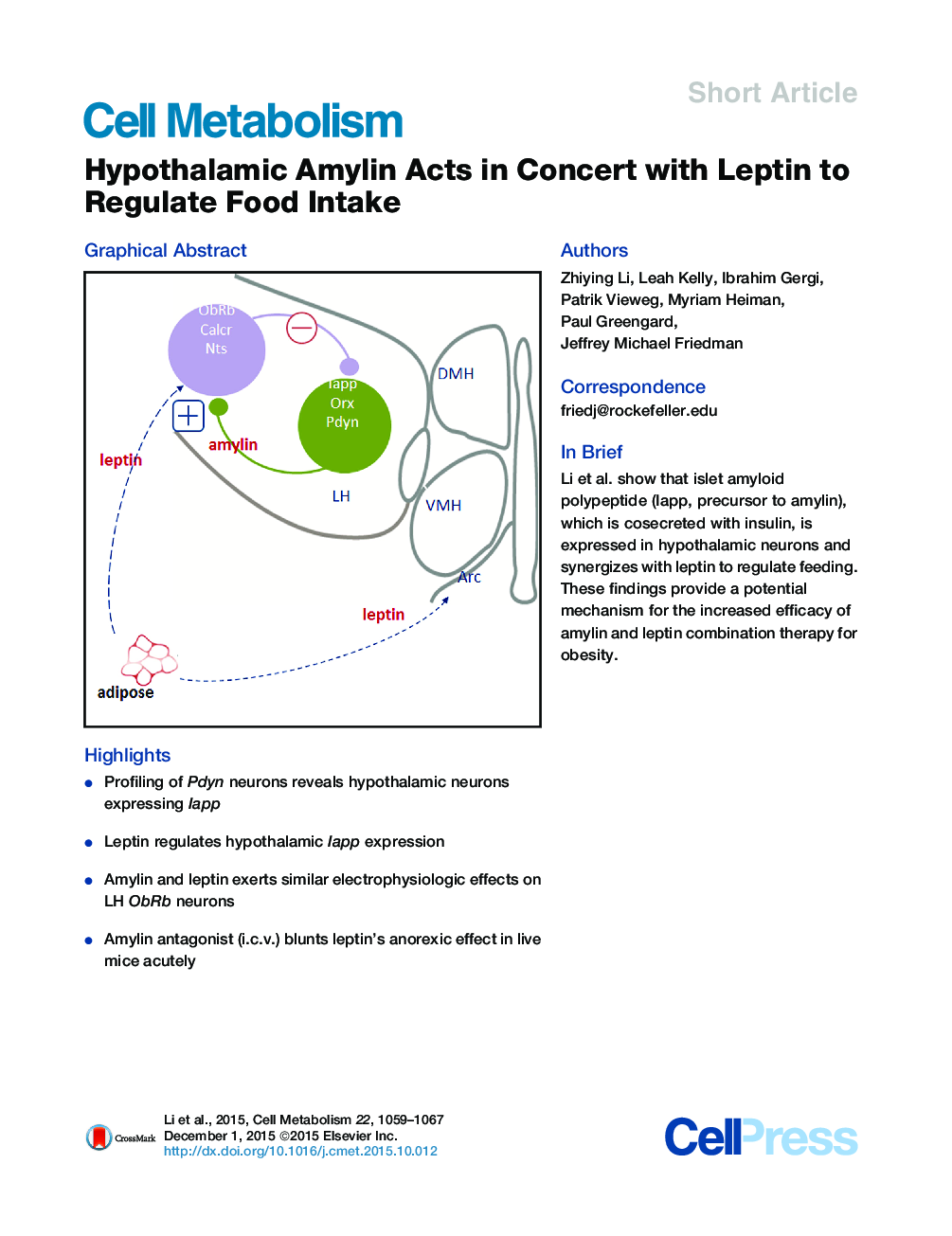
•Profiling of Pdyn neurons reveals hypothalamic neurons expressing Iapp•Leptin regulates hypothalamic Iapp expression•Amylin and leptin exerts similar electrophysiologic effects on LH ObRb neurons•Amylin antagonist (i.c.v.) blunts leptin’s anorexic effect in live mice acutely
SummaryIn this report we evaluated the functions of hypothalamic amylin in vivo and in vitro. Profiling of hypothalamic neurons revealed that islet amyloid polypeptide (Iapp, precursor to amylin) is expressed in neurons in the lateral hypothalamus, arcuate nucleus, medial preoptic area, and elsewhere. Hypothalamic expression of lapp is markedly decreased in ob/ob mice and normalized by exogenous leptin. In slices, amylin and leptin had similar electrophysiologic effects on lateral hypothalamic leptin receptor ObRb-expressing neurons, while the amylin antagonist AC187 inhibited their activity and blunted the effect of leptin. Finally, i.c.v. infusion of AC187 acutely reduced the anorectic effects of leptin. These data show that hypothalamic amylin is transcriptionally regulated by leptin, that it can act directly on ObRb neurons in concert with leptin, and that it regulates feeding. These findings provide a potential mechanism for the increased efficacy of a metreleptin/pramlintide combination therapy for obesity.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (118 K)Download as PowerPoint slide