| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2792554 | Cell Metabolism | 2015 | 14 Pages |
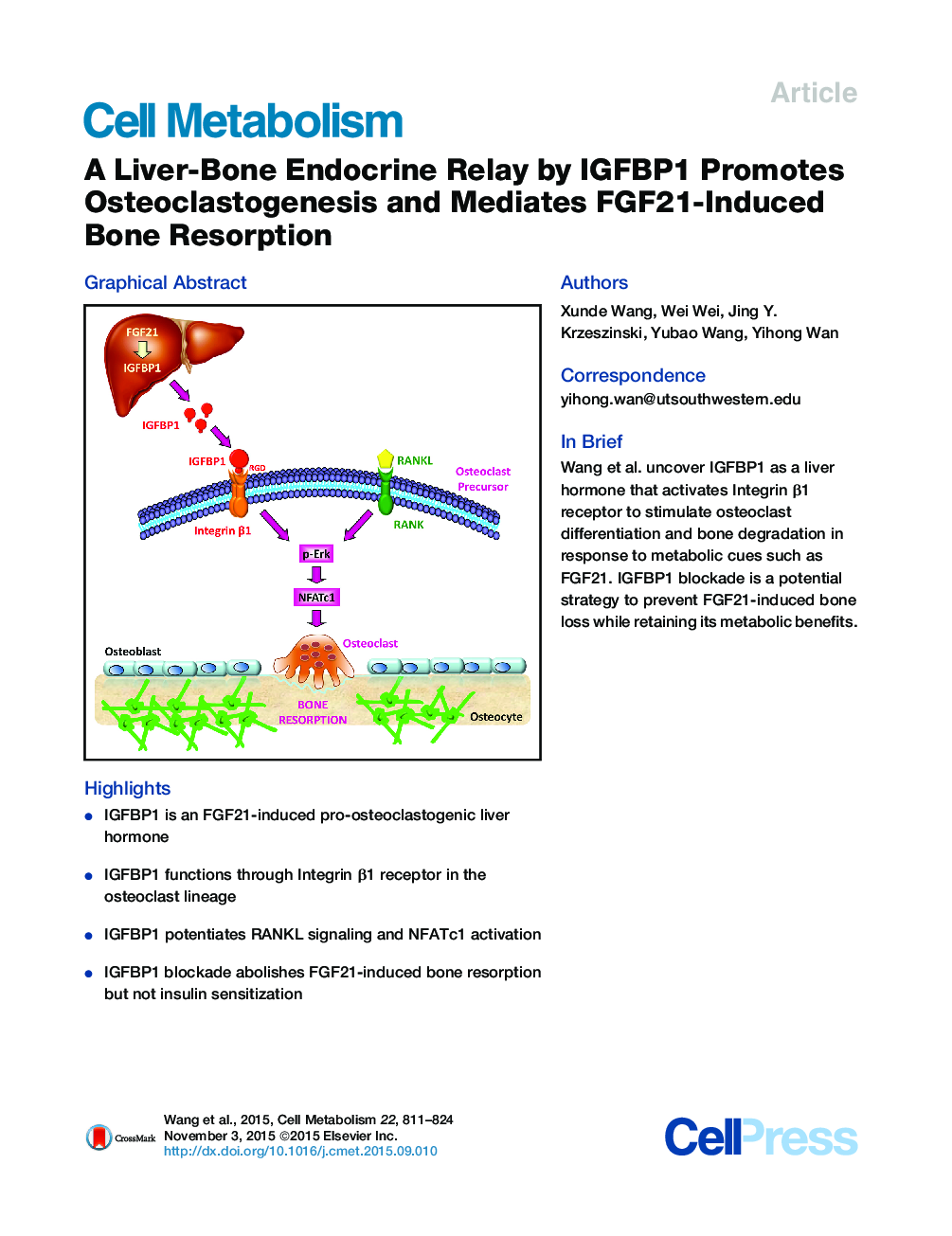
•IGFBP1 is an FGF21-induced pro-osteoclastogenic liver hormone•IGFBP1 functions through Integrin β1 receptor in the osteoclast lineage•IGFBP1 potentiates RANKL signaling and NFATc1 activation•IGFBP1 blockade abolishes FGF21-induced bone resorption but not insulin sensitization
SummaryFibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) promotes insulin sensitivity but causes bone loss. It elevates bone resorption by an undefined non-osteoclast-autonomous mechanism. We have detected a pro-osteoclastogenic activity in the hepatic secretome that is increased by FGF21 and largely attributed to insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (IGFBP1). Ex vivo osteoclast differentiation and in vivo bone resorption are both enhanced by recombinant IGFBP1 but suppressed by an IGFBP1-blocking antibody. Anti-IGFBP1 treatment attenuates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis and abolishes FGF21-induced bone loss while maintaining its insulin-sensitizing metabolic benefit. Mechanistically, IGFBP1 functions via its RGD domain to bind to its receptor integrin β1 on osteoclast precursors, thereby potentiating RANKL-stimulated Erk-phosphorylation and NFATc1 activation. Consequently, osteoclastic integrin β1 deletion confers resistance to the resorption-enhancing effects of both IGFBP1 and FGF21. Therefore, the hepatokine IGFBP1 is a critical liver-bone hormonal relay that promotes osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption as well as an essential mediator of FGF21-induced bone loss.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (245 K)Download as PowerPoint slide